Monday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P3177 - Semaglutide-Linked Dry Beriberi: A Rare Adverse Reaction
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Faris Shweikeh, MD
Cleveland Clinic Akron General
Akron, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Lisnaldy C. Ramirez-Osoria, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Anamay N. Sharma, MD6
1University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX; 2University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 3Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 4St. Barnabas Hospital, Bronx, NY; 5Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 6Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, is a therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Studies have shown the use of this drug with lifestyle modifications can cause significant weight loss, up to 33.7 pounds. We report a case where the patient developed dry beri beri due to nutritional deficiencies due to excessive weight loss associated with its use.
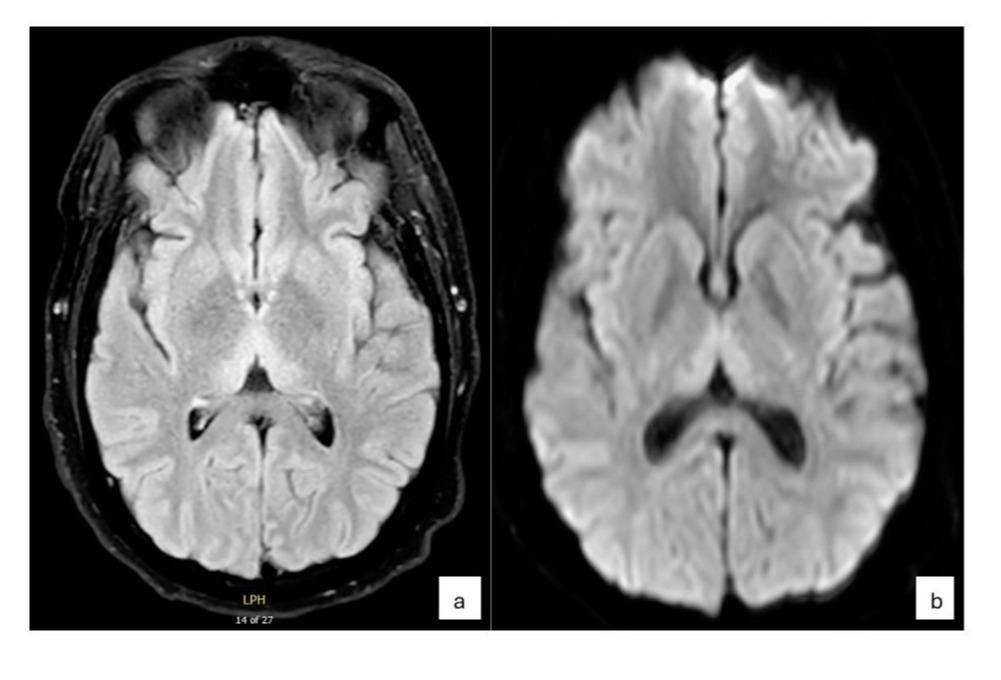
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old nonalcoholic male with a history of morbid obesity with a BMI of 58.7 (175 kg) in early 2022 was started on Semaglutide for weight loss in May 2022, and by August 2022; BMI was decreased to 50 (135 kg) was admitted with weakness, fatigue and decreased sensation in lower extremities. He lost 40 kg (88 pounds) in 3-4 months. He underwent imaging of the brain with MRI and LP, which showed possible Wernicke encephalopathy based on hyperintense bilateral thalamic lesions in both FLAIR/DWI sequences. He was treated for possible GBS Miller Fisher-variant syndrome based on presentation and increased CSF protein with IVIG. Ganglioside antibody profile ultimately resulted in unremarkable levels (including GQ1B ab associated with Miller Fisher syndrome). Labs showed low thiamine (29), for which he received a high dose of IV thiamine. He continued to have multiple readmissions for falls, weakness, ongoing weight loss, malnutrition, cognitive impairment (MOCA 5/22), constipation, and urinary retention. Other workups included normal heavy metal screen, folate, copper, zinc, negative Lyme, and EMG testing, which was unremarkable. He was found to have significant vitamin deficiencies, including low B1, B2, B6, Vit D, folate, and Vit C, which were repleted. By early 2024, his BMI is down to 20.4 (61 kg) despite nutritional support. He was diagnosed with dry beriberi and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Discussion: Beriberi and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome were reported as acute and chronic complications of weight loss surgery. Thiamine deficiency could also occur in alcoholics and as a complication of TPN if adequate thiamine is not provided in the formulation. Treatment of beriberi starts as IV, followed by oral replacement. Wernicke encephalopathy is reversible if treated promptly with high-dose IV thiamine. However, Korsakoff's psychosis is less reversible. No reports in the literature have identified an association between GLP-1 agonists and beriberi. Further studies are needed to determine the prevalence of this complication, as it may be higher than currently recognized.
