Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
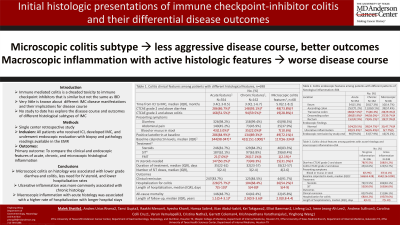
P2643 - Initial Histologic Presentations of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis and Their Differential Disease Outcomes
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
- MS
Malek Satila, MD
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Malek Satila, MD1, Andres Rivera, MD2, Tanvi Gupta, MD3, Raakhi Menon, DO4, Ayesha Khan, DO4, Hamza Salim, MD4, Kian Abdul-Baki, DO4, Kei Takigawa, MD2, Elliot Axel. Baerman, MD2, Linfeng Lu, MD2, Irene J. Lee, MD2, Andrew Sullivan, MD5, Carolina Colli Cruz, MD1, Varun Vemulapalli, MD3, Cristina M. Natha, MD3, Garrett T. Coleman, 6, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD7, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD8
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 6University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy School of Medicine, Galveston, TX; 7The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 8University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Immune-mediated colitis (IMC) is a frustrating toxicity to immune-checkpoint inhibition (ICI) that frequently necessitates the discontinuation of treatment. While similar to inflammatory bowel disease, IMC has a unique spectrum of clinical, endoscopic, and histological presentations that are not fully understood. In this study, we aim to compare the differential disease behavior of IMC with normal and inflammatory histologic presentations.
Methods: This was a single center, retrospective review including all patients who received ICIs between 01/2010 to 02/2024 and developed IMC and underwent endoscopic evaluation within one month of disease onset. Patients were screened for IMC based on stool tests, then divided into groups based on their initial histological findings. We collected patient demographic and colitis clinical data.
Results: 698 patients met the study criteria, 114 (16.3%) with completely normal endoscopic evaluation, 354 (50.7%) with features of acute inflammation, 162 (23.2%) with those of chronic inflammation, and 68 (9.7%) with elements of microscopic colitis. We found that patients with histologic inflammation were more likely to present with more severe symptoms and require aggressive treatment with selective immunosuppressive therapy, IV steroids, and a longer duration of steroids (p< 0.05). These patients were likely to have longer symptom durations but surprisingly, were less frequently re-hospitalized for colitis (p< 0.05). Patients with microscopic colitis were less likely to need IV steroids or hospitalization than those with acute or chronic inflammation, and were more likely to have normal macroscopic findings (p< 0.05). Chronic histology was most frequently associated with ulcers compared to both acute and microscopic colitis-like inflammation. Finally, macroscopic endoscopic inflammation was associated with a need for more aggressive treatment and hospitalization for patients with acute histological inflammation, but not for those with chronic or microscopic histology.
Discussion: This is the largest study to date reporting patterns of histologic findings among patients with IMC. Patients with normal initial findings may require less aggressive treatment but may need closer monitoring to prevent rehospitalization. Patients with microscopic colitis histology may have a milder disease course than those with acute or chronic inflammation. Finally, macroscopic findings may predict more severe disease among patients with acute histological inflammation.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Malek Satila, MD1, Andres Rivera, MD2, Tanvi Gupta, MD3, Raakhi Menon, DO4, Ayesha Khan, DO4, Hamza Salim, MD4, Kian Abdul-Baki, DO4, Kei Takigawa, MD2, Elliot Axel. Baerman, MD2, Linfeng Lu, MD2, Irene J. Lee, MD2, Andrew Sullivan, MD5, Carolina Colli Cruz, MD1, Varun Vemulapalli, MD3, Cristina M. Natha, MD3, Garrett T. Coleman, 6, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD7, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD8. P2643 - Initial Histologic Presentations of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis and Their Differential Disease Outcomes, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 6University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy School of Medicine, Galveston, TX; 7The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 8University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Immune-mediated colitis (IMC) is a frustrating toxicity to immune-checkpoint inhibition (ICI) that frequently necessitates the discontinuation of treatment. While similar to inflammatory bowel disease, IMC has a unique spectrum of clinical, endoscopic, and histological presentations that are not fully understood. In this study, we aim to compare the differential disease behavior of IMC with normal and inflammatory histologic presentations.
Methods: This was a single center, retrospective review including all patients who received ICIs between 01/2010 to 02/2024 and developed IMC and underwent endoscopic evaluation within one month of disease onset. Patients were screened for IMC based on stool tests, then divided into groups based on their initial histological findings. We collected patient demographic and colitis clinical data.
Results: 698 patients met the study criteria, 114 (16.3%) with completely normal endoscopic evaluation, 354 (50.7%) with features of acute inflammation, 162 (23.2%) with those of chronic inflammation, and 68 (9.7%) with elements of microscopic colitis. We found that patients with histologic inflammation were more likely to present with more severe symptoms and require aggressive treatment with selective immunosuppressive therapy, IV steroids, and a longer duration of steroids (p< 0.05). These patients were likely to have longer symptom durations but surprisingly, were less frequently re-hospitalized for colitis (p< 0.05). Patients with microscopic colitis were less likely to need IV steroids or hospitalization than those with acute or chronic inflammation, and were more likely to have normal macroscopic findings (p< 0.05). Chronic histology was most frequently associated with ulcers compared to both acute and microscopic colitis-like inflammation. Finally, macroscopic endoscopic inflammation was associated with a need for more aggressive treatment and hospitalization for patients with acute histological inflammation, but not for those with chronic or microscopic histology.
Discussion: This is the largest study to date reporting patterns of histologic findings among patients with IMC. Patients with normal initial findings may require less aggressive treatment but may need closer monitoring to prevent rehospitalization. Patients with microscopic colitis histology may have a milder disease course than those with acute or chronic inflammation. Finally, macroscopic findings may predict more severe disease among patients with acute histological inflammation.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Malek Satila indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanvi Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raakhi Menon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Salim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kian Abdul-Baki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kei Takigawa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elliot Baerman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Linfeng Lu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irene Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Sullivan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carolina Colli Cruz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Varun Vemulapalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cristina Natha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Garrett Coleman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnavathana Varatharajalu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yinghong Wang: AzurRx – Consultant. Ilyapharma – Consultant. IOTA – Consultant. Sorriso – Consultant. Tillotts – Consultant.
Malek Satila, MD1, Andres Rivera, MD2, Tanvi Gupta, MD3, Raakhi Menon, DO4, Ayesha Khan, DO4, Hamza Salim, MD4, Kian Abdul-Baki, DO4, Kei Takigawa, MD2, Elliot Axel. Baerman, MD2, Linfeng Lu, MD2, Irene J. Lee, MD2, Andrew Sullivan, MD5, Carolina Colli Cruz, MD1, Varun Vemulapalli, MD3, Cristina M. Natha, MD3, Garrett T. Coleman, 6, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD7, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD8. P2643 - Initial Histologic Presentations of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis and Their Differential Disease Outcomes, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
