Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3464 - Evaluation of Interobserver Agreement in Dysplasia Classification for IPMNs and the Impact on Pre-Surgical Risk Stratification
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Matt Leupold, MD
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Matthew Leupold, MD1, Wei Chen, 1, Ashwini Esnakula, MBBS1, Wendy Frankel, MD1, Stacey Culp, PhD2, Phil Hart, MD1, Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Zarine K. Shah, MD1, Erica Park, MD1, Peter J Lee, MD1, Mitchell L. Ramsey, MD1, Sam Han, MD1, Hamza Shah, MD1, Jordan Burlen, MD1, Georgios Papachristou, MD, PhD1, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, PhD1, Mary Dillhoff, MD1, Jordan Cloyd, MD1, Timothy Pawlik, MD1, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
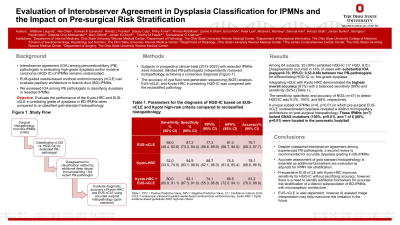
Introduction: Interobserver agreement (IOA) among pancreaticobiliary (PB) pathologists in evaluating high-grade dysplasia and/or invasive carcinoma (HGD-IC) of IPMNs remains understudied. EUS-guided needle-based confocal endomicroscopy (nCLE) can evaluate papillary architecture in branch-duct (BD)-IPMNs. We assessed IOA among PB pathologists in classifying dysplasia in resected IPMNs. We compared the performance of the Kyoto guidelines’ high-risk criteria (HRC) and pre-surgical EUS-nCLE against reclassified pathology.
Methods: Subjects in prospective clinical trials (2015-2023) with resected IPMNs were included. Blinded PB-pathologists independently reviewed histopathology, achieving a consensus diagnosis. The accuracy of cyst fluid next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis, EUS-nCLE, and Kyoto-HRC in predicting HGD-IC was compared with the reclassified pathology.
Results: Among 64 subjects, 25 (39%) exhibited HGD-IC (17 HGD, 8 IC). Disagreements occurred in 14% of cases with substantial IOA (kappa=0.70; 95%CI: 0.53-0.88) between two PB-pathologists for differentiating HGD-IC vs. low-grade dysplasia.
To detect HGD-IC, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of Kyoto-HRC and EUS-nCLE were 52%, 95%, 78%, and 68%, 87%, 80%, respectively. Integrating nCLE with Kyoto-HRC improved sensitivity to 80%, with specificity and accuracy at 82% and 81%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of NGS (n=47) to detect HGD-IC was 6.3%, 100%, and 68%, respectively.
A unique subset of IPMNs (n=8, p=0.01) in which pre-surgical EUS-nCLE underestimated dysplasia revealed a distinct micropapillary architecture on post-surgical histopathology. These IPMNs (n=7) lacked GNAS mutations (100%, p=0.01), and 7 of 8 (88%, p=0.01) were located in the pancreatic body/tail.
