Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2969 - Evolving Burden of Liver Cancer Attributable to High BMI in the United States and Its Trend from 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Analysis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- SS
Saifullah Syed, MBBCh
Royal College of Surgeons
Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Presenting Author(s)
Saifullah Syed, MBBCh1, Madiha Haseeb, MBBS2, Sravani Bhavanam, MBBS, MD3, Muhammad Waqas, MBBS2, Ratan Pal Yadav, MBBS4, Adan Irfan, MBBS5, Vishwesh Patel, MBBS6, George Mathew Mukalil, MD7, Ashwinikumar Shandilya, MBBS8, Bhargav Koyani, MD9, Rajkumar Patel, MBBS, MD10, Mohit Lakkimsetti, MBBS11, Vishrant P. Amin, MBBS12, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS13
1Royal College of Surgeons, Dublin, Dublin, Ireland; 2Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4NRI Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 5Shalamar Medical and Dental College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6M. P. Shah Government Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat, India; 7Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI; 8Rural Medical College, Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India; 9Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, Evanston, IL; 10Rutgers Trinitas Medical Centre, Newark, NJ; 11Mamata Medical College, Khammam, Telangana, India; 12GMERS Medical College Valsad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 13Gujarat Adani Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India
Introduction: Liver Cancer (LC) ranks as the 8th leading cause of death in the United States, with obesity being a major metabolic risk factor that inflicts significant economic and physical burdens. High BMI, a key contributor to LC, links obesity directly to increased liver cancer risks. This groundbreaking study estimates the burden of LC attributable to high BMI in the United States over the last three decades, including the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, a period that significantly complicated the management of cancer-related outcomes.
