Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3639 - Interoperable Artificial Intelligence for High-Resolution Anoscopy: A Transatlantic Collaborative Study in Anal Cancer Precursor Detection and Differentiation
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD
Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João
Porto, Porto, Portugal
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD1, Luis Barroso, MD2, Lucas Spindler, MD3, Thiago Manzione, MD4, Miguel Martins, MD1, Nadia Fathallah, MD3, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Joao Ferreira, PhD.5, Sidney Nadal, MD, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD, FACG1, Vincent de Parades, MD, PhD3
1Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 2Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, NC; 3Hospital Paris Saint Joseph, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; 4Emilio RIbas Infectology Institute, Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 5University of Porto, Porto, Porto, Portugal
Introduction: High Resolution Anoscopy (HRA) is the preferred method to detect and treat Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ASCC) precursors. Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (LSIL) can be monitored, whereas High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL) are considered precancerous and require treatment to reduce the risk of ASCC. This study aimed to develop and validate a CNN to differentiate HSIL from LSIL in HRA in different subsets of patients (nonstained, acetic acid, lugol, and after manipulation), different devices and different clinical workflows.
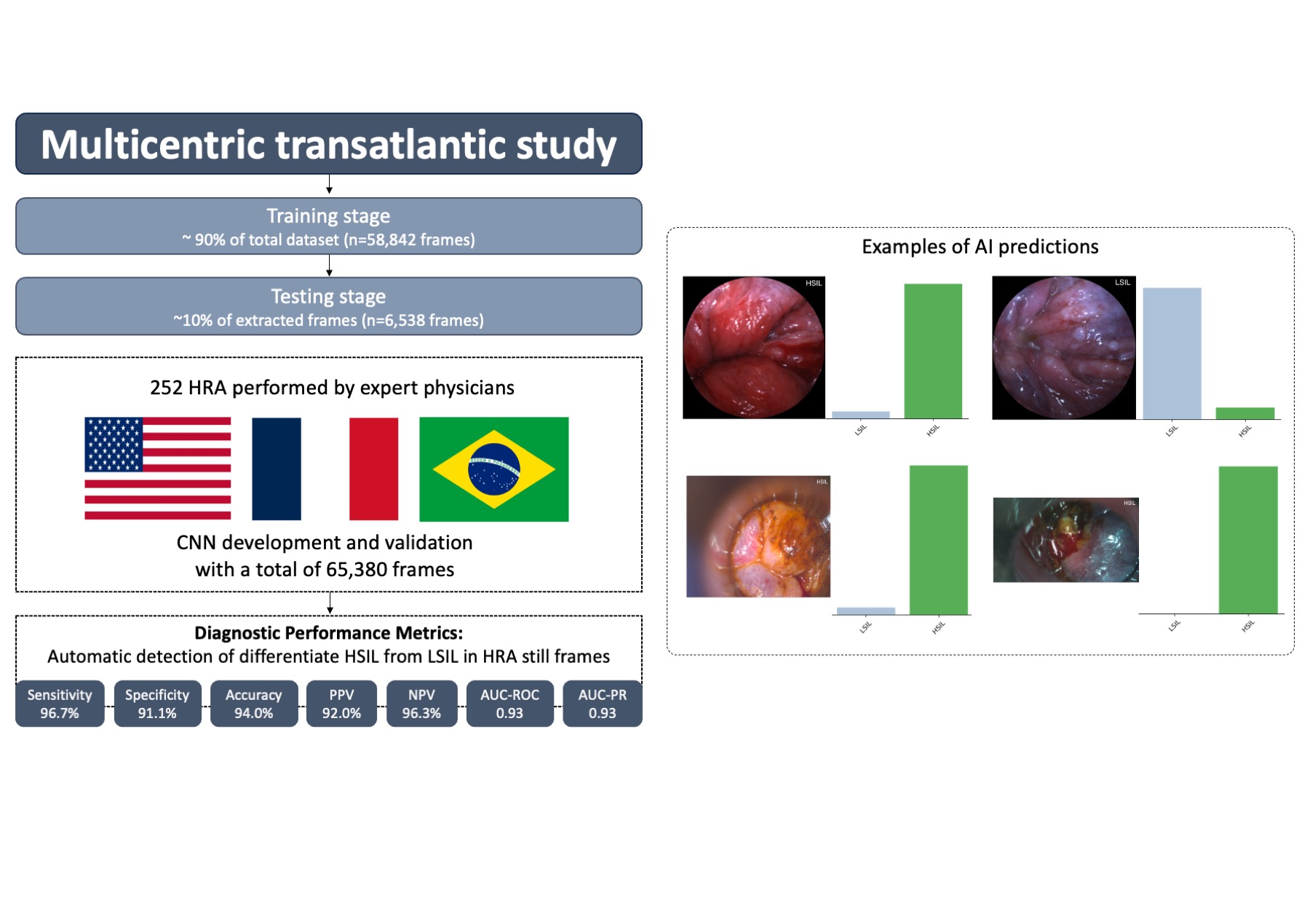
Methods: A multicentric study was conducted across three centers, involving a total of 65,380 frames from 252 HRA procedures using three different types of devices. The lesions were categorized into HSIL and LSIL based on histopathological assessments, which served as the ground truth.
