Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3724 - Think Twice “Could it be a Metastatic Lesion?” – A Case Report
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Fatma Mahmoud, MD
Cleveland Clinic
Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Presenting Author(s)
Fatma Mahmoud, MD, Osama Yousef, MD
Cleveland Clinic, Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Introduction: Adenocarcinoma is the most common lung cancer in the United States.1 It commonly spreads to the liver (34.3%), with stomach and intestinal spread accounting for 2.3% and 3.4% respectively.2
Case Description/Methods: A 73-year-old male with cough and weight loss was investigated with a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest showing a right upper lobe mass lesion with adrenal and vertebral metastases.
Staging CT revealed diffuse small bowel, left colon thickening with mesenteric lymphadenopathy, and soft tissue thickening along the greater and lesser curvatures of the stomach.
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) demonstrated a centrally necrotic peripherally FDG avid right lung malignancy with extensive metastatic disease in the mediastinum, liver, adrenals, and multifocal segmental bowel involvement.
CT-guided lung mass biopsy confirmed adenocarcinoma with pleomorphic features.
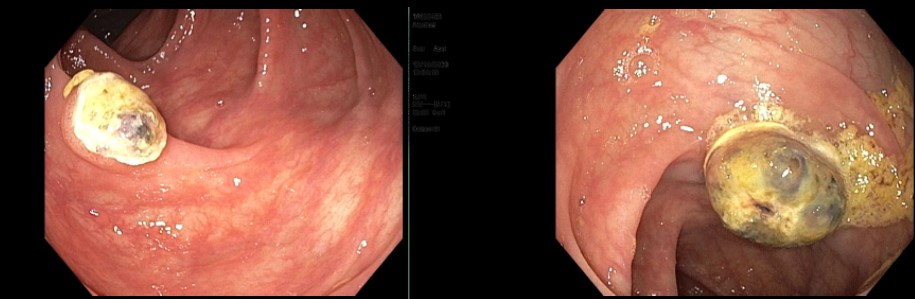
Colonoscopy displayed multiple necrotic ulcerated colonic polypoid lesions in the transverse, splenic flexure, and sigmoid colon. (Figure 1)
Biopsies affirmed necrotic, high-grade, and very poorly differentiated carcinoma. The appearances and immunostaining favored metastatic carcinoma from a primary lung non-small cell carcinoma.
Discussion: The incidence of gastrointestinal metastasis of primary lung cancer (GMLC) ranges from 0.3 to 1.7%.3
In an analysis of 366 patients with GMLC; the small bowel was the commonest location (59.6%) with the jejunum counting for 63.4%, followed by the colorectum (25.6%).4
Squamous cell carcinoma was responsible for 28.5% of GMLC followed by adenocarcinoma (27.6%).5
GMLC can occur synchronously or before the diagnosis of lung cancer, but more frequently after the diagnosis of lung cancer.5 It is associated with poor prognosis, with a mean survival time of 4–8 weeks.6
GMLC can present incidentally or cause abdominal pain, constipation, hemorrhage, perforation, and obstruction.4
Immunostaining helps to distinguish primary gastrointestinal carcinoma from lung cancer metastasis.7
Lung carcinomas stain positively for TTF-1, CK5/6, or p63 and negatively for CK20 and CDX-2.
Our patient’s lung mass immunostaining was positive for TTF-1 and negative for CDX-2 and CK20. The colonic biopsy was positive for CK7; with patchy weak TTF-1 staining and negative CK20, CDX2 staining suggesting metastatic adenocarcinoma.
Management includes resection +/- palliative chemoimmunotherapy.8 Unfortunately; our patient died around 8 weeks post-diagnosis confirming the related poor prognosis.
Disclosures:
Fatma Mahmoud, MD, Osama Yousef, MD. P3724 - Think Twice “Could it be a Metastatic Lesion?” – A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Cleveland Clinic, Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Introduction: Adenocarcinoma is the most common lung cancer in the United States.1 It commonly spreads to the liver (34.3%), with stomach and intestinal spread accounting for 2.3% and 3.4% respectively.2
Case Description/Methods: A 73-year-old male with cough and weight loss was investigated with a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest showing a right upper lobe mass lesion with adrenal and vertebral metastases.
Staging CT revealed diffuse small bowel, left colon thickening with mesenteric lymphadenopathy, and soft tissue thickening along the greater and lesser curvatures of the stomach.
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) demonstrated a centrally necrotic peripherally FDG avid right lung malignancy with extensive metastatic disease in the mediastinum, liver, adrenals, and multifocal segmental bowel involvement.
CT-guided lung mass biopsy confirmed adenocarcinoma with pleomorphic features.
Colonoscopy displayed multiple necrotic ulcerated colonic polypoid lesions in the transverse, splenic flexure, and sigmoid colon. (Figure 1)
Biopsies affirmed necrotic, high-grade, and very poorly differentiated carcinoma. The appearances and immunostaining favored metastatic carcinoma from a primary lung non-small cell carcinoma.
Discussion: The incidence of gastrointestinal metastasis of primary lung cancer (GMLC) ranges from 0.3 to 1.7%.3
In an analysis of 366 patients with GMLC; the small bowel was the commonest location (59.6%) with the jejunum counting for 63.4%, followed by the colorectum (25.6%).4
Squamous cell carcinoma was responsible for 28.5% of GMLC followed by adenocarcinoma (27.6%).5
GMLC can occur synchronously or before the diagnosis of lung cancer, but more frequently after the diagnosis of lung cancer.5 It is associated with poor prognosis, with a mean survival time of 4–8 weeks.6
GMLC can present incidentally or cause abdominal pain, constipation, hemorrhage, perforation, and obstruction.4
Immunostaining helps to distinguish primary gastrointestinal carcinoma from lung cancer metastasis.7
Lung carcinomas stain positively for TTF-1, CK5/6, or p63 and negatively for CK20 and CDX-2.
Our patient’s lung mass immunostaining was positive for TTF-1 and negative for CDX-2 and CK20. The colonic biopsy was positive for CK7; with patchy weak TTF-1 staining and negative CK20, CDX2 staining suggesting metastatic adenocarcinoma.
Management includes resection +/- palliative chemoimmunotherapy.8 Unfortunately; our patient died around 8 weeks post-diagnosis confirming the related poor prognosis.

Figure: Figure 1. Colonoscopy images showing sigmoid (left) and transverse colon (right) necrotic masses
Disclosures:
Fatma Mahmoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Yousef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatma Mahmoud, MD, Osama Yousef, MD. P3724 - Think Twice “Could it be a Metastatic Lesion?” – A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
