Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2792 - Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage With Lumen Apposing Metal Stent vs Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage for Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction After Failed ERCP
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Fnu Faheela, MBBS
Nishtar Medical University
Multan, Punjab, Pakistan
Presenting Author(s)
Fnu Faheela, MBBS1, Muhammad Haseeb, MD, MSc2, Aamir Saeed, MD3, Sandesh Parajuli, MD4, Maham Waqar, MD5, Muhammad Kamal, MD6, Umar Hayat, MD7, Zubair Khan, MD8, Sultan Mahmood, MD9
1Nishtar Medical University, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 2University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 3Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 4Reading Hospital - Tower Health, Reading, PA; 5Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA; 6Hackensack Meridian Health, Roselle Park, NJ; 7Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 8Mercy Hospital Jefferson, Festus, MO; 9University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Wexford, PA
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) using AXIOS lumen apposing metal stent (LAMS) and percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) are two modalities for biliary drainage (BD) in patients with unresectable malignant distant biliary obstruction (MDBO) after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Our study aimed to analyze the cost-effectiveness of EUS using AXIOS LAMS compared to PTBD for BD in patients with MDBO after failed ERCP.
Methods: A systematic search of 4 major databases was performed to retrieve studies comparing the safety and efficacy of EUS using AXIOS LAMS compared to PTBD for BD in MDBO after failed ERCP. Our outcomes of interest were technical success, clinical success, adverse events, re-intervention rate, and stent patency time. Probabilities, costs, and quality of life (QOL) data were extracted from published literature. A state transition Markov cohort model was then constructed from the U.S. healthcare system’s perspective. The base case was a patient with locally advanced unresectable cancer with MDBO. Costs were reported in U.S. dollars ($) adjusted to the year 2023 using the consumer price index with health outcomes recorded in quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). A two-year time horizon with a cycle length of one month with the application of a 3% discount rate was utilized. The main outcome measure was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) with a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000/QALY. One-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were also performed.
Results: At 2 years, EUS demonstrated higher effectiveness than PTBD (0.68 QALY vs. 0.64 QALY). EUS was cost-effective compared to PTBD with an ICER of $15,008/QALY at a WTP threshold of $100,000/QALY. The additional cost for EUS was calculated to be $636 per patient. The results remained robust on one-way sensitivity analysis with no single parameter able to change the preferred strategy. Furthermore, in probabilistic sensitivity analysis, EUS was preferred strategy compared to PTBD, with a probability of 100% using 10,000 iterations.
Discussion: EUS with AXIOS LAMS was cost-effective compared to PTBD in patients with MDBO who have failed initial ERCP with an ICER of $15,008/QALY. Our results suggest that biliary drainage with EUS should be the treatment of choice in this patient population in centers with the required expertise.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Fnu Faheela, MBBS1, Muhammad Haseeb, MD, MSc2, Aamir Saeed, MD3, Sandesh Parajuli, MD4, Maham Waqar, MD5, Muhammad Kamal, MD6, Umar Hayat, MD7, Zubair Khan, MD8, Sultan Mahmood, MD9. P2792 - Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage With Lumen Apposing Metal Stent vs Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage for Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction After Failed ERCP, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Nishtar Medical University, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 2University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 3Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 4Reading Hospital - Tower Health, Reading, PA; 5Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA; 6Hackensack Meridian Health, Roselle Park, NJ; 7Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 8Mercy Hospital Jefferson, Festus, MO; 9University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Wexford, PA
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) using AXIOS lumen apposing metal stent (LAMS) and percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) are two modalities for biliary drainage (BD) in patients with unresectable malignant distant biliary obstruction (MDBO) after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Our study aimed to analyze the cost-effectiveness of EUS using AXIOS LAMS compared to PTBD for BD in patients with MDBO after failed ERCP.
Methods: A systematic search of 4 major databases was performed to retrieve studies comparing the safety and efficacy of EUS using AXIOS LAMS compared to PTBD for BD in MDBO after failed ERCP. Our outcomes of interest were technical success, clinical success, adverse events, re-intervention rate, and stent patency time. Probabilities, costs, and quality of life (QOL) data were extracted from published literature. A state transition Markov cohort model was then constructed from the U.S. healthcare system’s perspective. The base case was a patient with locally advanced unresectable cancer with MDBO. Costs were reported in U.S. dollars ($) adjusted to the year 2023 using the consumer price index with health outcomes recorded in quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). A two-year time horizon with a cycle length of one month with the application of a 3% discount rate was utilized. The main outcome measure was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) with a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000/QALY. One-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were also performed.
Results: At 2 years, EUS demonstrated higher effectiveness than PTBD (0.68 QALY vs. 0.64 QALY). EUS was cost-effective compared to PTBD with an ICER of $15,008/QALY at a WTP threshold of $100,000/QALY. The additional cost for EUS was calculated to be $636 per patient. The results remained robust on one-way sensitivity analysis with no single parameter able to change the preferred strategy. Furthermore, in probabilistic sensitivity analysis, EUS was preferred strategy compared to PTBD, with a probability of 100% using 10,000 iterations.
