Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3478 - Diclofenac as Post-ERCP Pancreatitis Prophylaxis: A Cost-Effective Intervention
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- AK
Ayesha Khan, DO
University of Texas Medical Branch
Galveston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Ayesha Khan, DO, Ernesto Zamora, MD, Jordan Malone, DO, Muhammad Mushtaq, DO, Gabriel Reep, MD, Sreeram Parupudi, MD
University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Introduction: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a common procedure used to treat a variety of pancreaticobiliary diseases. The most feared complication of ERCP is post-ERCP pancreatitis (PEP). PEP occurs at an incidence rate between 1-10% and carries significant associated morbidity as well as high health care expenditures exceeding $150-200 million annually. Current guidelines recommend rectally administered indomethacin or diclofenac in the preprocedural period as PEP prophylaxis. Rectal diclofenac is not commercially available in the U.S. and rectal indomethacin costs continue to rise substantially. We sought out to determine the cost and feasibility of bringing the ability to compound diclofenac suppositories in-house at UTMB for use in place of indomethacin.
Methods: We reviewed the quantity of ERCPs performed at our institution from January 2023 – January 2024. We then reviewed the frequency of rectally administered indomethacin and each unit’s individual price to determine the total cost to the institution. We then discussed the pricing of in-house compounding of rectal diclofenac per unit with our pharmacy and compared this to our current expenditure on rectal indomethacin and created a hypothetical expenditure model comparing the two medications.
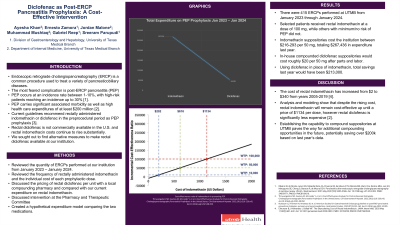
Results: There were 415 ERCPs performed at UTMB from January 2023 through January 2024. Selected patients received rectal indomethacin at a dose of 100 mg, while others with minimum/no risk of PEP did not. Indomethacin suppositories currently cost the institution between $216-293 per 50 mg dose totaling $267,436 in expenditure for fiscal year 2023. In-house compounding of diclofenac 50 mg suppositories would cost $20 per 50 mg suppository after materials and labor with a total annual savings associated with in-house preparation of diclofenac suppositories of $213,000 (figure 1).
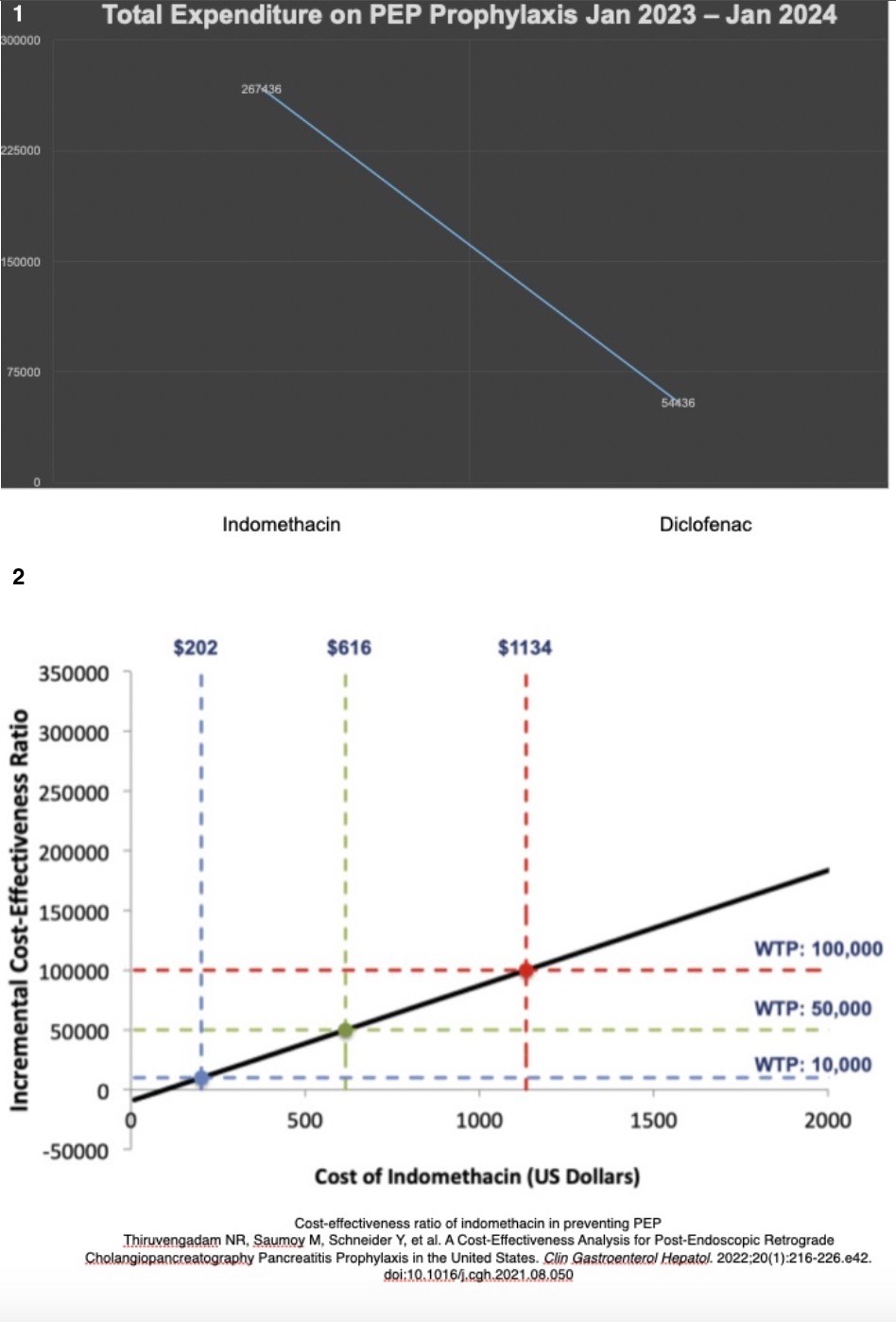
Discussion: The cost of rectal indomethacin increased from $2 to $340 from years 2005-2019 (figure 2). Analysis and modeling show that despite the rising cost, rectal indomethacin will remain cost-effective up until a price of $1134 per dose, however rectal diclofenac is significantly less expensive. We can significantly reduce our spending by utilizing rectal diclofenac in place of indomethacin, saving the institution over $200k based on data from last year.
Disclosures:
Ayesha Khan, DO, Ernesto Zamora, MD, Jordan Malone, DO, Muhammad Mushtaq, DO, Gabriel Reep, MD, Sreeram Parupudi, MD. P3478 - Diclofenac as Post-ERCP Pancreatitis Prophylaxis: A Cost-Effective Intervention, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Introduction: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a common procedure used to treat a variety of pancreaticobiliary diseases. The most feared complication of ERCP is post-ERCP pancreatitis (PEP). PEP occurs at an incidence rate between 1-10% and