Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2642 - The When, the Where, and the How: Temporal and Quantitative Trends in Fecal Calprotectin Levels and the Implications for Checkpoint-Inhibitor Colitis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
- MS
Malek Satila, MD
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Malek Satila, MD1, Linfeng Lu, MD2, Tanvi Gupta, MD3, Andres Rivera, MD2, Kian Abdul-Baki, DO4, Elliot Axel. Baerman, MD2, Hamza Salim, MD4, Kei Takigawa, MD2, Andrew Sullivan, MD5, Irene J. Lee, MD2, Carolina Colli Cruz, MD1, Raakhi Menon, DO4, Varun Vemulapalli, MD3, Cristina M. Natha, MD3, Ayesha Khan, DO4, Garrett T. Coleman, 6, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD7, Anusha Thomas, MD7, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD8
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 6University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy School of Medicine, Galveston, TX; 7The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 8University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
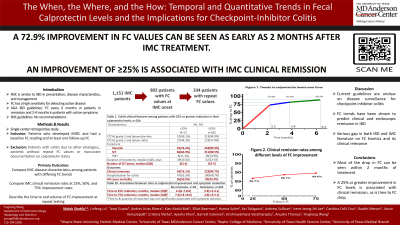
Introduction: Immune-mediated colitis (IMC) is a common toxicity secondary to immune-checkpoint inhibition (ICI) that can interfere with cancer treatment. There is a massive gap in the literature on how to monitor this disease. Fecal calprotectin (FC) has been useful in the initial evaluation and surveillance of this toxicity. However, there is no information on the interval of FC testing and the dynamics of FC values over time for this disease entity and how they impact clinical outcomes. We present the first study to explore the dynamics of FC monitoring for IMC.
Methods: This was a single center, retrospective review including all patients who received ICIs between 01/2010 to 02/2024, developed IMC, and had FC levels available at the time of diagnosis. We collected data on patient demographic information and colitis clinical information including presentation, endoscopic features, treatments, and outcomes. SPSS 26.0 was used to analyze the data.
Results: 802 patients met the study criteria. Elevated baseline FC was associated with a higher grade of diarrhea, hospitalization and re-hospitalization for colitis, and ulcers on endoscopy (p< 0.05 for all). Normalization of FC levels was significantly associated with symptom remission (p< 0.05) and occurred in a median of 4.1 months (IQR: 2.4-6.9). As low as a 25% decrease from baseline FC was associated with clinical remission (p< 0.05), with a 75% decrease showing a higher trend in the rate of endoscopic remission (60.8% vs. 41.9% of those without a 75% decrease; p=0.069). FC dropped by 72.9% from an initially elevated baseline within a median of 2.2 months (IQR: 1.3-3.5). The time taken for FC to improve by 25% or 75% was associated with symptom resolution (p< 0.05). Finally, normalization of FC was associated with improved overall survival (OR: 0.5, CI: 0.3-0.8; p=0.028) among patients with colitis.
Discussion: This is the largest study to date reporting the quantitative and temporal changes in fecal calprotectin levels among patients with IMC. We found that baseline FC is a useful prognostic marker for future disease course. Normalization of FC and improvement in elevated baseline levels of at least 25% were associated with clinical remission, and typically occur at around 4 and 2 months respectively. These results support the utility of obtaining baseline calprotectin levels and re-checking them at 2-3 months after disease onset.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Malek Satila, MD1, Linfeng Lu, MD2, Tanvi Gupta, MD3, Andres Rivera, MD2, Kian Abdul-Baki, DO4, Elliot Axel. Baerman, MD2, Hamza Salim, MD4, Kei Takigawa, MD2, Andrew Sullivan, MD5, Irene J. Lee, MD2, Carolina Colli Cruz, MD1, Raakhi Menon, DO4, Varun Vemulapalli, MD3, Cristina M. Natha, MD3, Ayesha Khan, DO4, Garrett T. Coleman, 6, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD7, Anusha Thomas, MD7, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD8. P2642 - The When, the Where, and the How: Temporal and Quantitative Trends in Fecal Calprotectin Levels and the Implications for Checkpoint-Inhibitor Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 6University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy School of Medicine, Galveston, TX; 7The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 8University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Immune-mediated colitis (IMC) is a common toxicity secondary to immune-checkpoint inhibition (ICI) that can interfere with cancer treatment. There is a massive gap in the literature on how to monitor this disease. Fecal calprotectin (FC) has been useful in the initial evaluation and surveillance of this toxicity. However, there is no information on the interval of FC testing and the dynamics of FC values over time for this disease entity and how they impact clinical outcomes. We present the first study to explore the dynamics of FC monitoring for IMC.
Methods: This was a single center, retrospective review including all patients who received ICIs between 01/2010 to 02/2024, developed IMC, and had FC levels available at the time of diagnosis. We collected data on patient demographic information and colitis clinical information including presentation, endoscopic features, treatments, and outcomes. SPSS 26.0 was used to analyze the data.
Results: 802 patients met the study criteria. Elevated baseline FC was associated with a higher grade of diarrhea, hospitalization and re-hospitalization for colitis, and ulcers on endoscopy (p< 0.05 for all). Normalization of FC levels was significantly associated with symptom remission (p< 0.05) and occurred in a median of 4.1 months (IQR: 2.4-6.9). As low as a 25% decrease from baseline FC was associated with clinical remission (p< 0.05), with a 75% decrease showing a higher trend in the rate of endoscopic remission (60.8% vs. 41.9% of those without a 75% decrease; p=0.069). FC dropped by 72.9% from an initially elevated baseline within a median of 2.2 months (IQR: 1.3-3.5). The time taken for FC to improve by 25% or 75% was associated with symptom resolution (p< 0.05). Finally, normalization of FC was associated with improved overall survival (OR: 0.5, CI: 0.3-0.8; p=0.028) among patients with colitis.
Discussion: This is the largest study to date reporting the quantitative and temporal changes in fecal calprotectin levels among patients with IMC. We found that baseline FC is a useful prognostic marker for future disease course. Normalization of FC and improvement in elevated baseline levels of at least 25% were associated with clinical remission, and typically occur at around 4 and 2 months respectively. These results support the utility of obtaining baseline calprotectin levels and re-checking them at 2-3 months after disease onset.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Malek Satila indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Linfeng Lu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanvi Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kian Abdul-Baki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elliot Baerman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Salim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kei Takigawa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Sullivan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irene Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carolina Colli Cruz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raakhi Menon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Varun Vemulapalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cristina Natha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Garrett Coleman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnavathana Varatharajalu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Thomas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yinghong Wang: AzurRx – Consultant. Ilyapharma – Consultant. IOTA – Consultant. Sorriso – Consultant. Tillotts – Consultant.
Malek Satila, MD1, Linfeng Lu, MD2, Tanvi Gupta, MD3, Andres Rivera, MD2, Kian Abdul-Baki, DO4, Elliot Axel. Baerman, MD2, Hamza Salim, MD4, Kei Takigawa, MD2, Andrew Sullivan, MD5, Irene J. Lee, MD2, Carolina Colli Cruz, MD1, Raakhi Menon, DO4, Varun Vemulapalli, MD3, Cristina M. Natha, MD3, Ayesha Khan, DO4, Garrett T. Coleman, 6, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD7, Anusha Thomas, MD7, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD8. P2642 - The When, the Where, and the How: Temporal and Quantitative Trends in Fecal Calprotectin Levels and the Implications for Checkpoint-Inhibitor Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
