Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P3263 - An Unexpected Discovery: A Suspicious Duodenal Mass Revealed as Burkitt Lymphoma
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- HG
Harneet Grewal, MD
Abrazo Health
Glendale, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Harneet Grewal, MD1, Aaron Sidhu, MD1, Anna E. Schwab, DO2, Candice Hanna, DO1, Khushbir Bath, MD3
1Abrazo Health, Glendale, AZ; 2Abrazo Health, Chandler, AZ; 3Arizona Gastrointestinal Associates, Chandler, AZ
Introduction: Primary malignant tumors of the small bowel are rare and account for 3 to 6 percent of all GI neoplasms. Of these, lymphomas make up 15 to 20 percent, with the ileum being the most common and the duodenum being the least common site of occurrence. Burkitt Lymphoma (BL) is a rare and aggressive non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma that is classified into three separate categories: endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-related subtypes. Each of these subtypes has distinct pathological and clinical features, however, all are characterized to be rapidly progressive tumors with high rates of extra-nodal involvement. Although aggressive, these tumors have good outcomes with modern treatments. Here, we present a rare finding of a primary duodenal BL.
Case Description/Methods: A 40-year-old male with a past medical history of GERD, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia presented to the hospital with intermittent melena, epigastric pain, and coffee-ground emesis. He was trialed on sucralfate, famotidine, and omeprazole without relief. Bloodwork was significant for leukocytosis and thrombocytosis. CT abdomen and pelvis revealed an irregular mass-like wall thickening of the gastric antrum and proximal duodenum with adjacent inflammatory change measuring 5.9 x 6.8 x 6.7 cm. Patient underwent EGD which showed erosive esophagitis and an obstructive mass involving the duodenal bulb and the second portion of the duodenum. CA19-9 and CEA returned negative, LDH was elevated at 632. Biopsy of the mass revealed Burkitt Lymphoma which expressed cMYC, CD10, CD20, Ki-67, MUM1, and Pax5. CT chest for initial staging showed no evidence of pulmonary or mediastinal metastases. He was subsequently discharged with close hematology/ oncology follow-up and ultimately referred for stem cell transplantation.
Discussion: Primary small bowel neoplasms have a low community-based prevalence and there is no recommended population-based screening for these tumors. Thus, incidental tumors tend to be detected in the setting of cross-sectional imaging. Although much less common than duodenal MALT lymphoma and carcinoid tumors, BL tends to be a rapidly growing human tumor requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. This case illustrated a BL causing obstructive symptoms prompting EGD and tissue sampling. The mainstay of treatment is chemotherapy, but stem cell transplantation can be trialed to mitigate relapse.
Disclosures:
Harneet Grewal, MD1, Aaron Sidhu, MD1, Anna E. Schwab, DO2, Candice Hanna, DO1, Khushbir Bath, MD3. P3263 - An Unexpected Discovery: A Suspicious Duodenal Mass Revealed as Burkitt Lymphoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Abrazo Health, Glendale, AZ; 2Abrazo Health, Chandler, AZ; 3Arizona Gastrointestinal Associates, Chandler, AZ
Introduction: Primary malignant tumors of the small bowel are rare and account for 3 to 6 percent of all GI neoplasms. Of these, lymphomas make up 15 to 20 percent, with the ileum being the most common and the duodenum being the least common site of occurrence. Burkitt Lymphoma (BL) is a rare and aggressive non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma that is classified into three separate categories: endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-related subtypes. Each of these subtypes has distinct pathological and clinical features, however, all are characterized to be rapidly progressive tumors with high rates of extra-nodal involvement. Although aggressive, these tumors have good outcomes with modern treatments. Here, we present a rare finding of a primary duodenal BL.
Case Description/Methods: A 40-year-old male with a past medical history of GERD, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia presented to the hospital with intermittent melena, epigastric pain, and coffee-ground emesis. He was trialed on sucralfate, famotidine, and omeprazole without relief. Bloodwork was significant for leukocytosis and thrombocytosis. CT abdomen and pelvis revealed an irregular mass-like wall thickening of the gastric antrum and proximal duodenum with adjacent inflammatory change measuring 5.9 x 6.8 x 6.7 cm. Patient underwent EGD which showed erosive esophagitis and an obstructive mass involving the duodenal bulb and the second portion of the duodenum. CA19-9 and CEA returned negative, LDH was elevated at 632. Biopsy of the mass revealed Burkitt Lymphoma which expressed cMYC, CD10, CD20, Ki-67, MUM1, and Pax5. CT chest for initial staging showed no evidence of pulmonary or mediastinal metastases. He was subsequently discharged with close hematology/ oncology follow-up and ultimately referred for stem cell transplantation.
Discussion: Primary small bowel neoplasms have a low community-based prevalence and there is no recommended population-based screening for these tumors. Thus, incidental tumors tend to be detected in the setting of cross-sectional imaging. Although much less common than duodenal MALT lymphoma and carcinoid tumors, BL tends to be a rapidly growing human tumor requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. This case illustrated a BL causing obstructive symptoms prompting EGD and tissue sampling. The mainstay of treatment is chemotherapy, but stem cell transplantation can be trialed to mitigate relapse.

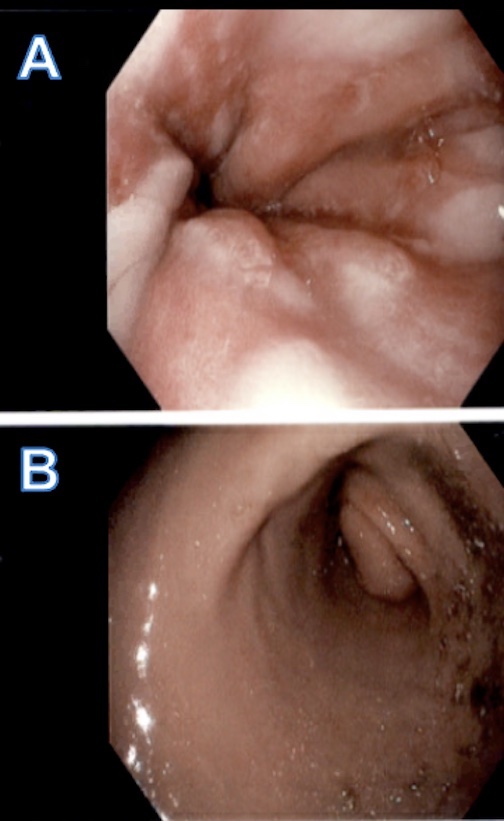
Figure: Panel A: Distal erosive esophagitis. Panel B: Obstructive mass involving the bulb and the second portion of the duodenum.
Disclosures:
Harneet Grewal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Sidhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anna Schwab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Candice Hanna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khushbir Bath indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harneet Grewal, MD1, Aaron Sidhu, MD1, Anna E. Schwab, DO2, Candice Hanna, DO1, Khushbir Bath, MD3. P3263 - An Unexpected Discovery: A Suspicious Duodenal Mass Revealed as Burkitt Lymphoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
