Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P3290 - RUQ Pain Leading to Rare Primary Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- MT
Michael Tran, MD
Ochsner LSU Health
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Tran, MD1, Khadija Khan, MD2, Farhan Mohiuddin, MD3, Hassaan A. Zia, MD2
1Ochsner LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 2LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 3LSU Health, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Primary duodenal follicular lymphoma (FL) is rare and patients usually are asymptomatic. Incidence of primary duodenal FL is 1-3%. In the United States, primary FL is usually seen in the stomach. Discovery of the disease is usually incidental by esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). We present a case of primary duodenal FL in a patient with right upper quadrant pain (RUQ).
Case Description/Methods: 61-year-old female with history of neuroendocrine tumor of the liver and treated with Yttrium-90 (Y-90) who presented for EGD for RUQ postprandial pain and possible acid reflux symptoms. EGD was completed with normal findings in the esophagus, stomach, and duodenal bulb. Further inspection past the bulb revealed localized white speckled appearance in the duodenum which were biopsied. Pathology showed atypical lymphoid infiltrate expanding the lamina propria. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization was positive for BCL2 rearrangement and CD10 stain positive. Diagnosis was malignant lymphoma, B-phenotype, compatible with neoplasm of follicle center cell origin (grade 1/2). Gastric emptying study was later completed and suggested biliary dyskinesia. Cholecystectomy was done and pathology showed subacute cholecystitis with fibrosis and Y-90 emboli consistent with radiation-induced cholecystitis.
Discussion: Primary duodenal FL is asymptomatic, patients do not usually know they have the disease unless other symptoms warrant an EGD. FL presents as multiple whitish granules or submucosal nodules in the duodenal mucosa past the bulb. Most common symptom associated with FL is abdominal pain. EGD is crucial in diagnosis of FL in the duodenum due to the ability to biopsy lesions seen. Due to its indolent presentation and slow growth, usually a watch and wait policy is implemented. Radiation or chemotherapy is reserved if symptoms or disease progression is seen like pancytopenia. The patient’s RUQ pain could have been due to radiation-induced cholecystitis, however if the patient did not have the pain, EGD would not have been completed. This rare case stresses the importance of EGD in the diagnosis of primary duodenal FL and the importance of biopsy of abnormal lesions.
Disclosures:
Michael Tran, MD1, Khadija Khan, MD2, Farhan Mohiuddin, MD3, Hassaan A. Zia, MD2. P3290 - RUQ Pain Leading to Rare Primary Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Ochsner LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 2LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 3LSU Health, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Primary duodenal follicular lymphoma (FL) is rare and patients usually are asymptomatic. Incidence of primary duodenal FL is 1-3%. In the United States, primary FL is usually seen in the stomach. Discovery of the disease is usually incidental by esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). We present a case of primary duodenal FL in a patient with right upper quadrant pain (RUQ).
Case Description/Methods: 61-year-old female with history of neuroendocrine tumor of the liver and treated with Yttrium-90 (Y-90) who presented for EGD for RUQ postprandial pain and possible acid reflux symptoms. EGD was completed with normal findings in the esophagus, stomach, and duodenal bulb. Further inspection past the bulb revealed localized white speckled appearance in the duodenum which were biopsied. Pathology showed atypical lymphoid infiltrate expanding the lamina propria. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization was positive for BCL2 rearrangement and CD10 stain positive. Diagnosis was malignant lymphoma, B-phenotype, compatible with neoplasm of follicle center cell origin (grade 1/2). Gastric emptying study was later completed and suggested biliary dyskinesia. Cholecystectomy was done and pathology showed subacute cholecystitis with fibrosis and Y-90 emboli consistent with radiation-induced cholecystitis.
Discussion: Primary duodenal FL is asymptomatic, patients do not usually know they have the disease unless other symptoms warrant an EGD. FL presents as multiple whitish granules or submucosal nodules in the duodenal mucosa past the bulb. Most common symptom associated with FL is abdominal pain. EGD is crucial in diagnosis of FL in the duodenum due to the ability to biopsy lesions seen. Due to its indolent presentation and slow growth, usually a watch and wait policy is implemented. Radiation or chemotherapy is reserved if symptoms or disease progression is seen like pancytopenia. The patient’s RUQ pain could have been due to radiation-induced cholecystitis, however if the patient did not have the pain, EGD would not have been completed. This rare case stresses the importance of EGD in the diagnosis of primary duodenal FL and the importance of biopsy of abnormal lesions.

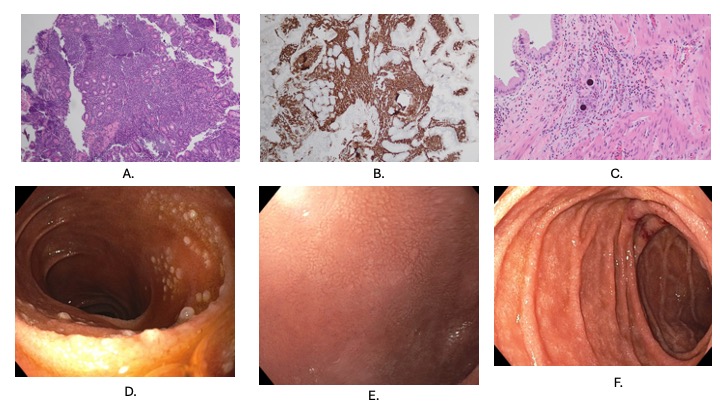
Figure: A. Duodenum H and E 10x showing B cell lymphoma
B. Duodenum CD20 stain 10x
C. Radiation Y-90 cholecystitis
D. White granules in duodenum representing B cell lymphoma
E. Normal appearing duodenal bulb
F. Normal appearing 2nd portion duodenum
B. Duodenum CD20 stain 10x
C. Radiation Y-90 cholecystitis
D. White granules in duodenum representing B cell lymphoma
E. Normal appearing duodenal bulb
F. Normal appearing 2nd portion duodenum
Disclosures:
Michael Tran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farhan Mohiuddin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassaan A. Zia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Tran, MD1, Khadija Khan, MD2, Farhan Mohiuddin, MD3, Hassaan A. Zia, MD2. P3290 - RUQ Pain Leading to Rare Primary Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