Methods: Using global burden of disease 2021 methodology, we estimated deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), years lived with disability (YLDs), years of life lost (YLL) due to LC attributable to high BMI stratified by age, sex, year, location across the USA from 1990-2021.
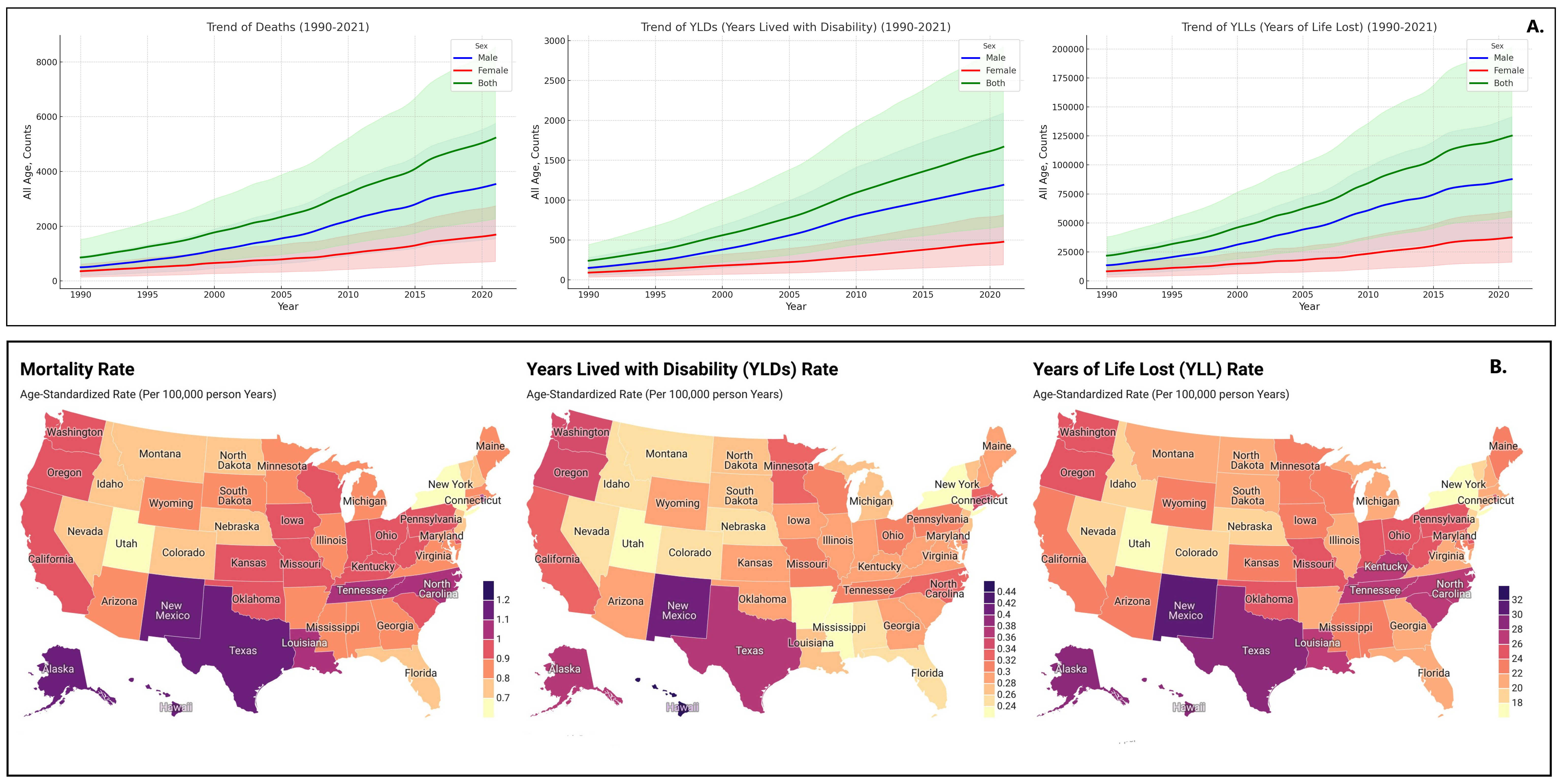
Results: The total number of deaths due to LC attributable to high BMI rose from 858 (95% uncertainty interval: 343-1525) in 1990 to 5226 (2266-8554) in 2021. Over the same period, the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) increased from 0.28 (0.11-0.49) to 0.90 (0.39-1.47) cases per 100,000 person-years. Additionally, the rate of YLDs per 100,000 rose from 0.08 to 0.30, and the rate of YLLs escalated from 7.36 to 22.90. Oklahoma experienced the largest increase in total percentage change (TPC) in ASMR by 435%, followed by New Mexico with a 391% increase from 1990 to 2021. New Mexico also saw the highest total percentage change in age-standardized YLD rate, at 486%. By age, the 65-69 group recorded the highest number of deaths at 989 (432-1575), while the 60-64 age group had the highest YLD count at 329 (140-565) in 2021. In terms of gender, males exhibited a greater overall increase in burden compared to females, with TPC in death counts at 605% versus 373%, YLDs at 698% versus 427%, and YLLs at 549% versus 354% from 1990 to 2021.
Discussion: Deaths due to LC attributable to high BMI accounted for 21.09% of all LC related causalities. The substantial rise in liver cancer mortality linked to high BMI underscores the urgent need for targeted public health interventions. Policymakers should prioritize preventive measures, including the integration of e-health and m-health platforms for education and outreach. Leveraging new media and influencers can effectively promote evidence-based healthcare practices, ultimately reducing the burden of liver cancer and improving population health outcomes.
