Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1797 - An Unusual Case of Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome With ASC
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- KC
Kelly Y. Chen, BS
Wayne State School of Medicine
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Kelly Y. Chen, BS1, Syed-Mohammed Jafri, MD2
1Wayne State School of Medicine, Detroit, MI; 2Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI
Introduction: PJS is a rare genetic disorder that clinically presents as mucocutaneous hyperpigmented macules caused by increased melanin in basal cells and hamartomatous gastrointestinal polyps. We present an unusual case of elevated liver enzymes and hematochezia with diagnosis of PJS and ASC.
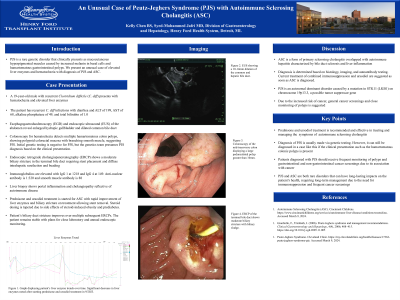
Case Description/Methods: A 19-year-old male with recurrent Clostridium difficile (C. diff) presents with hematochezia and elevated liver enzymes. The patient has recurrent C. diff infections with diarrhea and ALT of 199, AST of 68, alkaline phosphatase of 49, and total bilirubin of 1.0. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) of the abdomen reveal enlarged hydropic gallbladder and dilated common bile duct. Colonoscopy for hematochezia detects multiple hamartomatous colon polyps, showing polypoid colorectal mucosa with branching smooth muscle, suggesting PJS. Initial genetic testing is negative for PJS, but the genetics team presumes PJS diagnosis based on the clinical presentation. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) shows a moderate biliary stricture in the terminal bile duct requiring stent placement and diffuse intrahepatic rarefaction and beading. Immunoglobulins are elevated with IgG 1 at 1218 and IgG 4 at 149. Anti-nuclear antibody is 1:320 and smooth muscle antibody is 88. Liver biopsy shows portal inflammation and cholangiopathy reflective of autoimmune disease. Prednisone and ursodiol treatment is started for ASC with rapid improvement of liver enzymes and biliary stricture on treatment allowing stent removal. Steroid dosing is tapered due to side effects of steroid-induced obesity and prediabetes. Patient’s biliary duct stricture improves over multiple subsequent ERCPs. The patient remains stable with plans for close laboratory and annual endoscopic monitoring.
Discussion: ASC is a form of primary sclerosing cholangitis overlapped with autoimmune hepatitis characterized by bile duct sclerosis and liver inflammation. Diagnosis is determined based on histology, imaging, and autoantibody testing. Current treatment of combined immunosuppression and ursodiol are suggested as soon as ASC is diagnosed. PJS is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a mutation in STK11 (LKB1) on chromosome 19p13.3, a possible tumor suppressor gene. Due to the increased risk of cancer, general cancer screenings and close monitoring of polyps is suggested.
Disclosures:
Kelly Y. Chen, BS1, Syed-Mohammed Jafri, MD2. P1797 - An Unusual Case of Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome With ASC, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Wayne State School of Medicine, Detroit, MI; 2Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI
Introduction: PJS is a rare genetic disorder that clinically presents as mucocutaneous hyperpigmented macules caused by increased melanin in basal cells and hamartomatous gastrointestinal polyps. We present an unusual case of elevated liver enzymes and hematochezia with diagnosis of PJS and ASC.
Case Description/Methods: A 19-year-old male with recurrent Clostridium difficile (C. diff) presents with hematochezia and elevated liver enzymes. The patient has recurrent C. diff infections with diarrhea and ALT of 199, AST of 68, alkaline phosphatase of 49, and total bilirubin of 1.0. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) of the abdomen reveal enlarged hydropic gallbladder and dilated common bile duct. Colonoscopy for hematochezia detects multiple hamartomatous colon polyps, showing polypoid colorectal mucosa with branching smooth muscle, suggesting PJS. Initial genetic testing is negative for PJS, but the genetics team presumes PJS diagnosis based on the clinical presentation. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) shows a moderate biliary stricture in the terminal bile duct requiring stent placement and diffuse intrahepatic rarefaction and beading. Immunoglobulins are elevated with IgG 1 at 1218 and IgG 4 at 149. Anti-nuclear antibody is 1:320 and smooth muscle antibody is 88. Liver biopsy shows portal inflammation and cholangiopathy reflective of autoimmune disease. Prednisone and ursodiol treatment is started for ASC with rapid improvement of liver enzymes and biliary stricture on treatment allowing stent removal. Steroid dosing is tapered due to side effects of steroid-induced obesity and prediabetes. Patient’s biliary duct stricture improves over multiple subsequent ERCPs. The patient remains stable with plans for close laboratory and annual endoscopic monitoring.
Discussion: ASC is a form of primary sclerosing cholangitis overlapped with autoimmune hepatitis characterized by bile duct sclerosis and liver inflammation. Diagnosis is determined based on histology, imaging, and autoantibody testing. Current treatment of combined immunosuppression and ursodiol are suggested as soon as ASC is diagnosed. PJS is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a mutation in STK11 (LKB1) on chromosome 19p13.3, a possible tumor suppressor gene. Due to the increased risk of cancer, general cancer screenings and close monitoring of polyps is suggested.
Disclosures:
Kelly Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed-Mohammed Jafri: Gilead, Takeda, Abbvie, Intercept, VectivBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau.
Kelly Y. Chen, BS1, Syed-Mohammed Jafri, MD2. P1797 - An Unusual Case of Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome With ASC, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