Discussion: Despite substantial interobserver agreement among experienced PB-pathologists, a second review is recommended for accurate dysplasia grading in BD-IPMNs due to its impact on patient prognosis and biomarker research validity. Preoperative EUS-nCLE with Kyoto-HRC improves sensitivity for HGD-IC without sacrificing accuracy; however, there is a need to identify additional biomarkers for accurate risk stratification of a distinct subpopulation of BD-IPMNs with micropapillary architecture.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Matthew Leupold, MD1, Wei Chen, 1, Ashwini Esnakula, MBBS1, Wendy Frankel, MD1, Stacey Culp, PhD2, Phil Hart, MD1, Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Zarine K. Shah, MD1, Erica Park, MD1, Peter J Lee, MD1, Mitchell L. Ramsey, MD1, Sam Han, MD1, Hamza Shah, MD1, Jordan Burlen, MD1, Georgios Papachristou, MD, PhD1, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, PhD1, Mary Dillhoff, MD1, Jordan Cloyd, MD1, Timothy Pawlik, MD1, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1. P3464 - Evaluation of Interobserver Agreement in Dysplasia Classification for IPMNs and the Impact on Pre-Surgical Risk Stratification, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Introduction: Interobserver agreement (IOA) among pancreaticobiliary (PB) pathologists in evaluating high-grade dysplasia and/or invasive carcinoma (HGD-IC) of IPMNs remains understudied. EUS-guided needle-based confocal endomicroscopy (nCLE) can evaluate papillary architecture in branch-duct (BD)-IPMNs. We assessed IOA among PB pathologists in classifying dysplasia in resected IPMNs. We compared the performance of the Kyoto guidelines’ high-risk criteria (HRC) and pre-surgical EUS-nCLE against reclassified pathology.
Methods: Subjects in prospective clinical trials (2015-2023) with resected IPMNs were included. Blinded PB-pathologists independently reviewed histopathology, achieving a consensus diagnosis. The accuracy of cyst fluid next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis, EUS-nCLE, and Kyoto-HRC in predicting HGD-IC was compared with the reclassified pathology.
Results: Among 64 subjects, 25 (39%) exhibited HGD-IC (17 HGD, 8 IC). Disagreements occurred in 14% of cases with substantial IOA (kappa=0.70; 95%CI: 0.53-0.88) between two PB-pathologists for differentiating HGD-IC vs. low-grade dysplasia.
To detect HGD-IC, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of Kyoto-HRC and EUS-nCLE were 52%, 95%, 78%, and 68%, 87%, 80%, respectively. Integrating nCLE with Kyoto-HRC improved sensitivity to 80%, with specificity and accuracy at 82% and 81%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of NGS (n=47) to detect HGD-IC was 6.3%, 100%, and 68%, respectively.
