Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3489 - Compliance to NCCN Germline Testing Recommendations in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Large Multi-Center Review
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Konstantinos Damiris, DO
Geisinger Health System
Danville, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Konstantinos Damiris, DO1, Malak Al-Bitar, MD1, Vyshnavi Kodali, DO2, Idorenyin Udoeyo, MPH1, Bradley D.. Confer, DO1
1Geisinger Health System, Danville, PA; 2Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, PA
Introduction: It is predicted that pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) will escalate to the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States by the year 2030. In 2019 the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) recommended genetic testing, including universal germline testing (GT) and tumor gene profiling in all PDAC cases. Identification of cancer predisposing genes has implications for both genetic counseling and treatment. We aim to evaluate recommendation compliance across a large tertiary health system and determine factors associated with obtaining GT.
Methods: A quality assurance retrospective review was done to identify patients with biopsy proven PDAC from 2018 - June 2023 within an academic health system. Patients were subclassified into those offered GT and those not. The frequency and percentages were displayed for categorical characteristics; the mean and SD for continuous characteristics. A Cochran-Armitage test was conducted to examine offering of GT over the years. Chi-square and Wilcoxon two-sample tests were performed for categorical and continuous characteristics, respectively. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were conducted to determine factors associated with GT.
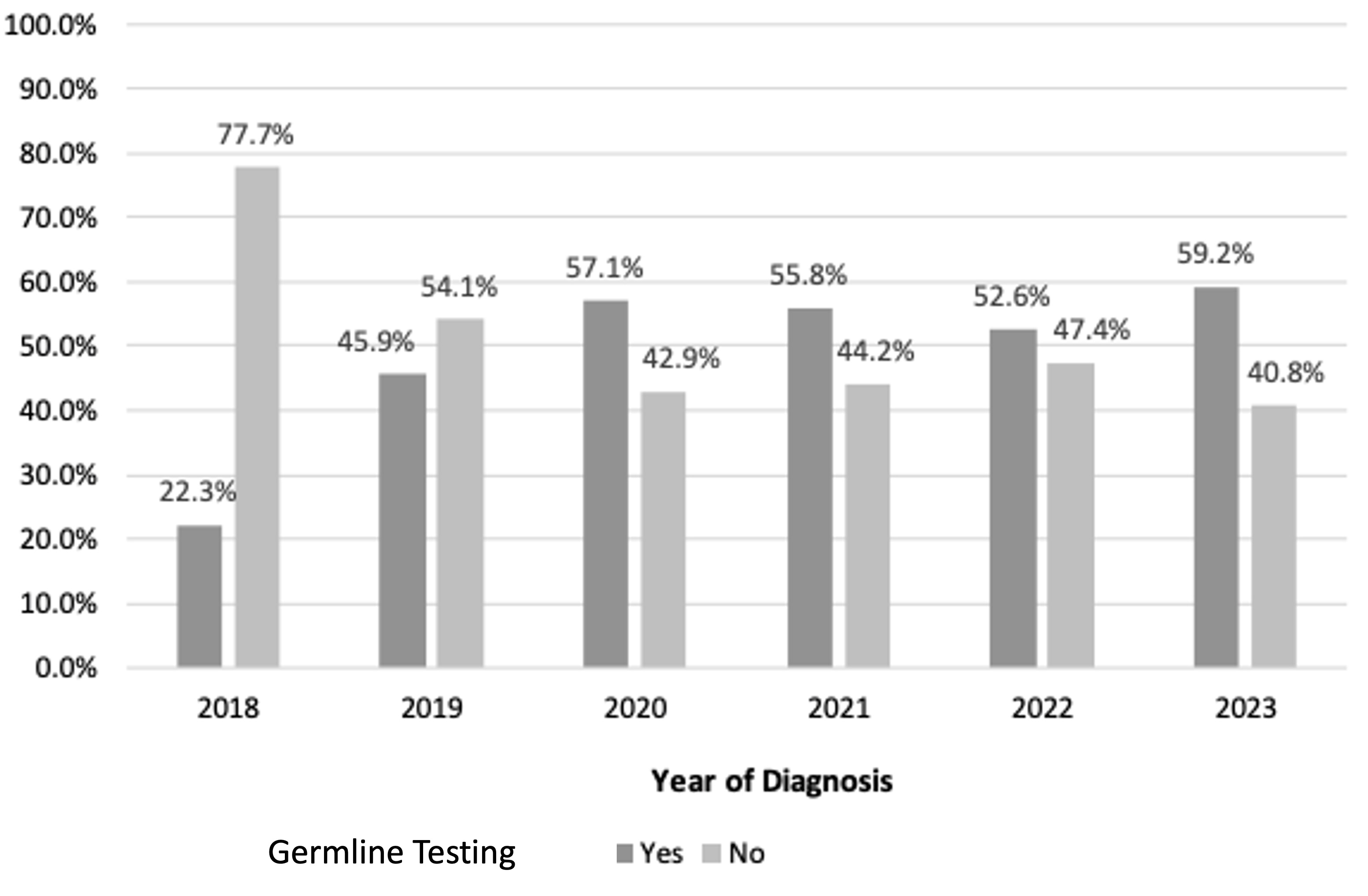
Results: 587 patients were included. The median age at diagnosis was 70 years, with 50.4% males and 97.4% Caucasian. GT was offered to 48.8 % of patients with 41.1% completing testing at time of analysis. Figure 1 demonstrates frequency of patients offered GT per year. There is a significant trend of GT being offered over time, with more patients undergoing testing following the 2019 NCCN recommendations (p< 0.0001). Characteristics of patients undergoing GT are outlined (Table 1). In multivariable analysis, GT was offered more frequently to younger patients, lower ECOG scores, and metastatic disease at diagnosis. Additionally, diagnosis at a later year and treatment at larger hospitals within the health system were more likely to offer GT. Pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) mutations were found in 10.4% of the cohort and 19.1% were found to have a variant of unknown significance. The most frequently encountered P/LP mutations were seen in 9 patients (39.1%) with ATM and 6 patients (24.0%) with BRCA2.
Discussion: Implementation of universal genetic testing remains a challenge. Results of both germline and somatic testing significantly impact treatment decisions and patient outcomes. Initiatives to increase universal testing with feasibility is of utmost importance to maintain adherence.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Konstantinos Damiris, DO1, Malak Al-Bitar, MD1, Vyshnavi Kodali, DO2, Idorenyin Udoeyo, MPH1, Bradley D.. Confer, DO1. P3489 - Compliance to NCCN Germline Testing Recommendations in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Large Multi-Center Review, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Geisinger Health System, Danville, PA; 2Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, PA
