Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3927 - The Efficacy of Antireflux Mucosectomy (ARMS) and Antireflux Mucosal Ablation (ARMA) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) by 24-Hour pH Monitoring: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
.jpg)
Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Briarwood, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD1, Nooraldin Merza, MD2, Omar Saab, MD3, Mustafa Al-Obaidi, MD4, Iya Agha, MS5, Ali Wakil, MD6
1Jamaica Hospital Medical Center, Briarwood, NY; 2University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 4Lund University, Malmö, Skane Lan, Sweden; 5New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine, New York, NY; 6Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a prevalent and chronic disorder impacting a significant proportion of the global population of almost 15%. Antireflux mucosal ablation (ARMA) and antireflux mucosal resection (ARMS) are minimally invasive endoscopic procedures for treating Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate their efficacy through DeMeester score, acid exposure time (AET), and clinical success rate.
Methods: Studies reporting pre- and post-procedure esophageal 24-hr pH monitoring following ARMA and ARMS were included. Pooled data analysis assessed changes in DeMeester score and AET. Clinical success rate, defined as significant symptom improvement or reduced reliance on proton pump inhibitors, was also analyzed.
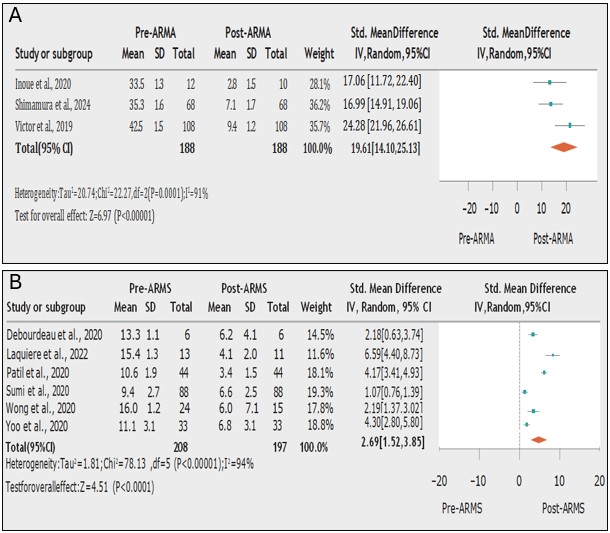
Results: Pooled data from three ARMA studies showed a significant post-procedure decrease in median AET (19.61 [14.10, 25.13], p< 0.0001). Similarly, six ARMS studies demonstrated a significant reduction in DeMeester score (2.69 [1.52, 3.85], p< 0.0001). The overall clinical success rate for ARMS was 85.8% (moderate heterogeneity, I²=59%) and 88.3% for ARMA (moderate heterogeneity, I²=51%).
Discussion: Both ARMA and ARMS displayed promising efficacy in improving GERD-related outcomes, based on reductions in AET and DeMeester score, and achieving high clinical success rates. However, moderate heterogeneity observed suggests further research is needed to identify patient-specific factors influencing treatment response.
Disclosures:
Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD1, Nooraldin Merza, MD2, Omar Saab, MD3, Mustafa Al-Obaidi, MD4, Iya Agha, MS5, Ali Wakil, MD6. P3927 - The Efficacy of Antireflux Mucosectomy (ARMS) and Antireflux Mucosal Ablation (ARMA) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) by 24-Hour pH Monitoring: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Jamaica Hospital Medical Center, Briarwood, NY; 2University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 4Lund University, Malmö, Skane Lan, Sweden; 5New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine, New York, NY; 6Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a prevalent and chronic disorder impacting a significant proportion of the global population of almost 15%. Antireflux mucosal ablation (ARMA) and antireflux mucosal resection (ARMS) are minimally invasive endoscopic procedures for treating Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate their efficacy through DeMeester score, acid exposure time (AET), and clinical success rate.
Methods: Studies reporting pre- and post-procedure esophageal 24-hr pH monitoring following ARMA and ARMS were included. Pooled data analysis assessed changes in DeMeester score and AET. Clinical success rate, defined as significant symptom improvement or reduced reliance on proton pump inhibitors, was also analyzed.
Results: Pooled data from three ARMA studies showed a significant post-procedure decrease in median AET (19.61 [14.10, 25.13], p< 0.0001). Similarly, six ARMS studies demonstrated a significant reduction in DeMeester score (2.69 [1.52, 3.85], p< 0.0001). The overall clinical success rate for ARMS was 85.8% (moderate heterogeneity, I²=59%) and 88.3% for ARMA (moderate heterogeneity, I²=51%).
Discussion: Both ARMA and ARMS displayed promising efficacy in improving GERD-related outcomes, based on reductions in AET and DeMeester score, and achieving high clinical success rates. However, moderate heterogeneity observed suggests further research is needed to identify patient-specific factors influencing treatment response.

Figure: Figure A. Forest plot for pre-ARMA and post-ARMA 24 hr-ph monitoring score evaluation by AET.
Figure B. Forest plot for pre-ARMS and post-ARMS 24 hr-ph monitoring score evaluation by DeMeester score.
Figure B. Forest plot for pre-ARMS and post-ARMS 24 hr-ph monitoring score evaluation by DeMeester score.
Disclosures:
Hasan Al-Obaidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nooraldin Merza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Saab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mustafa Al-Obaidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iya Agha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Wakil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD1, Nooraldin Merza, MD2, Omar Saab, MD3, Mustafa Al-Obaidi, MD4, Iya Agha, MS5, Ali Wakil, MD6. P3927 - The Efficacy of Antireflux Mucosectomy (ARMS) and Antireflux Mucosal Ablation (ARMA) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) by 24-Hour pH Monitoring: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