Disclosures:
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Lisnaldy C. Ramirez-Osoria, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Anamay N. Sharma, MD6. P3177 - Semaglutide-Linked Dry Beriberi: A Rare Adverse Reaction, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Lisnaldy C. Ramirez-Osoria, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Anamay N. Sharma, MD6
1University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX; 2University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 3Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 4St. Barnabas Hospital, Bronx, NY; 5Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 6Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, is a therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Studies have shown the use of this drug with lifestyle modifications can cause significant weight loss, up to 33.7 pounds. We report a case where the patient developed dry beri beri due to nutritional deficiencies due to excessive weight loss associated with its use.
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old nonalcoholic male with a history of morbid obesity with a BMI of 58.7 (175 kg) in early 2022 was started on Semaglutide for weight loss in May 2022, and by August 2022; BMI was decreased to 50 (135 kg) was admitted with weakness, fatigue and decreased sensation in lower extremities. He lost 40 kg (88 pounds) in 3-4 months. He underwent imaging of the brain with MRI and LP, which showed possible Wernicke encephalopathy based on hyperintense bilateral thalamic lesions in both FLAIR/DWI sequences. He was treated for possible GBS Miller Fisher-variant syndrome based on presentation and increased CSF protein with IVIG. Ganglioside antibody profile ultimately resulted in unremarkable levels (including GQ1B ab associated with Miller Fisher syndrome). Labs showed low thiamine (29), for which he received a high dose of IV thiamine. He continued to have multiple readmissions for falls, weakness, ongoing weight loss, malnutrition, cognitive impairment (MOCA 5/22), constipation, and urinary retention. Other workups included normal heavy metal screen, folate, copper, zinc, negative Lyme, and EMG testing, which was unremarkable. He was found to have significant vitamin deficiencies, including low B1, B2, B6, Vit D, folate, and Vit C, which were repleted. By early 2024, his BMI is down to 20.4 (61 kg) despite nutritional support. He was diagnosed with dry beriberi and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Discussion: Beriberi and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome were reported as acute and chronic complications of weight loss surgery. Thiamine deficiency could also occur in alcoholics and as a complication of TPN if adequate thiamine is not provided in the formulation. Treatment of beriberi starts as IV, followed by oral replacement. Wernicke encephalopathy is reversible if treated promptly with high-dose IV thiamine. However, Korsakoff's psychosis is less reversible. No reports in the literature have identified an association between GLP-1 agonists and beriberi. Further studies are needed to determine the prevalence of this complication, as it may be higher than currently recognized.

Figure: a. FLAIR image showing hyperintense lesions on bilateral thalami. b. DWI showing hyperintense lesions on bilateral thalami diagnostic of Wernicke encephalopathy
Disclosures:
Neha Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faris Shweikeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisnaldy Ramirez-Osoria indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Chandra Chakinala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anamay Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Lisnaldy C. Ramirez-Osoria, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Anamay N. Sharma, MD6. P3177 - Semaglutide-Linked Dry Beriberi: A Rare Adverse Reaction, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

