Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3748 - A Case of Radiation Proctitis With Concern for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Hyder Alikhan, BA
Cooper Medical School of Rowan University
Camden, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Hyder Alikhan, BA1, Kathy N. Williams, MD, MS2, Kunal Dalal, MD3
1Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 3Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ
Introduction: Cancer treatments have evolved to include chemoradiation and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI); however, both therapy modalities can have adverse effects and now are widely used. ICI, pembrolizumab, has been shown to cause colitis, and chemoradiation can cause radiation proctitis. We present a case of a patient with previous cervical cancer treated with chemoradiation, maintained on pembrolizumab presenting with rectal bleeding in the setting of radiation proctitis with concerns for ICI colitis.
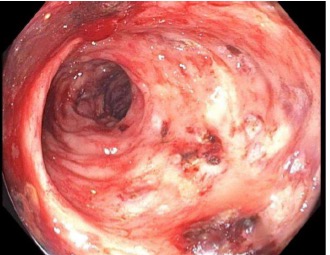
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old female with past medical history of recurrent cervical cancer stage III T3 N0 M0 s/p chemoradiation and maintained on carboplatin, paclitaxel, and pembrolizumab, and diverticulosis presented with rectal bleeding. She was initially hospitalized for rectal bleeding due to radiation proctosigmoiditis treated with argon plasma coagulation (APC). She was discharged once rectal bleeding resolved. However, she presented with new onset of rectal bleeding, one week after pembrolizumab treatment. Due to pembrolizumab therapy, there was concern for ICI colitis. Flexible sigmoidoscopy revealed a diffuse area of moderately friable mucosa and continuous bleeding of ulcerated mucosa from rectum, sigmoid, and descending colon. A colonoscopy was performed and revealed friability in sigmoid colon and rectum, as well as ulcer in recto-sigmoid colon (Figure 1). Biopsies revealed no specific changes indicating ICI colitis and were consistent with radiation proctitis, treated with APC. Colorectal surgery was consulted for possible resection; however, they recommended no surgical interventions. Sucralfate enemas and mesalamine suppositories were started with resolution of bleeding and transition to butyrate enemas as outpatient.
Discussion: Radiation proctitis and ICI colitis are diagnoses made by clinical history and colonoscopy findings, where both can present with mimicking symptoms. This case is unique because the patient had radiation proctitis in the setting of pembrolizumab use where ICI colitis was considered. Even though ICI colitis was not the final diagnosis, it underscores the importance of maintaining a broad differential diagnosis in patients receiving pembrolizumab therapy as colonoscopy findings for ICI colitis are nonspecific and treatment options are different. With our rapidly changing and revolutionized cancer treatment options, awareness of side effects is vital.
Disclosures:
Hyder Alikhan, BA1, Kathy N. Williams, MD, MS2, Kunal Dalal, MD3. P3748 - A Case of Radiation Proctitis With Concern for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 3Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ
Introduction: Cancer treatments have evolved to include chemoradiation and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI); however, both therapy modalities can have adverse effects and now are widely used. ICI, pembrolizumab, has been shown to cause colitis, and chemoradiation can cause radiation proctitis. We present a case of a patient with previous cervical cancer treated with chemoradiation, maintained on pembrolizumab presenting with rectal bleeding in the setting of radiation proctitis with concerns for ICI colitis.
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old female with past medical history of recurrent cervical cancer stage III T3 N0 M0 s/p chemoradiation and maintained on carboplatin, paclitaxel, and pembrolizumab, and diverticulosis presented with rectal bleeding. She was initially hospitalized for rectal bleeding due to radiation proctosigmoiditis treated with argon plasma coagulation (APC). She was discharged once rectal bleeding resolved. However, she presented with new onset of rectal bleeding, one week after pembrolizumab treatment. Due to pembrolizumab therapy, there was concern for ICI colitis. Flexible sigmoidoscopy revealed a diffuse area of moderately friable mucosa and continuous bleeding of ulcerated mucosa from rectum, sigmoid, and descending colon. A colonoscopy was performed and revealed friability in sigmoid colon and rectum, as well as ulcer in recto-sigmoid colon (Figure 1). Biopsies revealed no specific changes indicating ICI colitis and were consistent with radiation proctitis, treated with APC. Colorectal surgery was consulted for possible resection; however, they recommended no surgical interventions. Sucralfate enemas and mesalamine suppositories were started with resolution of bleeding and transition to butyrate enemas as outpatient.
Discussion: Radiation proctitis and ICI colitis are diagnoses made by clinical history and colonoscopy findings, where both can present with mimicking symptoms. This case is unique because the patient had radiation proctitis in the setting of pembrolizumab use where ICI colitis was considered. Even though ICI colitis was not the final diagnosis, it underscores the importance of maintaining a broad differential diagnosis in patients receiving pembrolizumab therapy as colonoscopy findings for ICI colitis are nonspecific and treatment options are different. With our rapidly changing and revolutionized cancer treatment options, awareness of side effects is vital.

Figure: Figure 1. Colonoscopy revealing friability and single ulcer in recto-sigmoid colon
Disclosures:
Hyder Alikhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathy Williams indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kunal Dalal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hyder Alikhan, BA1, Kathy N. Williams, MD, MS2, Kunal Dalal, MD3. P3748 - A Case of Radiation Proctitis With Concern for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
