Sunday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P0664 - Bowel Preparation Quality and Colonoscopy Safety With Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists vs Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study From a Large Tertiary Care Health System
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Vismaya S. Bachu, MD
University of California Los Angeles Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Vismaya S.. Bachu, MD1, Firas Bahdi, MD2, Giuliana Perini Villanueva, MPH3, Songjingyi Liang, MS, MPH3, Arzoo Manandhar, BS3, Vahagn Aldzhyan, MS3, Lynn S.. Connolly, MD3, Kevin A.. Ghassemi, MD3, Danny Issa, MD3, Venkataraman R. Muthusamy, MD4
1University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 2David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Glendora, CA; 3David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 4David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Sherman Oaks, CA
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) are widely-prescribed medications for diabetes mellitus and obesity. While diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of poor bowel prep, it is unclear if GLP1-RAs augment that risk through their effect on gastrointestinal motility. We compared the bowel prep quality and aspiration risk in patients on GLP1-RAs versus matched diabetics off GLP1-RAs who underwent colonoscopy.
Methods: A retrospective case-control study of patients ≥18 years on GLP1-RAs versus matched diabetics off GLP1-RAs who underwent outpatient colonoscopy at a large tertiary health care system between January 2018 and June 2023, before the anesthesia guidance on preprocedural dose holding was issued. The GLP1-RAs group included diabetic or pre-diabetic patients. Exclusion criteria included unconfirmed GLP1-RAs intake, prior bowel resection, and prescription of promotility agents or opioids. The primary outcomes were the rates of aborted colonoscopy and inadequate bowel prep defined as poor or fair bowel prep warranting a repeat colonoscopy ≤1 year or earlier surveillance interval. Secondary outcomes were the rates of periprocedural aspiration and urgent intubation.
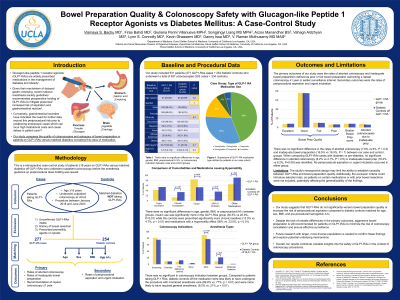
Results: Our study included 531 patients (277 GLP1-RAs cases + 254 diabetic controls) who underwent a total of 637 colonoscopies (303 cases + 334 controls). [Table 1] There were no significant differences in age, gender, BMI, preprocedural A1c%, or colonoscopy indication between groups. Insulin use was significantly more in the GLP1-RAs group (30.3% vs 20.9%, P=0.01) while the controls were prescribed significantly more chronic laxatives (13.5% vs 4.7%, p < 0.01) and medications with a hypomotility effect (36% vs. 23.5%, p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in the rates of aborted colonoscopy (7.6% vs 6%, P=0.4) and inadequate bowel prep (16.5% vs 16.5%, P=1) between cases and controls. When comparing GLP1-RAs cases with diabetes vs pre-diabetes, no significant difference in aborted colonoscopy (8.2% vs 4.1%, P=0.5) or inadequate bowel prep (18.4% vs 8.2%, P=0.09) was identified between groups. No periprocedural aspiration or urgent intubation occurred in either group.
Discussion: Compared to diabetes mellitus, it does not appear that GLP1-RAs worsen bowel prep quality or increase periprocedural aspiration risk. However, aggressive bowel prep is recommended in these patients to prevent colonoscopy abortion and the need for expedited surveillance.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Vismaya S.. Bachu, MD1, Firas Bahdi, MD2, Giuliana Perini Villanueva, MPH3, Songjingyi Liang, MS, MPH3, Arzoo Manandhar, BS3, Vahagn Aldzhyan, MS3, Lynn S.. Connolly, MD3, Kevin A.. Ghassemi, MD3, Danny Issa, MD3, Venkataraman R. Muthusamy, MD4. P0664 - Bowel Preparation Quality and Colonoscopy Safety With Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists vs Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study From a Large Tertiary Care Health System, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 2David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Glendora, CA; 3David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 4David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Sherman Oaks, CA
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) are widely-prescribed medications for diabetes mellitus and obesity. While diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of poor bowel prep, it is unclear if GLP1-RAs augment that risk through their effect on gastrointestinal motility. We compared the bowel prep quality and aspiration risk in patients on GLP1-RAs versus matched diabetics off GLP1-RAs who underwent colonoscopy.
Methods: A retrospective case-control study of patients ≥18 years on GLP1-RAs versus matched diabetics off GLP1-RAs who underwent outpatient colonoscopy at a large tertiary health care system between January 2018 and June 2023, before the anesthesia guidance on preprocedural dose holding was issued. The GLP1-RAs group included diabetic or pre-diabetic patients. Exclusion criteria included unconfirmed GLP1-RAs intake, prior bowel resection, and prescription of promotility agents or opioids. The primary outcomes were the rates of aborted colonoscopy and inadequate bowel prep defined as poor or fair bowel prep warranting a repeat colonoscopy ≤1 year or earlier surveillance interval. Secondary outcomes were the rates of periprocedural aspiration and urgent intubation.
Results: Our study included 531 patients (277 GLP1-RAs cases + 254 diabetic controls) who underwent a total of 637 colonoscopies (303 cases + 334 controls). [Table 1] There were no significant differences in age, gender, BMI, preprocedural A1c%, or colonoscopy indication between groups. Insulin use was significantly more in the GLP1-RAs group (30.3% vs 20.9%, P=0.01) while the controls were prescribed significantly more chronic laxatives (13.5% vs 4.7%, p < 0.01) and medications with a hypomotility effect (36% vs. 23.5%, p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in the rates of aborted colonoscopy (7.6% vs 6%, P=0.4) and inadequate bowel prep (16.5% vs 16.5%, P=1) between cases and controls. When comparing GLP1-RAs cases with diabetes vs pre-diabetes, no significant difference in aborted colonoscopy (8.2% vs 4.1%, P=0.5) or inadequate bowel prep (18.4% vs 8.2%, P=0.09) was identified between groups. No periprocedural aspiration or urgent intubation occurred in either group.
Discussion: Compared to diabetes mellitus, it does not appear that GLP1-RAs worsen bowel prep quality or increase periprocedural aspiration risk. However, aggressive bowel prep is recommended in these patients to prevent colonoscopy abortion and the need for expedited surveillance.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Vismaya Bachu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Firas Bahdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Giuliana Perini Villanueva indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Songjingyi Liang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arzoo Manandhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vahagn Aldzhyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lynn Connolly indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Ghassemi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danny Issa: Boston Scientific – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Speakers Bureau.
Venkataraman Muthusamy: Boston Scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Capsovision – Stock Options, Stock-privately held company. Castle Biosciences – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Endogastric Solutions – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Medtronic – Consultant. Pentax Medical – Consultant.
Vismaya S.. Bachu, MD1, Firas Bahdi, MD2, Giuliana Perini Villanueva, MPH3, Songjingyi Liang, MS, MPH3, Arzoo Manandhar, BS3, Vahagn Aldzhyan, MS3, Lynn S.. Connolly, MD3, Kevin A.. Ghassemi, MD3, Danny Issa, MD3, Venkataraman R. Muthusamy, MD4. P0664 - Bowel Preparation Quality and Colonoscopy Safety With Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists vs Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study From a Large Tertiary Care Health System, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
