Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2855 - Regional Variability in Liver Fat Content in Pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH Assessed by Proton Density Fat Fraction Imaging
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- AZ
Ali Zifan, PhD
UC San Diego
La Jolla, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Ali Zifan, PhD1, Malaika Wauters, 1, Jake Weeks, BS1, Michael Middleton, PhD1, Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc2, Claude Sirlin, MD1
1UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA; 2University of California San Diego School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF) imaging has recently emerged as a critical tool for diagnosing and assessing liver fat content in non-alcoholic associated fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). PDFF provides a non-invasive, quantitative measure of liver fat, aiding in the identification and differentiation of these conditions. Understanding the regional distribution of PDFF within the liver can enhance diagnostic accuracy and guide targeted clinical interventions. The aim of this study was to analyze the distribution of PDFF across the eight regions of the Couinaud liver segmentation in patients with NAFLD and NASH.
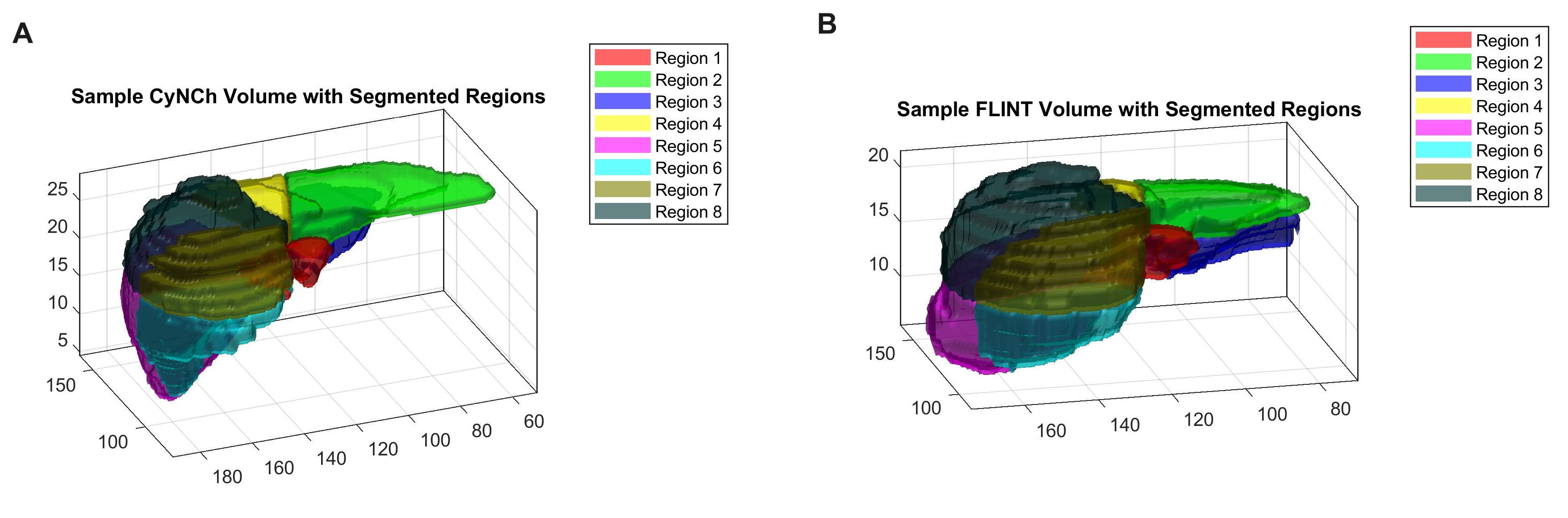
Methods: This study utilized data from two cohorts: 111 adult patients from the FLINT study(age: 50.1 ±10.2; BMI: 33.6±5.14) diagnosed with NASH, and 111 pediatric patients from the CyNCh study(age: 13.8 ±2.51; BMI: 33.1±6.4) diagnosed with NAFLD. The volumes from were segmented, and PDFF maps were overlaid with radiologist-segmented regions. For each of the eight Couinaud regions, median and interquartile range (IQR), as well as minimum and maximum PDFF values, were extracted.
