Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1001 - Fungal Appendicitis: A Rare Case Associated With Vedolizumab Therapy
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- ST
Shunsa Tarar, DO
Albany Medical Center
Albany, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Shunsa Tarar, DO, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD, Amjad Shaikh, MD, Robert Gianotti, MD
Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY
Introduction: Vedolizumab, an anti-integrin monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), poses a rare yet significant risk of fungal infections. While nasopharyngitis remains the most common infectious adverse effect observed in patients on Vedolizumab, the potential for fungal infections cannot be overlooked. This risk arises from the drug's interference with integrin-B lymphocyte interactions and subsequent disruption of the intestinal barrier, creating a conducive environment for opportunistic infections. Here, we present a unique case of fungal appendicitis in a young male with ulcerative colitis (UC) following Vedolizumab therapy.
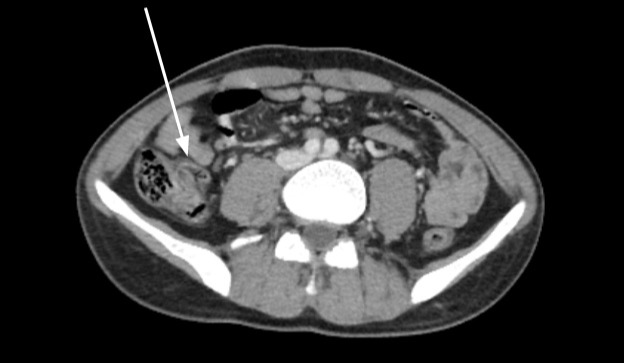
Case Description/Methods: A 21-year-old male diagnosed with UC experienced recurrent flares while on Sulfasalazine therapy in 2019, prompting a transition to Vedolizumab. Over the subsequent four years, he underwent regular infusions of Vedolizumab. In January 2023, the patient presented with symptoms of fatigue and jaundice, ultimately diagnosed as warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Abdominal CT revealed splenomegaly and incidentally detected a tubular fluid-filled structure near the appendix, suggestive of appendicitis with potential underlying mucinous neoplasm. Subsequent ileocectomy revealed a large ileocecal mass adhered to the terminal ileum and cecum. Pathological examination unveiled a tortuous appendix embedded within the cecal wall, characterized by acute and chronic inflammation and focal non-caseating granulomas. Staining revealed yeast in the subserosal tissue and rare hyphae. Post-operatively, the patient developed yeast bacteremia secondary to appendiceal infection, necessitating treatment with Fluconazole and Amoxicillin.
Discussion: Fungal appendicitis is an exceedingly rare condition, accounting for only 1.15% of all appendicitis cases and typically observed in immunocompromised individuals. While clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance of Vedolizumab have reported a low incidence of opportunistic infections, fungal infections remain exceptionally rare, with isolated cases such as esophageal candidiasis documented. This case underscores the emergence of fungal appendicitis in a previously non-immunocompromised patient following four years of Vedolizumab therapy. Awareness of this potential adverse effect before initiating Vedolizumab is crucial, particularly those with underlying immunocompromised states or heightened susceptibility to opportunistic infections.
Disclosures:
Shunsa Tarar, DO, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD, Amjad Shaikh, MD, Robert Gianotti, MD. P1001 - Fungal Appendicitis: A Rare Case Associated With Vedolizumab Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY
Introduction: Vedolizumab, an anti-integrin monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), poses a rare yet significant risk of fungal infections. While nasopharyngitis remains the most common infectious adverse effect observed in patients on Vedolizumab, the potential for fungal infections cannot be overlooked. This risk arises from the drug's interference with integrin-B lymphocyte interactions and subsequent disruption of the intestinal barrier, creating a conducive environment for opportunistic infections. Here, we present a unique case of fungal appendicitis in a young male with ulcerative colitis (UC) following Vedolizumab therapy.
Case Description/Methods: A 21-year-old male diagnosed with UC experienced recurrent flares while on Sulfasalazine therapy in 2019, prompting a transition to Vedolizumab. Over the subsequent four years, he underwent regular infusions of Vedolizumab. In January 2023, the patient presented with symptoms of fatigue and jaundice, ultimately diagnosed as warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Abdominal CT revealed splenomegaly and incidentally detected a tubular fluid-filled structure near the appendix, suggestive of appendicitis with potential underlying mucinous neoplasm. Subsequent ileocectomy revealed a large ileocecal mass adhered to the terminal ileum and cecum. Pathological examination unveiled a tortuous appendix embedded within the cecal wall, characterized by acute and chronic inflammation and focal non-caseating granulomas. Staining revealed yeast in the subserosal tissue and rare hyphae. Post-operatively, the patient developed yeast bacteremia secondary to appendiceal infection, necessitating treatment with Fluconazole and Amoxicillin.
Discussion: Fungal appendicitis is an exceedingly rare condition, accounting for only 1.15% of all appendicitis cases and typically observed in immunocompromised individuals. While clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance of Vedolizumab have reported a low incidence of opportunistic infections, fungal infections remain exceptionally rare, with isolated cases such as esophageal candidiasis documented. This case underscores the emergence of fungal appendicitis in a previously non-immunocompromised patient following four years of Vedolizumab therapy. Awareness of this potential adverse effect before initiating Vedolizumab is crucial, particularly those with underlying immunocompromised states or heightened susceptibility to opportunistic infections.

Figure: Figure: A rare case of fungal appendicitis with the use of Vedolizumab
Disclosures:
Shunsa Tarar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Alshakhatreh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amjad Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Robert Gianotti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shunsa Tarar, DO, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD, Amjad Shaikh, MD, Robert Gianotti, MD. P1001 - Fungal Appendicitis: A Rare Case Associated With Vedolizumab Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
