Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3133 - Clinical Course of Acute Liver Failure in Postpartum Patient With Herpes Simplex Viremia
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Aaron Goffinet, MD
University of Chicago Medicine
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Aaron Goffinet, MD, Sonali Paul, MD, MSc, Alan L. Hutchison, MD, PhD
University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Elevated liver tests in peripartum patients present a diagnostic challenge given the spectrum of liver diseases associated with pregnancy. The severity of liver disease can range from mild, asymptomatic elevated liver enzymes to acute liver injury (ALI) and failure (ALF). Early recognition and appropriate treatment of the underlying etiology is essential to reduce morbidity and mortality.
Case Description/Methods: A 26-year-old female underwent an emergency cesarean section for fetal bradycardia and was found to have elevated liver tests following delivery. She was transferred to our medical center three days following delivery and her labs upon arrival were notable for AST 2364, ALT 677, Alk Phos 414, Total bilirubin 2.2 (Direct 2.0), Factor V 27%, and INR 1.6 (Day 0, Table 1). Notable exam findings included RUQ tenderness, asterixis, and slowed response with orientation to self and location only. No fevers, rashes, or other mucocutaneous lesions were seen on exam. N acetyl-cystine (NAC) was given without significant improvement in 24 hours. Empiric acyclovir, continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH), and Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) therapy were initiated, and the patient was listed for liver transplant. Her INR, AST, and ALT peaked on day 2 (2.8, 5873, 1341 respectively; Table 1). Her labs and clinical status improved within 48 hours of CVVH, Acyclovir, and MARS initiation. HSV2 DNA PCR resulted as >2,000,000 copies/mL 10 days later. Her liver function recovered and she and her child remain well 6 months later.
Discussion: HSV hepatitis is a rare cause of ALF. It can be an especially difficult to diagnose in a peripartum patient given the broad differential for liver disease in pregnancy. As with our patient, mucocutaneous lesions are not present in more than 50% of the patients with disseminated HSV [PMID: 17902129]. The three most common causes of ALF in pregnancy are HELLP syndrome (25%), acute fatty liver of pregnancy (25%), and acetaminophen toxicity (30%). HSV infection presents as ALF 5.5% of the time making it the fourth most common cause of ALF in pregnancy [PMID: 37377263]. Pregnancy results in an immunocompromised state and increases the risk of HSV infection. Acyclovir is the treatment of choice for HSV in all patients, including in pregnancy, and was started empirically in this patient given the degree of liver test elevation [PMID: 32332408].
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Aaron Goffinet, MD, Sonali Paul, MD, MSc, Alan L. Hutchison, MD, PhD. P3133 - Clinical Course of Acute Liver Failure in Postpartum Patient With Herpes Simplex Viremia, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Elevated liver tests in peripartum patients present a diagnostic challenge given the spectrum of liver diseases associated with pregnancy. The severity of liver disease can range from mild, asymptomatic elevated liver enzymes to acute liver injury (ALI) and failure (ALF). Early recognition and appropriate treatment of the underlying etiology is essential to reduce morbidity and mortality.
Case Description/Methods: A 26-year-old female underwent an emergency cesarean section for fetal bradycardia and was found to have elevated liver tests following delivery. She was transferred to our medical center three days following delivery and her labs upon arrival were notable for AST 2364, ALT 677, Alk Phos 414, Total bilirubin 2.2 (Direct 2.0), Factor V 27%, and INR 1.6 (Day 0, Table 1). Notable exam findings included RUQ tenderness, asterixis, and slowed response with orientation to self and location only. No fevers, rashes, or other mucocutaneous lesions were seen on exam. N acetyl-cystine (NAC) was given without significant improvement in 24 hours. Empiric acyclovir, continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH), and Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) therapy were initiated, and the patient was listed for liver transplant. Her INR, AST, and ALT peaked on day 2 (2.8, 5873, 1341 respectively; Table 1). Her labs and clinical status improved within 48 hours of CVVH, Acyclovir, and MARS initiation. HSV2 DNA PCR resulted as >2,000,000 copies/mL 10 days later. Her liver function recovered and she and her child remain well 6 months later.
Discussion: HSV hepatitis is a rare cause of ALF. It can be an especially difficult to diagnose in a peripartum patient given the broad differential for liver disease in pregnancy. As with our patient, mucocutaneous lesions are not present in more than 50% of the patients with disseminated HSV [PMID: 17902129]. The three most common causes of ALF in pregnancy are HELLP syndrome (25%), acute fatty liver of pregnancy (25%), and acetaminophen toxicity (30%). HSV infection presents as ALF 5.5% of the time making it the fourth most common cause of ALF in pregnancy [PMID: 37377263]. Pregnancy results in an immunocompromised state and increases the risk of HSV infection. Acyclovir is the treatment of choice for HSV in all patients, including in pregnancy, and was started empirically in this patient given the degree of liver test elevation [PMID: 32332408].

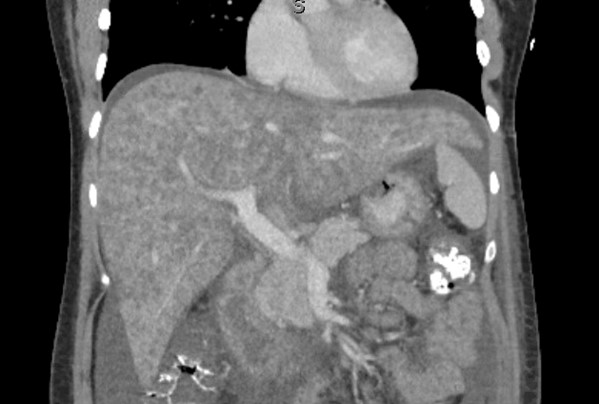
Figure: Marked hepatomegaly, steatosis, and heterogenous enhancement of the liver on CT scan initially postpartum.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Aaron Goffinet indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sonali Paul: Intercept – Grant/Research Support. TARGET PharmaSolutions – Grant/Research Support.
Alan Hutchison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Goffinet, MD, Sonali Paul, MD, MSc, Alan L. Hutchison, MD, PhD. P3133 - Clinical Course of Acute Liver Failure in Postpartum Patient With Herpes Simplex Viremia, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
