Monday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P3170 - Influence of Insulin Dosage on Type 2 Diabetes Remission After Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: A Comparative Analysis of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Wissam Ghusn, MD
Boston Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Wissam Ghusn, MD1, Yara Salameh, MD2, Kamal Abi Mosleh, MD2, Donna Maria Abboud, MD3, Meera Shah, MD2, Andrew Storm, MD2, Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD2, Omar Ghanem, MD2
1Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3Mayo Clinic, Miami, FL
Introduction: The escalating health and economic burdens associated with obesity and type-2 diabetes (T2D) have intensified the need for effective treatment strategies. Metabolic and bariatric surgeries (MBS) such as Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) are recognized for their role in inducing T2D remission (DR). However, conventional predictive models for remission have not considered the influence of insulin dosage, a gap that this study aims to address.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study on individuals with T2D who underwent MBS between 2008 and 2020. Insulin dosage was meticulously documented, and patients were categorized into quartiles based on their total daily insulin doses. The primary objective was to examine the association between insulin dosage and DR at follow-up intervals of one, three-, and five-years post-MBS. Our secondary endpoint was evaluating the effectiveness of RYGB compared to SG in achieving DR across the different levels of insulin use.
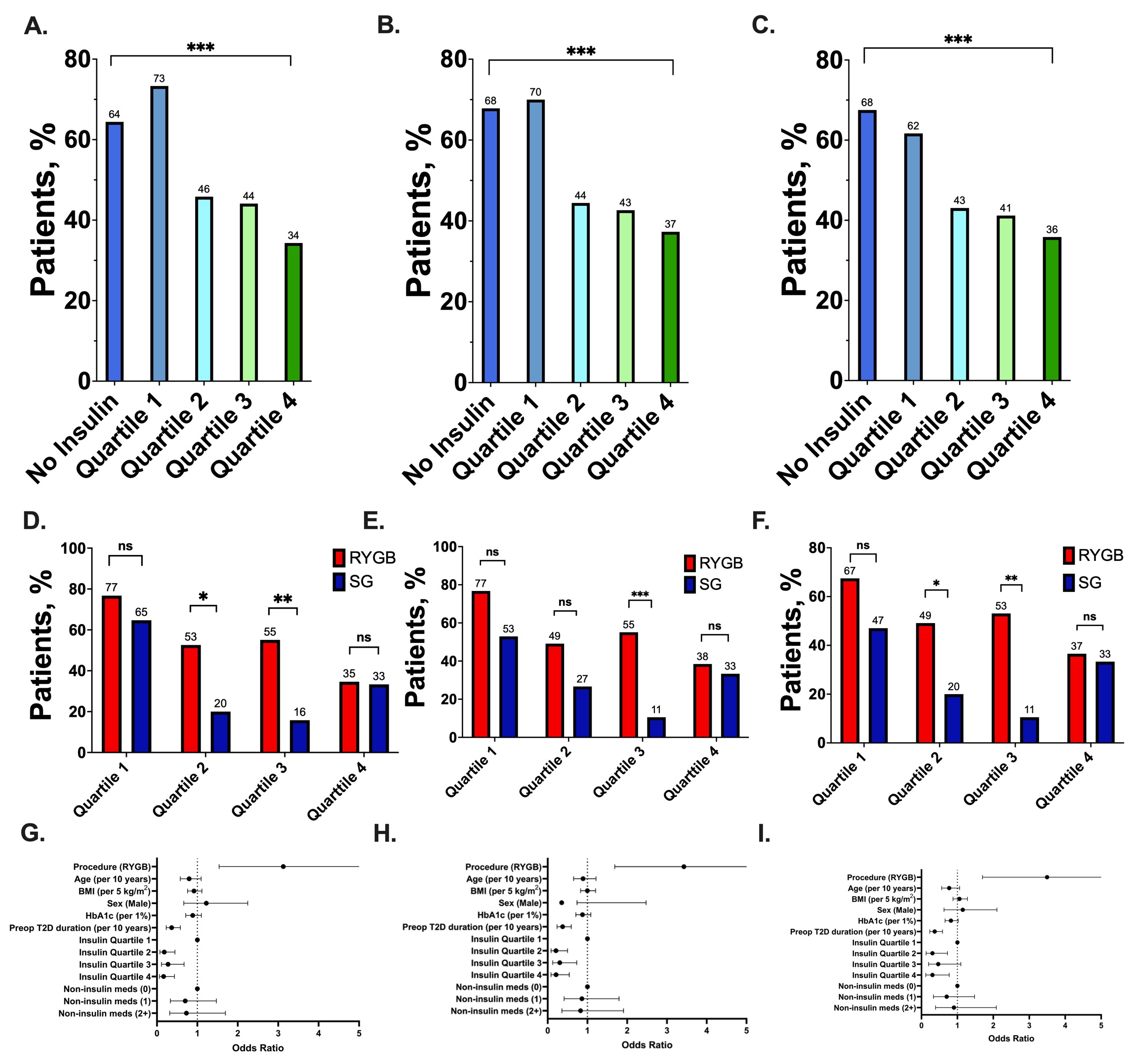
Results: A total of 508 patients (64% female, 94.9% White, mean age 53.5 ± 10.5 years, BMI (46.0± 8.3 kg/m2) were included in the analysis (Table 1). The study's findings highlight a significant inverse relationship between insulin dosage and DR rates. Patients in the lowest quartile of insulin dosage exhibited notably higher DR rates compared to those in the highest quartile; remission was achieved by 73%, 70%, and 62% of patients in the lowest quartile at one, three, and five years, respectively, compared to 34%, 37%, and 36% in the highest quartile (Figure 1A-C). The effectiveness of RYGB over SG was particularly pronounced for patients with moderate insulin dosages, indicating that RYGB may be more suitable for this patient subgroup (Figure 1D-F). In a multivariate analysis, insulin quartiles, procedure type, HbA1c, number of T2D medications, and duration of preoperative T2D were significantly associated with DR at years 1, 3 and 5 years (p< 0.01; Figure 1G-I).
