Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3114 - A Case of EBV Hepatitis Treated With N-Acetylcysteine: A Placebo or True Effect?
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ariel Ahl, MD
Los Robles Regional Medical Center
Thousand Oaks, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Ariel Ahl, MD, Sandra Abadir, MD, Garo Kalfayan, MD, Mario Saldana, MD
Los Robles Regional Medical Center, Thousand Oaks, CA
Introduction: Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), a herpesvirus discovered in 1964, has been associated with various malignancies and autoimmune conditions. Infectious mononucleosis (IM), a common manifestation of EBV infection, presents with pharyngitis, adenopathy, and systemic symptoms. Rarely, IM can lead to complications such as splenic rupture and hepatitis. N-acetylcysteine (NAC), known for its antioxidant properties, has shown promise in reducing inflammation associated with viral hepatitis. Understanding the spectrum of complications in IM is crucial for timely management and follow-up.
Case Description/Methods: A 31-year-old male with flu-like symptoms developed progressive jaundice, left upper quadrant pain, and greasy stools. Initial labs showed elevated liver enzymes (AST 261 IU/L, ALT 383 IU/L, ALP 345 IU/L), hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin 6.1 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 4.79 mg/dL), and lymphocytosis. Imaging revealed splenomegaly and diffuse lymphadenopathy of the abdomen and chest. Viral panels were negative, but EBV serology was positive. Liver enzymes continued to rise, prompting N-acetylcysteine treatment. Liver function gradually improved, correlating with declining EBV titers. By discharge, symptoms were at near resolution. On follow-up, liver function was normalized. This case highlights the challenge of diagnosing IM in adults with unexplained jaundice and highlights the potential role of N-acetylcysteine in managing severe hepatic involvement. IM should be considered in the differential diagnosis of jaundice, especially when viral hepatitis is ruled out.
Discussion: EBV is a common cause of IM. Complications include hepatitis, splenic rupture, and rare but serious conditions like acute liver failure. NAC, known for its antioxidant properties, has shown promise in mitigating transaminitis and improving overall survival in acute liver failure, regardless of the underlying cause. Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of NAC in various liver conditions by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing cellular integrity. Recent meta-analyses and randomized trials have highlighted the potential of NAC, emphasizing its role as a therapeutic option with a favorable safety profile. This abstract underscores the evolving landscape of NAC as a potential treatment modality in viral hepatitis-induced liver injury, shedding light on its promise in improving outcomes and mitigating liver damage in patients with acute liver failure. With minimal adverse effects, NAC's use in viral hepatitis merits exploration.
Disclosures:
Ariel Ahl, MD, Sandra Abadir, MD, Garo Kalfayan, MD, Mario Saldana, MD. P3114 - A Case of EBV Hepatitis Treated With N-Acetylcysteine: A Placebo or True Effect?, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Los Robles Regional Medical Center, Thousand Oaks, CA
Introduction: Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), a herpesvirus discovered in 1964, has been associated with various malignancies and autoimmune conditions. Infectious mononucleosis (IM), a common manifestation of EBV infection, presents with pharyngitis, adenopathy, and systemic symptoms. Rarely, IM can lead to complications such as splenic rupture and hepatitis. N-acetylcysteine (NAC), known for its antioxidant properties, has shown promise in reducing inflammation associated with viral hepatitis. Understanding the spectrum of complications in IM is crucial for timely management and follow-up.
Case Description/Methods: A 31-year-old male with flu-like symptoms developed progressive jaundice, left upper quadrant pain, and greasy stools. Initial labs showed elevated liver enzymes (AST 261 IU/L, ALT 383 IU/L, ALP 345 IU/L), hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin 6.1 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 4.79 mg/dL), and lymphocytosis. Imaging revealed splenomegaly and diffuse lymphadenopathy of the abdomen and chest. Viral panels were negative, but EBV serology was positive. Liver enzymes continued to rise, prompting N-acetylcysteine treatment. Liver function gradually improved, correlating with declining EBV titers. By discharge, symptoms were at near resolution. On follow-up, liver function was normalized. This case highlights the challenge of diagnosing IM in adults with unexplained jaundice and highlights the potential role of N-acetylcysteine in managing severe hepatic involvement. IM should be considered in the differential diagnosis of jaundice, especially when viral hepatitis is ruled out.
Discussion: EBV is a common cause of IM. Complications include hepatitis, splenic rupture, and rare but serious conditions like acute liver failure. NAC, known for its antioxidant properties, has shown promise in mitigating transaminitis and improving overall survival in acute liver failure, regardless of the underlying cause. Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of NAC in various liver conditions by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing cellular integrity. Recent meta-analyses and randomized trials have highlighted the potential of NAC, emphasizing its role as a therapeutic option with a favorable safety profile. This abstract underscores the evolving landscape of NAC as a potential treatment modality in viral hepatitis-induced liver injury, shedding light on its promise in improving outcomes and mitigating liver damage in patients with acute liver failure. With minimal adverse effects, NAC's use in viral hepatitis merits exploration.

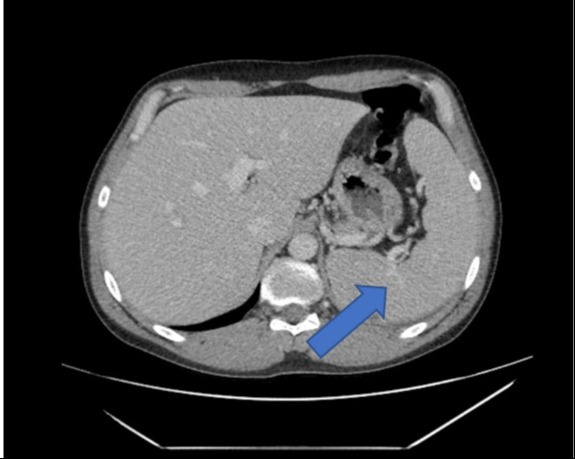
Figure: Figure 1: Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrating splenomegaly (blue arrow).
Disclosures:
Ariel Ahl indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandra Abadir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Garo Kalfayan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mario Saldana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ariel Ahl, MD, Sandra Abadir, MD, Garo Kalfayan, MD, Mario Saldana, MD. P3114 - A Case of EBV Hepatitis Treated With N-Acetylcysteine: A Placebo or True Effect?, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