Introduction: It is predicted that pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) will escalate to the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States by the year 2030. In 2019 the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) recommended genetic testing, including universal germline testing (GT) and tumor gene profiling in all PDAC cases. Identification of cancer predisposing genes has implications for both genetic counseling and treatment. We aim to evaluate recommendation compliance across a large tertiary health system and determine factors associated with obtaining GT.
Methods: A quality assurance retrospective review was done to identify patients with biopsy proven PDAC from 2018 - June 2023 within an academic health system. Patients were subclassified into those offered GT and those not. The frequency and percentages were displayed for categorical characteristics; the mean and SD for continuous characteristics. A Cochran-Armitage test was conducted to examine offering of GT over the years. Chi-square and Wilcoxon two-sample tests were performed for categorical and continuous characteristics, respectively. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were conducted to determine factors associated with GT.
Results: 587 patients were included. The median age at diagnosis was 70 years, with 50.4% males and 97.4% Caucasian. GT was offered to 48.8 % of patients with 41.1% completing testing at time of analysis. Figure 1 demonstrates frequency of patients offered GT per year. There is a significant trend of GT being offered over time, with more patients undergoing testing following the 2019 NCCN recommendations (p< 0.0001). Characteristics of patients undergoing GT are outlined (Table 1). In multivariable analysis, GT was offered more frequently to younger patients, lower ECOG scores, and metastatic disease at diagnosis. Additionally, diagnosis at a later year and treatment at larger hospitals within the health system were more likely to offer GT. Pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) mutations were found in 10.4% of the cohort and 19.1% were found to have a variant of unknown significance. The most frequently encountered P/LP mutations were seen in 9 patients (39.1%) with ATM and 6 patients (24.0%) with BRCA2.
Discussion: Implementation of universal genetic testing remains a challenge. Results of both germline and somatic testing significantly impact treatment decisions and patient outcomes. Initiatives to increase universal testing with feasibility is of utmost importance to maintain adherence.

Figure: Figure 1. Offering of germline testing per number of cases each year (Cochran-Armitage test, p<0.0001)
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Konstantinos Damiris indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Malak Al-Bitar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vyshnavi Kodali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Idorenyin Udoeyo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bradley Confer: Boston Scientific Corporation – Consultant. Exact Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, FDA advisory panel.
Konstantinos Damiris, DO1, Malak Al-Bitar, MD1, Vyshnavi Kodali, DO2, Idorenyin Udoeyo, MPH1, Bradley D.. Confer, DO1. P3489 - Compliance to NCCN Germline Testing Recommendations in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Large Multi-Center Review, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
