Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1000 - Infliximab-Induced Skin Eruption in a Patient With Perianal Crohn's Disease
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Jessica C. Petrov, MD, MSc
Mayo Clinic
Jacksonville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Jessica C. Petrov, MD, MSc, Jeremy K. Bray, MD, Yemi Sokumbi, MD, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc
Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease (CD) occurs in approximately 20% of patients with CD within 10 years of diagnosis. Perianal disease may be difficult to treat and is associated with impaired quality of life. Management often requires a multidisciplinary approach including both medical and surgical interventions. Infliximab, an anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy, is the only biologic demonstrating proven efficacy in treating fistulizing disease in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and is the first-line medical treatment for perianal CD.
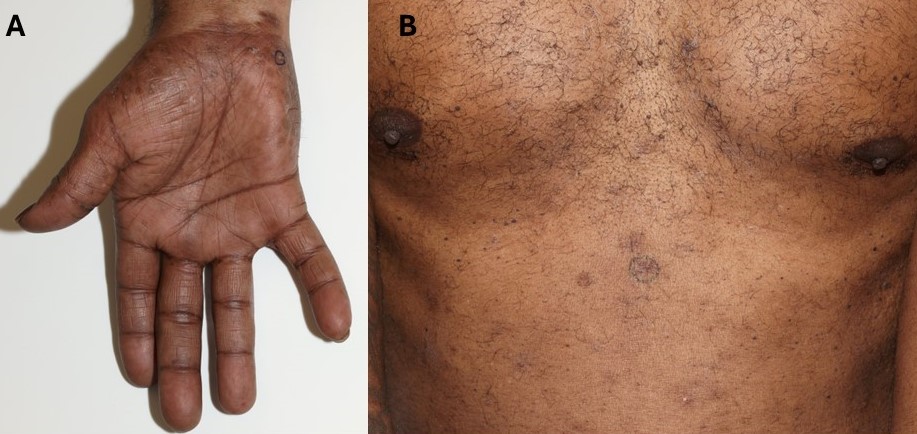
Case Description/Methods: A 47-year-old man with a history isolated perianal Crohn’s disease with recurrent perianal fistulae and abscesses requiring multiple surgeries (fistulotomies with seton placement) presented with a skin rash nine months after initiating infliximab therapy. The rash manifested as a vesicular and pustular eruption on his palms and soles with thin, scaly plaques on his trunk and extremities. He was evaluated by dermatology who performed skin punch biopsies of his palms (A) and trunk (B). Pathology revealed subacute spongiotic dermatitis with superficial perivascular eosinophils.
Discussion: The patient’s subacute to chronic dermatitis was deemed to be secondary to infliximab. Although his perianal disease was well-controlled with infliximab, the rash was unresponsive to topical steroids and infliximab was held. He was initiated on upadacitinib 15mg daily which led to complete resolution of his rash within several days. He was presented with options to either re-trial infliximab at a lower dose or continue upadacitinib with the hopes that his perianal disease would not recur. Cases of anti-TNF therapy-induced dermatitis have been previously reported. Our case presents a challenging clinical scenario regarding treatment options for perianal CD. Second-line therapies for perianal CD include other biologics such as ustekinumab, mesenchymal stem cell therapy, and surgical diversion although current data is limited to post-hoc analyses. The efficacy of upadacitinib in treating perianal CD has not yet been studied in RCTs. Future clinical trials investigating additional therapies for perianal CD are critical in guiding the management of this challenging and debilitating condition in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of anti-TNF therapy.
Disclosures:
Jessica C. Petrov, MD, MSc, Jeremy K. Bray, MD, Yemi Sokumbi, MD, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc. P1000 - Infliximab-Induced Skin Eruption in a Patient With Perianal Crohn's Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease (CD) occurs in approximately 20% of patients with CD within 10 years of diagnosis. Perianal disease may be difficult to treat and is associated with impaired quality of life. Management often requires a multidisciplinary approach including both medical and surgical interventions. Infliximab, an anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy, is the only biologic demonstrating proven efficacy in treating fistulizing disease in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and is the first-line medical treatment for perianal CD.
Case Description/Methods: A 47-year-old man with a history isolated perianal Crohn’s disease with recurrent perianal fistulae and abscesses requiring multiple surgeries (fistulotomies with seton placement) presented with a skin rash nine months after initiating infliximab therapy. The rash manifested as a vesicular and pustular eruption on his palms and soles with thin, scaly plaques on his trunk and extremities. He was evaluated by dermatology who performed skin punch biopsies of his palms (A) and trunk (B). Pathology revealed subacute spongiotic dermatitis with superficial perivascular eosinophils.
Discussion: The patient’s subacute to chronic dermatitis was deemed to be secondary to infliximab. Although his perianal disease was well-controlled with infliximab, the rash was unresponsive to topical steroids and infliximab was held. He was initiated on upadacitinib 15mg daily which led to complete resolution of his rash within several days. He was presented with options to either re-trial infliximab at a lower dose or continue upadacitinib with the hopes that his perianal disease would not recur. Cases of anti-TNF therapy-induced dermatitis have been previously reported. Our case presents a challenging clinical scenario regarding treatment options for perianal CD. Second-line therapies for perianal CD include other biologics such as ustekinumab, mesenchymal stem cell therapy, and surgical diversion although current data is limited to post-hoc analyses. The efficacy of upadacitinib in treating perianal CD has not yet been studied in RCTs. Future clinical trials investigating additional therapies for perianal CD are critical in guiding the management of this challenging and debilitating condition in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of anti-TNF therapy.

Figure: Appearance of infliximab-induced skin rash on palm (A) and trunk (B).
Disclosures:
Jessica Petrov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeremy Bray indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yemi Sokumbi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jana Hashash: Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant.
Jessica C. Petrov, MD, MSc, Jeremy K. Bray, MD, Yemi Sokumbi, MD, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc. P1000 - Infliximab-Induced Skin Eruption in a Patient With Perianal Crohn's Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