Discussion: The results underscore the critical role of insulin dosage in predicting DR post-MBS, suggesting that insulin dosage should be integrated into the preoperative assessment. This integration could lead to more personalized surgical planning, potentially enhancing remission outcomes for patients with diverse insulin sensitivities. The findings advocate for a revision of current predictive models to include insulin dosage as a significant predictor of DR.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Wissam Ghusn, MD1, Yara Salameh, MD2, Kamal Abi Mosleh, MD2, Donna Maria Abboud, MD3, Meera Shah, MD2, Andrew Storm, MD2, Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD2, Omar Ghanem, MD2. P3170 - Influence of Insulin Dosage on Type 2 Diabetes Remission After Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: A Comparative Analysis of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3Mayo Clinic, Miami, FL
Introduction: The escalating health and economic burdens associated with obesity and type-2 diabetes (T2D) have intensified the need for effective treatment strategies. Metabolic and bariatric surgeries (MBS) such as Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) are recognized for their role in inducing T2D remission (DR). However, conventional predictive models for remission have not considered the influence of insulin dosage, a gap that this study aims to address.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study on individuals with T2D who underwent MBS between 2008 and 2020. Insulin dosage was meticulously documented, and patients were categorized into quartiles based on their total daily insulin doses. The primary objective was to examine the association between insulin dosage and DR at follow-up intervals of one, three-, and five-years post-MBS. Our secondary endpoint was evaluating the effectiveness of RYGB compared to SG in achieving DR across the different levels of insulin use.
Results: A total of 508 patients (64% female, 94.9% White, mean age 53.5 ± 10.5 years, BMI (46.0± 8.3 kg/m2) were included in the analysis (Table 1). The study's findings highlight a significant inverse relationship between insulin dosage and DR rates. Patients in the lowest quartile of insulin dosage exhibited notably higher DR rates compared to those in the highest quartile; remission was achieved by 73%, 70%, and 62% of patients in the lowest quartile at one, three, and five years, respectively, compared to 34%, 37%, and 36% in the highest quartile (Figure 1A-C). The effectiveness of RYGB over SG was particularly pronounced for patients with moderate insulin dosages, indicating that RYGB may be more suitable for this patient subgroup (Figure 1D-F). In a multivariate analysis, insulin quartiles, procedure type, HbA1c, number of T2D medications, and duration of preoperative T2D were significantly associated with DR at years 1, 3 and 5 years (p< 0.01; Figure 1G-I).
Discussion: The results underscore the critical role of insulin dosage in predicting DR post-MBS, suggesting that insulin dosage should be integrated into the preoperative assessment. This integration could lead to more personalized surgical planning, potentially enhancing remission outcomes for patients with diverse insulin sensitivities. The findings advocate for a revision of current predictive models to include insulin dosage as a significant predictor of DR.

Figure: Figure 1: Percentage of diabetes remission in patients with no insulin use and different quartiles of insulin doses at 1 year (A), 3 years (B), and 5 years (C). RYGB vs SG in diabetes remission for patients within each quartile of insulin dose at 1 year (D), 3 years (E), and 5 years (F). Odds ratios of diabetes remission in a multivariate logistic regression at 1 year (G), 3 years (H), and 5 years (I).
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Wissam Ghusn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yara Salameh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kamal Abi Mosleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Donna Maria Abboud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meera Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Storm indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barham Abu Dayyeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Ghanem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wissam Ghusn, MD1, Yara Salameh, MD2, Kamal Abi Mosleh, MD2, Donna Maria Abboud, MD3, Meera Shah, MD2, Andrew Storm, MD2, Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD2, Omar Ghanem, MD2. P3170 - Influence of Insulin Dosage on Type 2 Diabetes Remission After Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: A Comparative Analysis of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