carries significant associated morbidity as well as high health care expenditures exceeding $150-200 million annually. Current guidelines recommend rectally administered indomethacin or diclofenac in the preprocedural period as PEP prophylaxis. Rectal diclofenac is not commercially available in the U.S. and rectal indomethacin costs continue to rise substantially. We sought out to determine the cost and feasibility of bringing the ability to compound diclofenac suppositories in-house at UTMB for use in place of indomethacin.
Methods: We reviewed the quantity of ERCPs performed at our institution from January 2023 – January 2024. We then reviewed the frequency of rectally administered indomethacin and each unit’s individual price to determine the total cost to the institution. We then discussed the pricing of in-house compounding of rectal diclofenac per unit with our pharmacy and compared this to our current expenditure on rectal indomethacin and created a hypothetical expenditure model comparing the two medications.
Results: There were 415 ERCPs performed at UTMB from January 2023 through January 2024. Selected patients received rectal indomethacin at a dose of 100 mg, while others with minimum/no risk of PEP did not. Indomethacin suppositories currently cost the institution between $216-293 per 50 mg dose totaling $267,436 in expenditure for fiscal year 2023. In-house compounding of diclofenac 50 mg suppositories would cost $20 per 50 mg suppository after materials and labor with a total annual savings associated with in-house preparation of diclofenac suppositories of $213,000 (figure 1).
Discussion: The cost of rectal indomethacin increased from $2 to $340 from years 2005-2019 (figure 2). Analysis and modeling show that despite the rising cost, rectal indomethacin will remain cost-effective up until a price of $1134 per dose, however rectal diclofenac is significantly less expensive. We can significantly reduce our spending by utilizing rectal diclofenac in place of indomethacin, saving the institution over $200k based on data from last year.

Figure: figure 1: Trend in total expenditure on PEP prophylaxis from January 2023- January 2024
figure 2: Cost-effectiveness ratio of indomethacin in preventing PEP
Thiruvengadam NR, Saumoy M, Schneider Y, et al. A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis Prophylaxis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):216-226.e42. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.08.050
figure 2: Cost-effectiveness ratio of indomethacin in preventing PEP
Thiruvengadam NR, Saumoy M, Schneider Y, et al. A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis Prophylaxis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):216-226.e42. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.08.050
Disclosures:
Ayesha Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ernesto Zamora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Malone indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Mushtaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gabriel Reep indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sreeram Parupudi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Khan, DO, Ernesto Zamora, MD, Jordan Malone, DO, Muhammad Mushtaq, DO, Gabriel Reep, MD, Sreeram Parupudi, MD. P3478 - Diclofenac as Post-ERCP Pancreatitis Prophylaxis: A Cost-Effective Intervention, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