Frames were taken from various phases of the HRA procedures, including non-stained, stained (with acetic acid or lugol), and post-manipulation stages. The dataset was divided into two parts: 90% of the frames were used to train the convolutional neural network (CNN) model, while the remaining 10% were reserved for testing its performance.
During the testing phase, the diagnostic performance of the CNN was evaluated by calculating the following metrics: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), accuracy, and the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) and the precision-recall curve (AUC-PR).
Results: In the validation dataset, the diagnostic metrics for distinguishing between HSIL and LSIL still frames were as follows: sensitivity of 96.7%, specificity of 91.1%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 92.0%, negative predictive value (NPV) of 96.3%, and a global accuracy of 94.0%. Both the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) and the area under the precision-recall curve (AUC-PR) were 0.93.
Discussion: Interoperability and managing dataset diversity are crucial for real-world AI model applications. This multicenter study, which includes data from two continents, showcases a strong model with excellent diagnostic accuracy for detecting and distinguishing anal cancer precursors. The study underscores how AI-assisted models can significantly enhance High Resolution Anoscopy (HRA), advancing its technological readiness. This progress is pivotal for improving clinical outcomes and enhancing patient care globally.
Disclosures:
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD1, Luis Barroso, MD2, Lucas Spindler, MD3, Thiago Manzione, MD4, Miguel Martins, MD1, Nadia Fathallah, MD3, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Joao Ferreira, PhD.5, Sidney Nadal, MD, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD, FACG1, Vincent de Parades, MD, PhD3. P3639 - Interoperable Artificial Intelligence for High-Resolution Anoscopy: A Transatlantic Collaborative Study in Anal Cancer Precursor Detection and Differentiation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD1, Luis Barroso, MD2, Lucas Spindler, MD3, Thiago Manzione, MD4, Miguel Martins, MD1, Nadia Fathallah, MD3, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Joao Ferreira, PhD.5, Sidney Nadal, MD, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD, FACG1, Vincent de Parades, MD, PhD3
1Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 2Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, NC; 3Hospital Paris Saint Joseph, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; 4Emilio RIbas Infectology Institute, Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 5University of Porto, Porto, Porto, Portugal
Introduction: High Resolution Anoscopy (HRA) is the preferred method to detect and treat Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ASCC) precursors. Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (LSIL) can be monitored, whereas High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL) are considered precancerous and require treatment to reduce the risk of ASCC. This study aimed to develop and validate a CNN to differentiate HSIL from LSIL in HRA in different subsets of patients (nonstained, acetic acid, lugol, and after manipulation), different devices and different clinical workflows.
Methods: A multicentric study was conducted across three centers, involving a total of 65,380 frames from 252 HRA procedures using three different types of devices. The lesions were categorized into HSIL and LSIL based on histopathological assessments, which served as the ground truth.
Frames were taken from various phases of the HRA procedures, including non-stained, stained (with acetic acid or lugol), and post-manipulation stages. The dataset was divided into two parts: 90% of the frames were used to train the convolutional neural network (CNN) model, while the remaining 10% were reserved for testing its performance.
During the testing phase, the diagnostic performance of the CNN was evaluated by calculating the following metrics: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), accuracy, and the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) and the precision-recall curve (AUC-PR).
Results: In the validation dataset, the diagnostic metrics for distinguishing between HSIL and LSIL still frames were as follows: sensitivity of 96.7%, specificity of 91.1%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 92.0%, negative predictive value (NPV) of 96.3%, and a global accuracy of 94.0%. Both the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) and the area under the precision-recall curve (AUC-PR) were 0.93.
Discussion: Interoperability and managing dataset diversity are crucial for real-world AI model applications. This multicenter study, which includes data from two continents, showcases a strong model with excellent diagnostic accuracy for detecting and distinguishing anal cancer precursors. The study underscores how AI-assisted models can significantly enhance High Resolution Anoscopy (HRA), advancing its technological readiness. This progress is pivotal for improving clinical outcomes and enhancing patient care globally.

Figure: Figure 1 provides a summary of the study design, the diagnostic performance metrics of the model, and an example of the output generated by the convolutional neural network; High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL); Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL).
Disclosures:
Miguel Mascarenhas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luis Barroso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lucas Spindler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thiago Manzione indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Martins indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nadia Fathallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tiago Ribeiro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pedro Cardoso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joao Ferreira indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sidney Nadal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guilherme Macedo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vincent de Parades indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD1, Luis Barroso, MD2, Lucas Spindler, MD3, Thiago Manzione, MD4, Miguel Martins, MD1, Nadia Fathallah, MD3, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Joao Ferreira, PhD.5, Sidney Nadal, MD, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD, FACG1, Vincent de Parades, MD, PhD3. P3639 - Interoperable Artificial Intelligence for High-Resolution Anoscopy: A Transatlantic Collaborative Study in Anal Cancer Precursor Detection and Differentiation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