Discussion: EUS with AXIOS LAMS was cost-effective compared to PTBD in patients with MDBO who have failed initial ERCP with an ICER of $15,008/QALY. Our results suggest that biliary drainage with EUS should be the treatment of choice in this patient population in centers with the required expertise.

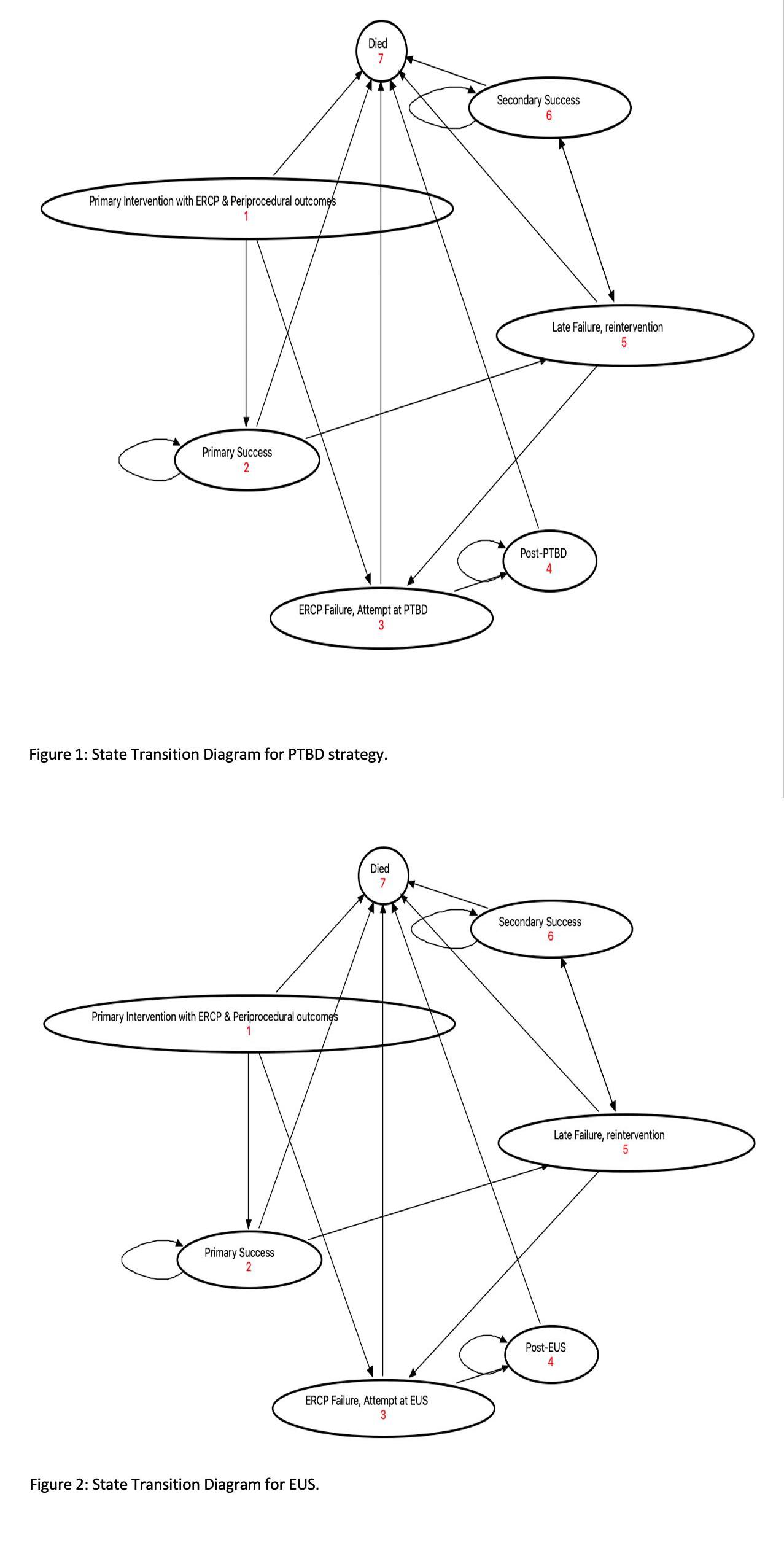
Figure: Figure 1: State Transition Diagram for PTBD strategy
Figure 2: State Transition Diagram for EUS
Figure 2: State Transition Diagram for EUS
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Fnu Faheela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Haseeb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandesh Parajuli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maham Waqar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zubair Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sultan Mahmood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Faheela, MBBS1, Muhammad Haseeb, MD, MSc2, Aamir Saeed, MD3, Sandesh Parajuli, MD4, Maham Waqar, MD5, Muhammad Kamal, MD6, Umar Hayat, MD7, Zubair Khan, MD8, Sultan Mahmood, MD9. P2792 - Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage With Lumen Apposing Metal Stent vs Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage for Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction After Failed ERCP, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