Disclosures:
Saifullah Syed, MBBCh1, Madiha Haseeb, MBBS2, Sravani Bhavanam, MBBS, MD3, Muhammad Waqas, MBBS2, Ratan Pal Yadav, MBBS4, Adan Irfan, MBBS5, Vishwesh Patel, MBBS6, George Mathew Mukalil, MD7, Ashwinikumar Shandilya, MBBS8, Bhargav Koyani, MD9, Rajkumar Patel, MBBS, MD10, Mohit Lakkimsetti, MBBS11, Vishrant P. Amin, MBBS12, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS13. P2969 - Evolving Burden of Liver Cancer Attributable to High BMI in the United States and Its Trend from 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Royal College of Surgeons, Dublin, Dublin, Ireland; 2Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4NRI Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 5Shalamar Medical and Dental College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6M. P. Shah Government Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat, India; 7Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI; 8Rural Medical College, Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India; 9Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, Evanston, IL; 10Rutgers Trinitas Medical Centre, Newark, NJ; 11Mamata Medical College, Khammam, Telangana, India; 12GMERS Medical College Valsad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 13Gujarat Adani Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India
Introduction: Liver Cancer (LC) ranks as the 8th leading cause of death in the United States, with obesity being a major metabolic risk factor that inflicts significant economic and physical burdens. High BMI, a key contributor to LC, links obesity directly to increased liver cancer risks. This groundbreaking study estimates the burden of LC attributable to high BMI in the United States over the last three decades, including the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, a period that significantly complicated the management of cancer-related outcomes.
Methods: Using global burden of disease 2021 methodology, we estimated deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), years lived with disability (YLDs), years of life lost (YLL) due to LC attributable to high BMI stratified by age, sex, year, location across the USA from 1990-2021.
Results: The total number of deaths due to LC attributable to high BMI rose from 858 (95% uncertainty interval: 343-1525) in 1990 to 5226 (2266-8554) in 2021. Over the same period, the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) increased from 0.28 (0.11-0.49) to 0.90 (0.39-1.47) cases per 100,000 person-years. Additionally, the rate of YLDs per 100,000 rose from 0.08 to 0.30, and the rate of YLLs escalated from 7.36 to 22.90. Oklahoma experienced the largest increase in total percentage change (TPC) in ASMR by 435%, followed by New Mexico with a 391% increase from 1990 to 2021. New Mexico also saw the highest total percentage change in age-standardized YLD rate, at 486%. By age, the 65-69 group recorded the highest number of deaths at 989 (432-1575), while the 60-64 age group had the highest YLD count at 329 (140-565) in 2021. In terms of gender, males exhibited a greater overall increase in burden compared to females, with TPC in death counts at 605% versus 373%, YLDs at 698% versus 427%, and YLLs at 549% versus 354% from 1990 to 2021.
Discussion: Deaths due to LC attributable to high BMI accounted for 21.09% of all LC related causalities. The substantial rise in liver cancer mortality linked to high BMI underscores the urgent need for targeted public health interventions. Policymakers should prioritize preventive measures, including the integration of e-health and m-health platforms for education and outreach. Leveraging new media and influencers can effectively promote evidence-based healthcare practices, ultimately reducing the burden of liver cancer and improving population health outcomes.

Figure: A: Burden and Trend of Liver Cancer Attributable to High BMI in the United States from 1990-2021, B: Statewide Burden of Liver Cancer Attributable to High BMI in the United States in 2021, Age-standardized rate (per 100,000)
Disclosures:
Saifullah Syed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madiha Haseeb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sravani Bhavanam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Waqas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ratan Pal Yadav indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adan Irfan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishwesh Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
George Mathew Mukalil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwinikumar Shandilya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhargav Koyani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajkumar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohit Lakkimsetti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishrant Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hardik Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saifullah Syed, MBBCh1, Madiha Haseeb, MBBS2, Sravani Bhavanam, MBBS, MD3, Muhammad Waqas, MBBS2, Ratan Pal Yadav, MBBS4, Adan Irfan, MBBS5, Vishwesh Patel, MBBS6, George Mathew Mukalil, MD7, Ashwinikumar Shandilya, MBBS8, Bhargav Koyani, MD9, Rajkumar Patel, MBBS, MD10, Mohit Lakkimsetti, MBBS11, Vishrant P. Amin, MBBS12, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS13. P2969 - Evolving Burden of Liver Cancer Attributable to High BMI in the United States and Its Trend from 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