Results: Region 7 showed the highest median PDFF value in the pediatric group (35.44) and Region 4b in the adult group (35.40). Region 2 had the lowest median PDFF value in both groups, with values of 32.49 (pediatric) and 34.18 (adult). Variability in PDFF values was highest in Region 1 for the pediatric group (IQR = 6.82) and Region 2 for the adult group (IQR = 5.56), while Region 6 showed the least variability in both groups (IQR = 4.92 for pediatric and 3.81 for adult). The minimum median value was in Region 2 for the pediatric group (12.50) and Region 3 for the adult group (14.33), while the maximum median value was in Region 8 for both groups, with values of 76.60 (pediatric) and 85.79 (adult). The minimum IQR was observed in Region 7 for the pediatric group (2.29) and Region 4b for the adult group (1.96), and the maximum IQR was in Region 8 for the pediatric group (35.85) and Region 4a for the adult group (19.86).
Discussion: : Couinaud regions 7 and 4b exhibited the highest median PDFF values, indicating these regions may be more prone to fat accumulation, while regions 2 and 3 had the lowest median values. These findings underscore the importance of regional analysis in liver fat quantification, potentially enhancing diagnostic precision and personalized treatment strategies in NAFLD and NASH.
Disclosures:
Ali Zifan, PhD1, Malaika Wauters, 1, Jake Weeks, BS1, Michael Middleton, PhD1, Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc2, Claude Sirlin, MD1. P2855 - Regional Variability in Liver Fat Content in Pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH Assessed by Proton Density Fat Fraction Imaging, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA; 2University of California San Diego School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF) imaging has recently emerged as a critical tool for diagnosing and assessing liver fat content in non-alcoholic associated fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). PDFF provides a non-invasive, quantitative measure of liver fat, aiding in the identification and differentiation of these conditions. Understanding the regional distribution of PDFF within the liver can enhance diagnostic accuracy and guide targeted clinical interventions. The aim of this study was to analyze the distribution of PDFF across the eight regions of the Couinaud liver segmentation in patients with NAFLD and NASH.
Methods: This study utilized data from two cohorts: 111 adult patients from the FLINT study(age: 50.1 ±10.2; BMI: 33.6±5.14) diagnosed with NASH, and 111 pediatric patients from the CyNCh study(age: 13.8 ±2.51; BMI: 33.1±6.4) diagnosed with NAFLD. The volumes from were segmented, and PDFF maps were overlaid with radiologist-segmented regions. For each of the eight Couinaud regions, median and interquartile range (IQR), as well as minimum and maximum PDFF values, were extracted.
Results: Region 7 showed the highest median PDFF value in the pediatric group (35.44) and Region 4b in the adult group (35.40). Region 2 had the lowest median PDFF value in both groups, with values of 32.49 (pediatric) and 34.18 (adult). Variability in PDFF values was highest in Region 1 for the pediatric group (IQR = 6.82) and Region 2 for the adult group (IQR = 5.56), while Region 6 showed the least variability in both groups (IQR = 4.92 for pediatric and 3.81 for adult). The minimum median value was in Region 2 for the pediatric group (12.50) and Region 3 for the adult group (14.33), while the maximum median value was in Region 8 for both groups, with values of 76.60 (pediatric) and 85.79 (adult). The minimum IQR was observed in Region 7 for the pediatric group (2.29) and Region 4b for the adult group (1.96), and the maximum IQR was in Region 8 for the pediatric group (35.85) and Region 4a for the adult group (19.86).
Discussion: : Couinaud regions 7 and 4b exhibited the highest median PDFF values, indicating these regions may be more prone to fat accumulation, while regions 2 and 3 had the lowest median values. These findings underscore the importance of regional analysis in liver fat quantification, potentially enhancing diagnostic precision and personalized treatment strategies in NAFLD and NASH.

Figure: Figure 1. Couinaud liver regions in the NAFLD and NASH datasets.
Disclosures:
Ali Zifan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Malaika Wauters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jake Weeks indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Middleton indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Loomba: 89BIO – Consultant. Aardvark – Consultant. Altimmune – Consultant. Madrigal Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Merck – Consultant. Novo Nordisk – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Terns – Consultant. Viking – Consultant.
Claude Sirlin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Zifan, PhD1, Malaika Wauters, 1, Jake Weeks, BS1, Michael Middleton, PhD1, Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc2, Claude Sirlin, MD1. P2855 - Regional Variability in Liver Fat Content in Pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH Assessed by Proton Density Fat Fraction Imaging, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
