Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1153 - Comparison of Inpatient Outcomes and Characteristics of Autoimmune Hepatitis-Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome, Autoimmune Hepatitis, and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Nationally Representative Study
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS
Rutgers New Jersey Medical School
Newark, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Sameer Rao, MBBS2, Bhavik Bansal, MBBS3, Mohamed Ismail, DO1, Ahmed Al-Khazraji, MD1
1Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) are autoimmune diseases of the hepatobiliary system that can coexist in some cases. Patients with AIH-PSC overlap poorly respond to immunosuppressive therapy alone and often need additional treatment. This study aimed to investigate and compare the demographic characteristics, extra-hepatic auto-immune diseases, and outcomes of hospitalized patients with AIH-PSC overlap with AIH and PSC. We hypothesized that there are differences in rates of major adverse liver outcomes when comparing these groups.
Methods: Hospitalized adult patients with AIH, PSC, and AIH-PSC overlap were identified using the ICD-10 codes from the National Inpatient Sample 2016-2019. We performed weighted logistic regression for predicting complications of cirrhosis, inpatient mortality, sepsis, and respiratory failure among AIH-PSC overlap cases when compared separately to AIH and PSC-only populations as controls.
Results: A total of 2117 AIH, 520 PSC, and 46 overlap patients were identified which represents 10,585; 2600, and 230 patients respectively when weighted. Patients with AIH/PSC overlap, AIH and PSC had a mean age of 36.5, 51.9, and 49.9 years respectively. On multivariate analysis, we found that patients with AIH/PSC are more likely to have liver transplants (OR 7.43, P< 0.001) compared to AIH; whereas no significant difference was found compared to PSC. The likelihood of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was greater in AIH/PSC patients when compared to PSC alone with an OR of 39.5 (P=0.019). AIH/PSC patients had a higher prevalence of celiac disease when compared to AIH (P< 0.001) and to PSC (P< 0.001), however, no significant differences were present in the prevalence of other extra-hepatic autoimmune diseases. There were no significant differences in inpatient mortality, sepsis, respiratory failure, ascites, and portal hypertension.
Discussion: Patients admitted with AIH/PSC overlap are younger than those with isolated AIH or PSC, suggesting an earlier onset or more rapid progression of the disease leading to early diagnosis. These patients are more likely to undergo liver transplantation compared to those with AIH and are more likely to develop HCC compared to those with PSC, indicating potentially worse long-term outcomes. However, short-term outcomes during hospitalization, such as inpatient mortality, ascites, portal hypertension, sepsis, and respiratory failure were similar to those with isolated AIH or PSC.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Sameer Rao, MBBS2, Bhavik Bansal, MBBS3, Mohamed Ismail, DO1, Ahmed Al-Khazraji, MD1. P1153 - Comparison of Inpatient Outcomes and Characteristics of Autoimmune Hepatitis-Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome, Autoimmune Hepatitis, and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Nationally Representative Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) are autoimmune diseases of the hepatobiliary system that can coexist in some cases. Patients with AIH-PSC overlap poorly respond to immunosuppressive therapy alone and often need additional treatment. This study aimed to investigate and compare the demographic characteristics, extra-hepatic auto-immune diseases, and outcomes of hospitalized patients with AIH-PSC overlap with AIH and PSC. We hypothesized that there are differences in rates of major adverse liver outcomes when comparing these groups.
Methods: Hospitalized adult patients with AIH, PSC, and AIH-PSC overlap were identified using the ICD-10 codes from the National Inpatient Sample 2016-2019. We performed weighted logistic regression for predicting complications of cirrhosis, inpatient mortality, sepsis, and respiratory failure among AIH-PSC overlap cases when compared separately to AIH and PSC-only populations as controls.
Results: A total of 2117 AIH, 520 PSC, and 46 overlap patients were identified which represents 10,585; 2600, and 230 patients respectively when weighted. Patients with AIH/PSC overlap, AIH and PSC had a mean age of 36.5, 51.9, and 49.9 years respectively. On multivariate analysis, we found that patients with AIH/PSC are more likely to have liver transplants (OR 7.43, P< 0.001) compared to AIH; whereas no significant difference was found compared to PSC. The likelihood of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was greater in AIH/PSC patients when compared to PSC alone with an OR of 39.5 (P=0.019). AIH/PSC patients had a higher prevalence of celiac disease when compared to AIH (P< 0.001) and to PSC (P< 0.001), however, no significant differences were present in the prevalence of other extra-hepatic autoimmune diseases. There were no significant differences in inpatient mortality, sepsis, respiratory failure, ascites, and portal hypertension.
Discussion: Patients admitted with AIH/PSC overlap are younger than those with isolated AIH or PSC, suggesting an earlier onset or more rapid progression of the disease leading to early diagnosis. These patients are more likely to undergo liver transplantation compared to those with AIH and are more likely to develop HCC compared to those with PSC, indicating potentially worse long-term outcomes. However, short-term outcomes during hospitalization, such as inpatient mortality, ascites, portal hypertension, sepsis, and respiratory failure were similar to those with isolated AIH or PSC.

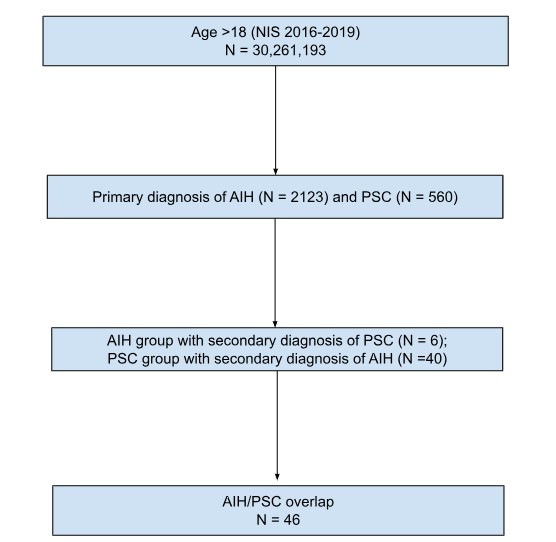
Figure: Screening of patients with AIH/PSC overlap from NIS database
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ritik Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameer Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavik Bansal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Al-Khazraji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Sameer Rao, MBBS2, Bhavik Bansal, MBBS3, Mohamed Ismail, DO1, Ahmed Al-Khazraji, MD1. P1153 - Comparison of Inpatient Outcomes and Characteristics of Autoimmune Hepatitis-Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome, Autoimmune Hepatitis, and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Nationally Representative Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