A unique subset of IPMNs (n=8, p=0.01) in which pre-surgical EUS-nCLE underestimated dysplasia revealed a distinct micropapillary architecture on post-surgical histopathology. These IPMNs (n=7) lacked GNAS mutations (100%, p=0.01), and 7 of 8 (88%, p=0.01) were located in the pancreatic body/tail.
Discussion: Despite substantial interobserver agreement among experienced PB-pathologists, a second review is recommended for accurate dysplasia grading in BD-IPMNs due to its impact on patient prognosis and biomarker research validity. Preoperative EUS-nCLE with Kyoto-HRC improves sensitivity for HGD-IC without sacrificing accuracy; however, there is a need to identify additional biomarkers for accurate risk stratification of a distinct subpopulation of BD-IPMNs with micropapillary architecture.

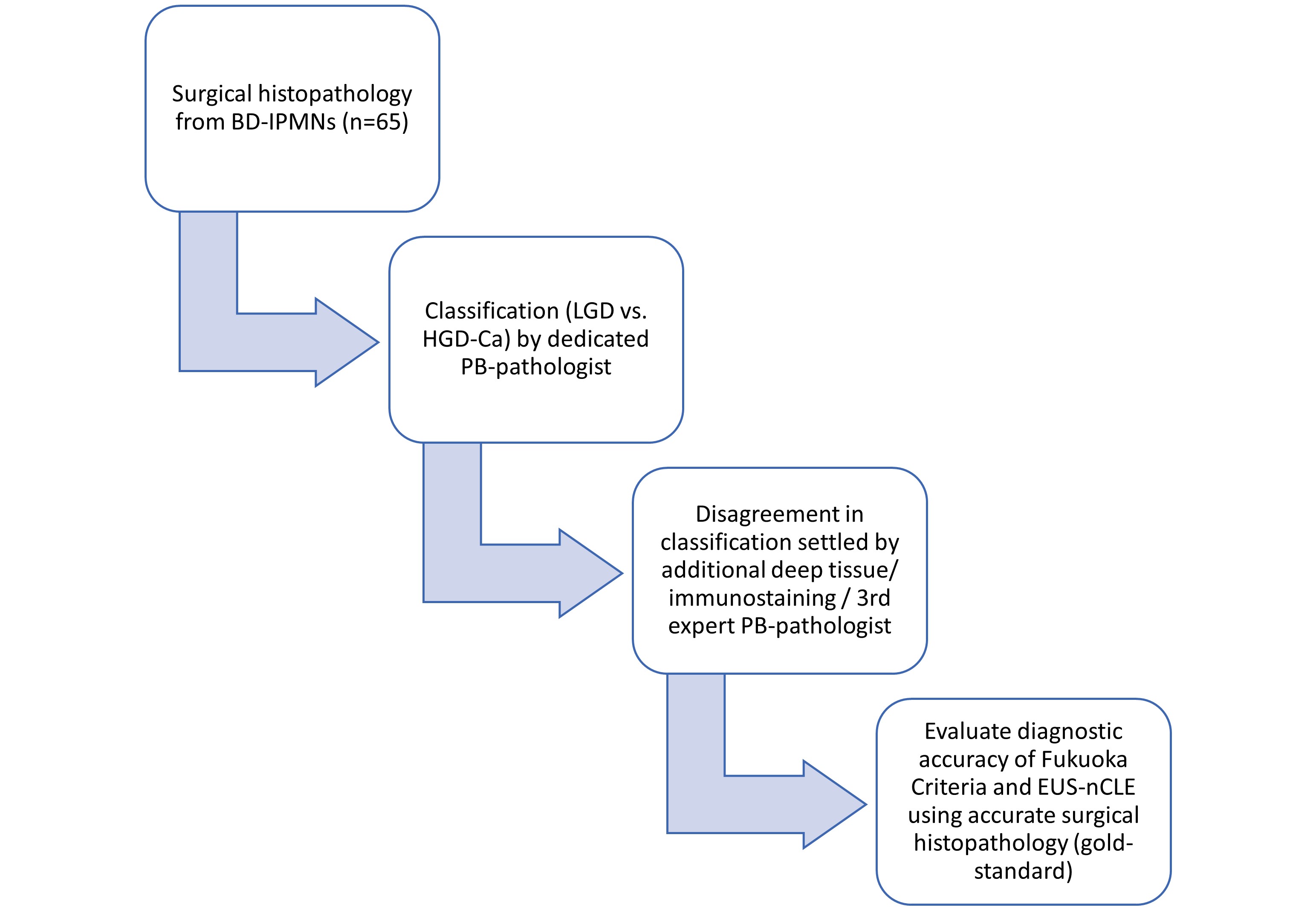
Figure: Figure 1. Study flow
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Matthew Leupold indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wei Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwini Esnakula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wendy Frankel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stacey Culp indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phil Hart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Abdelbaki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zarine Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erica Park indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter J Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mitchell Ramsey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sam Han indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Burlen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Georgios Papachristou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Dillhoff indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Cloyd indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Timothy Pawlik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somashekar G Krishna: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Mauna Kea Technologies, and TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support. TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support.
Matthew Leupold, MD1, Wei Chen, 1, Ashwini Esnakula, MBBS1, Wendy Frankel, MD1, Stacey Culp, PhD2, Phil Hart, MD1, Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Zarine K. Shah, MD1, Erica Park, MD1, Peter J Lee, MD1, Mitchell L. Ramsey, MD1, Sam Han, MD1, Hamza Shah, MD1, Jordan Burlen, MD1, Georgios Papachristou, MD, PhD1, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, PhD1, Mary Dillhoff, MD1, Jordan Cloyd, MD1, Timothy Pawlik, MD1, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1. P3464 - Evaluation of Interobserver Agreement in Dysplasia Classification for IPMNs and the Impact on Pre-Surgical Risk Stratification, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
