Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3607 - Decade to Diagnosis of Recurrent Gram-Negative Bacteremia Post-Pancreatectomy and Gastrointestinal Surgery in PNET Patient
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO
Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center
Spokane, WA
Presenting Author(s)
Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO, Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO
Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center, Spokane, WA
Introduction: Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNET) are a rare type of pancreatic cancer. Treatment is usually chemotherapy followed by complicated gastrointestinal (GI) surgery. This case highlights an uncommon complication encountered 11-years post-surgical resection.
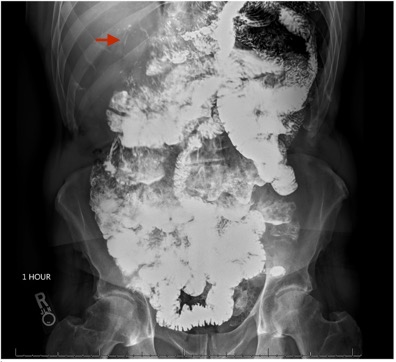
Case Description/Methods: A 66-year-old male with a history of PNET presented to his primary care physician for evaluation of recurrent gram-negative bacteremia. He was 6 years post total pancreatectomy and concomitant hepaticojejunostomy (HJ) and gastrojejunostomy (GJ). Additionally, there was a Braun anastomosis between the efferent and afferent limb of the GJ which was 50 cm away from the gastric anastomosis. The patient experienced recurrent Citrobacter and Escherichia coli bacteremia that resolved with antibiotic therapy. An extensive workup including a tagged white blood cell scan, computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging of the chest abdomen pelvis, transthoracic echocardiogram, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy, upper gastrointestinal (GI) follow-through along with Infectious Disease and GI consultation did not reveal a source for the infection. After discussion with the multidisciplinary team, the decision was to re-review the upper GI series. There was subtle evidence of reflux of contrast through the afferent limb into the bile duct, consistent with reflux cholangitis (RC). The patient is scheduled for conversion of his post-total pancreatectomy anatomy into Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy (HJ) of at least 80 to 90 cm in length to prevent bile RC.
Discussion: RC is usually observed after gastric bypass procedures such as a Roux-en-Y. Given the paucity of literature on RC, the diagnosis can be challenging. The proposed mechanism is reflux of intestinal contents through the biliary tract of a HJ due to the absence of Oddi sphincter versus bacterial translocation from jejunal loop dysmotility and impaired hepatic lymphatic drainage. RC differs from acute cholangitis (AC) in that obstruction is not the cause and response to antibiotic therapy is faster in RC, typically 24-48 hours. In a case-series of 25 patients diagnosed with RC, the median time to diagnosis was 4.5 months, and imaging is usually unremarkable. Several cases report that Roux-en-Y loop lengthening resolved recurrence. This case highlights the importance of recognition RC due to its indolent course after extensive GI surgery along with the utility of a team-based approach for better patient care.
Disclosures:
Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO, Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO. P3607 - Decade to Diagnosis of Recurrent Gram-Negative Bacteremia Post-Pancreatectomy and Gastrointestinal Surgery in PNET Patient, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center, Spokane, WA
Introduction: Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNET) are a rare type of pancreatic cancer. Treatment is usually chemotherapy followed by complicated gastrointestinal (GI) surgery. This case highlights an uncommon complication encountered 11-years post-surgical resection.
Case Description/Methods: A 66-year-old male with a history of PNET presented to his primary care physician for evaluation of recurrent gram-negative bacteremia. He was 6 years post total pancreatectomy and concomitant hepaticojejunostomy (HJ) and gastrojejunostomy (GJ). Additionally, there was a Braun anastomosis between the efferent and afferent limb of the GJ which was 50 cm away from the gastric anastomosis. The patient experienced recurrent Citrobacter and Escherichia coli bacteremia that resolved with antibiotic therapy. An extensive workup including a tagged white blood cell scan, computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging of the chest abdomen pelvis, transthoracic echocardiogram, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy, upper gastrointestinal (GI) follow-through along with Infectious Disease and GI consultation did not reveal a source for the infection. After discussion with the multidisciplinary team, the decision was to re-review the upper GI series. There was subtle evidence of reflux of contrast through the afferent limb into the bile duct, consistent with reflux cholangitis (RC). The patient is scheduled for conversion of his post-total pancreatectomy anatomy into Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy (HJ) of at least 80 to 90 cm in length to prevent bile RC.
Discussion: RC is usually observed after gastric bypass procedures such as a Roux-en-Y. Given the paucity of literature on RC, the diagnosis can be challenging. The proposed mechanism is reflux of intestinal contents through the biliary tract of a HJ due to the absence of Oddi sphincter versus bacterial translocation from jejunal loop dysmotility and impaired hepatic lymphatic drainage. RC differs from acute cholangitis (AC) in that obstruction is not the cause and response to antibiotic therapy is faster in RC, typically 24-48 hours. In a case-series of 25 patients diagnosed with RC, the median time to diagnosis was 4.5 months, and imaging is usually unremarkable. Several cases report that Roux-en-Y loop lengthening resolved recurrence. This case highlights the importance of recognition RC due to its indolent course after extensive GI surgery along with the utility of a team-based approach for better patient care.

Figure: Arrow pointing to subtle evidence of reflux through the afferent limb into the biliary duct at the 1 hour mark on upper GI series.
Disclosures:
Naomi Leon-Guerrero indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naomi Leon-Guerrero indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO, Naomi D. Leon-Guerrero, DO. P3607 - Decade to Diagnosis of Recurrent Gram-Negative Bacteremia Post-Pancreatectomy and Gastrointestinal Surgery in PNET Patient, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
