Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3131 - Piperacillin-Tazobactam and Hepatic Complications: A Case Report on Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
Priya Kumari Maheshwari, MD
University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME
Pensacola, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Priya Kumari Maheshwari, MD, Peter Fahim, MD, Jun Yoo, DO, Anil Harrison, MD
University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Pensacola, FL
Introduction: Piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP) is a widely used antibiotic combination for treating a variety of bacterial infections. Despite its broad therapeutic applications, reports have indicated instances of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) associated with its use. Here, we present a case involving a 73-year-old female who developed DILI secondary to TZP.
Case Description/Methods: A 73-year-old female with a significant past medical history including hypertension, pulmonary embolism, and right hemicolectomy was transported from a nursing facility to the ED due to abnormal laboratory results. The patient had been discharged ten days earlier following drainage of a right lower quadrant abscess secondary to an anastomotic leak, and was prescribed a two-week course of TZP upon discharge.
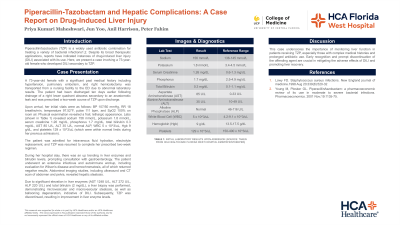
Upon arrival, her initial vitals were: BP 107/50 mmHg, RR 18 breaths/min, temperature 97.52°F, pulse 111 bpm, and SpO2 100% on room air. Physical examination revealed a frail, lethargic appearance. Labs revealed sodium 156 mmol/L, potassium 1.8 mmol/L, serum creatinine 1.26 mg/dL, phosphorus 1.7 mg/dL, total bilirubin 0.3 mg/dL, AST 85 U/L, ALT 35 U/L, normal ALP, WBC 5 x 10^3/uL, Hgb 9 g/dL, and platelets 129 x 10^3/uL (which were within normal limits during her previous admission).
The patient was admitted for intravenous fluid hydration, electrolyte replacement, and TZP was resumed to complete her prescribed two-week regimen.
During her hospital stay, there was an up trending in liver enzymes and bilirubin levels, prompting consultation with gastroenterology. The patient underwent an extensive infectious and autoimmune workup, including evaluation for Wilson's disease and hemochromatosis, all of which returned negative results. Abdominal imaging studies, including ultrasound and CT scan of abdomen and pelvis, revealed hepatic steatosis.
Due to significant elevation in liver enzymes (AST 1248 U/L, ALT 272 U/L, ALP 220 U/L) and total bilirubin (2 mg/dL), a liver biopsy was performed, demonstrating microvesicular and macrovesicular steatosis, as well as ballooning degeneration, indicative of DILI. Subsequently, TZP was discontinued, resulting in improvement in liver enzyme levels.
Discussion: This case underscores the importance of monitoring liver function in patients receiving TZP, especially those with complex medical histories and prolonged antibiotic use. Early recognition and prompt discontinuation of the offending agent are crucial in mitigating the adverse effects of DILI and promoting liver recovery.
Disclosures:
Priya Kumari Maheshwari, MD, Peter Fahim, MD, Jun Yoo, DO, Anil Harrison, MD. P3131 - Piperacillin-Tazobactam and Hepatic Complications: A Case Report on Drug-Induced Liver Injury, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Pensacola, FL
Introduction: Piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP) is a widely used antibiotic combination for treating a variety of bacterial infections. Despite its broad therapeutic applications, reports have indicated instances of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) associated with its use. Here, we present a case involving a 73-year-old female who developed DILI secondary to TZP.
Case Description/Methods: A 73-year-old female with a significant past medical history including hypertension, pulmonary embolism, and right hemicolectomy was transported from a nursing facility to the ED due to abnormal laboratory results. The patient had been discharged ten days earlier following drainage of a right lower quadrant abscess secondary to an anastomotic leak, and was prescribed a two-week course of TZP upon discharge.
Upon arrival, her initial vitals were: BP 107/50 mmHg, RR 18 breaths/min, temperature 97.52°F, pulse 111 bpm, and SpO2 100% on room air. Physical examination revealed a frail, lethargic appearance. Labs revealed sodium 156 mmol/L, potassium 1.8 mmol/L, serum creatinine 1.26 mg/dL, phosphorus 1.7 mg/dL, total bilirubin 0.3 mg/dL, AST 85 U/L, ALT 35 U/L, normal ALP, WBC 5 x 10^3/uL, Hgb 9 g/dL, and platelets 129 x 10^3/uL (which were within normal limits during her previous admission).
The patient was admitted for intravenous fluid hydration, electrolyte replacement, and TZP was resumed to complete her prescribed two-week regimen.
During her hospital stay, there was an up trending in liver enzymes and bilirubin levels, prompting consultation with gastroenterology. The patient underwent an extensive infectious and autoimmune workup, including evaluation for Wilson's disease and hemochromatosis, all of which returned negative results. Abdominal imaging studies, including ultrasound and CT scan of abdomen and pelvis, revealed hepatic steatosis.
Due to significant elevation in liver enzymes (AST 1248 U/L, ALT 272 U/L, ALP 220 U/L) and total bilirubin (2 mg/dL), a liver biopsy was performed, demonstrating microvesicular and macrovesicular steatosis, as well as ballooning degeneration, indicative of DILI. Subsequently, TZP was discontinued, resulting in improvement in liver enzyme levels.
Discussion: This case underscores the importance of monitoring liver function in patients receiving TZP, especially those with complex medical histories and prolonged antibiotic use. Early recognition and prompt discontinuation of the offending agent are crucial in mitigating the adverse effects of DILI and promoting liver recovery.
Disclosures:
Priya Kumari Maheshwari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter Fahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jun Yoo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anil Harrison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priya Kumari Maheshwari, MD, Peter Fahim, MD, Jun Yoo, DO, Anil Harrison, MD. P3131 - Piperacillin-Tazobactam and Hepatic Complications: A Case Report on Drug-Induced Liver Injury, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
