Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P3825 - Impact of Spanish Language Outreach on Multi-Target Stool DNA Test Adherence in a Spanish-Speaking Population in a Federally Qualified Health Center
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- MG
Mallik Greene, PhD
Exact Sciences
Madison, WI
Presenting Author(s)
Mallik Greene, PhD1, Timo Pew, MS1, A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD2, Juliana V. Rincón López, MSc3, Durado Brooks, MD, MPH1, Paul Limburg, MD, MPH4, Martha Duarte, MD, MHSA5
1Exact Sciences, Madison, WI; 2Exact Sciences, Lake Forest, IL; 3Fundación Universitaria Sanitas, Bogotá, Distrito Capital de Bogota, Colombia; 4Exact Sciences, Rochester, MN; 5Sanitas USA, Keralty Hospital, Miami, FL
Introduction: Nationwide, about 40% of the Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) colorectal cancer (CRC) screen-eligible population is reportedly up to date with guideline recommendations. More than 35% of Hispanic individuals seek their healthcare services at FQHCs and about 30% of the U.S. Hispanic individuals are fluent only in Spanish. The multi-target stool DNA test (mt-sDNA) is a guideline-recommended, at-home CRC screening option for average-risk individuals. The objective of this study is to examine the impact of Spanish-language patient navigation services on adherence to CRC screening with mt-sDNA test in a FQHC Spanish-speaking patient population.
Methods: A cohort of Spanish-speaking FQHC patients aged ≥45 years from a health system were included in this before-and-after study. The before study period was from 10/01/2022 to 01/22/2023, where all Spanish-speaking patients with a valid order for mt-sDNA test received English language patient outreach support. During the after period 01/23/2023 to 12/31/2023, outreach support was personalized so that Spanish-speaking patients would receive outreach support in their preferred language. The outcome of interest was patient adherence before and after the personalized outreach support, overall and across various payors and sub-groups, defined as completion, return of the test kit with a valid test result within 60 days from the initial shipment.
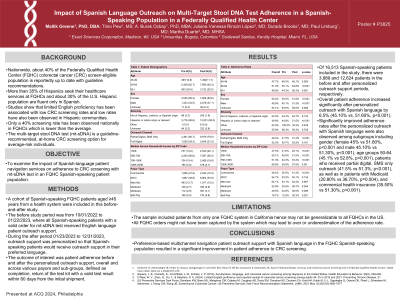
Results: Of 16,513 Spanish-speaking patients included in the study, there were 3,889 and 12,624 patients in the before and after personalized outreach support periods, respectively. Overall patient adherence increased significantly after personalized outreach with Spanish language by 6.5% (45.10% vs. 51.60%, p< 0.001). Significantly improved adherence rates after the personalized outreach with Spanish language were also observed among subgroups including gender (female 45% vs 51.80%, p< 0.001 and male 45.10% vs 51.30%, p< 0.001), age groups 50-64 (45.1% vs 52.8%, p< 0.001), new to mt-sDNA (45.10% vs 51.60%, p< 0.001), patients received partial digital SMS outreach (41.5% vs 51.3%, p< 0.001), as well as in patients with Medicaid (20.80% vs 36.70%, p=0.004), and commercial health insurance (35.50% vs 51.30%, p< 0.001).
Discussion: Preference-based multichannel navigation patient outreach support with Spanish language in the FQHC Spanish-speaking population resulted in a significant improvement in patient adherence to CRC screening.
Disclosures:
Mallik Greene, PhD1, Timo Pew, MS1, A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD2, Juliana V. Rincón López, MSc3, Durado Brooks, MD, MPH1, Paul Limburg, MD, MPH4, Martha Duarte, MD, MHSA5. P3825 - Impact of Spanish Language Outreach on Multi-Target Stool DNA Test Adherence in a Spanish-Speaking Population in a Federally Qualified Health Center, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Exact Sciences, Madison, WI; 2Exact Sciences, Lake Forest, IL; 3Fundación Universitaria Sanitas, Bogotá, Distrito Capital de Bogota, Colombia; 4Exact Sciences, Rochester, MN; 5Sanitas USA, Keralty Hospital, Miami, FL
Introduction: Nationwide, about 40% of the Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) colorectal cancer (CRC) screen-eligible population is reportedly up to date with guideline recommendations. More than 35% of Hispanic individuals seek their healthcare services at FQHCs and about 30% of the U.S. Hispanic individuals are fluent only in Spanish. The multi-target stool DNA test (mt-sDNA) is a guideline-recommended, at-home CRC screening option for average-risk individuals. The objective of this study is to examine the impact of Spanish-language patient navigation services on adherence to CRC screening with mt-sDNA test in a FQHC Spanish-speaking patient population.
Methods: A cohort of Spanish-speaking FQHC patients aged ≥45 years from a health system were included in this before-and-after study. The before study period was from 10/01/2022 to 01/22/2023, where all Spanish-speaking patients with a valid order for mt-sDNA test received English language patient outreach support. During the after period 01/23/2023 to 12/31/2023, outreach support was personalized so that Spanish-speaking patients would receive outreach support in their preferred language. The outcome of interest was patient adherence before and after the personalized outreach support, overall and across various payors and sub-groups, defined as completion, return of the test kit with a valid test result within 60 days from the initial shipment.
Results: Of 16,513 Spanish-speaking patients included in the study, there were 3,889 and 12,624 patients in the before and after personalized outreach support periods, respectively. Overall patient adherence increased significantly after personalized outreach with Spanish language by 6.5% (45.10% vs. 51.60%, p< 0.001). Significantly improved adherence rates after the personalized outreach with Spanish language were also observed among subgroups including gender (female 45% vs 51.80%, p< 0.001 and male 45.10% vs 51.30%, p< 0.001), age groups 50-64 (45.1% vs 52.8%, p< 0.001), new to mt-sDNA (45.10% vs 51.60%, p< 0.001), patients received partial digital SMS outreach (41.5% vs 51.3%, p< 0.001), as well as in patients with Medicaid (20.80% vs 36.70%, p=0.004), and commercial health insurance (35.50% vs 51.30%, p< 0.001).
Discussion: Preference-based multichannel navigation patient outreach support with Spanish language in the FQHC Spanish-speaking population resulted in a significant improvement in patient adherence to CRC screening.
Disclosures:
Mallik Greene: exact sciences – Employee.
Timo Pew: Exact Sciences – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
A. Burak Ozbay: Exact Sciences – Employee, Stock Options.
Juliana Rincón López indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Durado Brooks: Exact Sciences Corporation – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Paul Limburg: Exact Sciences Corporation – Consultant, Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Martha Duarte indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mallik Greene, PhD1, Timo Pew, MS1, A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD2, Juliana V. Rincón López, MSc3, Durado Brooks, MD, MPH1, Paul Limburg, MD, MPH4, Martha Duarte, MD, MHSA5. P3825 - Impact of Spanish Language Outreach on Multi-Target Stool DNA Test Adherence in a Spanish-Speaking Population in a Federally Qualified Health Center, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
