Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0473 - Repeated Liquid Nitrogen Spray Cryotherapy Treatment Results in Sustained Palliation for Some Patients With Esophageal Cancer
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

.jpeg.jpg)
Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine
Chapel Hill, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH1, Swathi Eluri, MD, MSCR2, Vivek Kaul, MD3, Neil Sharma, MD4, Stuart Gordon, MD5, Toufic Kachaamy, MD6, George Smallfield, MD7, Jason Samarasena, MD8, Arvind Trindade, MD9, Field Willingham, MD, MPH10, Eugene Zolotarevsky, MD11, Jeremy Barber, MD11, Shivangi Kothari, MD3, Kenneth J. Chang, MD, FACG12, Petros Benias, MD9, Mathew McKinley, MD13, Arjun Juneja, BS1, Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH14
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 3University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY; 4Peak Gastroenterology Associates, Colorado Springs, CO; 5Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH; 6City of Hope, Goodyear, AZ; 7Mitchell Endoscopy Center, Richmond, VA; 8University of California, Irvine, Orange, CA; 9Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY; 10Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 11Corewell Health, Grand Rapids, MI; 12University of California Irvine, Cerritos, CA; 13NYU Langone Health, Bethpage, NY; 14Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing, and Center for Gastrointestinal Biology and Disease, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC
Introduction: Esophageal stents and feeding tubes are traditional methods to palliate dysphagia in esophageal cancer but are limited by complications and diminished quality of life. Liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy offers an endoscopic treatment modality for palliation of esophageal cancer. While prior studies have described short-term improvement in dysphagia and other measures with LNSCT, we aimed to examine the long-term symptomatic outcomes of LNSCT treatment for esophageal cancer, and the durability and repeatability of any palliative benefits.
Methods: Data are from a prospective study of LNSCT in luminal esophageal cancer patients at 10 United States sites, 18-89 years old, not candidates for further therapy, naïve to LNSCT, and without esophageal stents at baseline. Patients completed the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life questionnaire (QLQ-C30), esophageal symptoms module (QLQ-OES18), and an ordinal dysphagia score. Symptom outcomes were assessed at baseline and 14 days after each treatment using small-sample-robust mixed linear regression models. We performed Kaplan-Meier survival analysis by clinical stage.
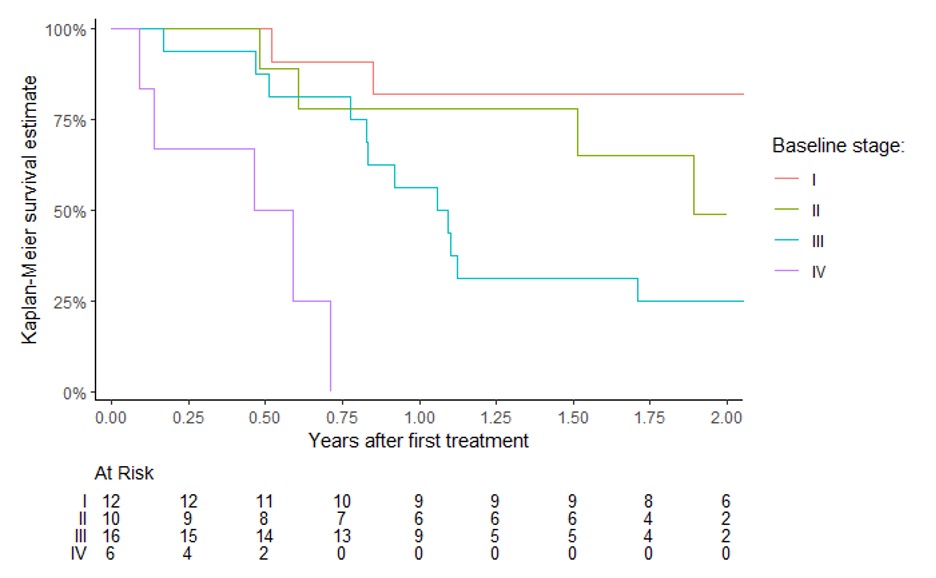
Results: Of 54 enrolled patients, 49 were treated and 48 with complete symptom indices were included for this analysis (5 squamous cell carcinoma and 43 adenocarcinoma), with a total of 261 treatments (average 5.4 per pt). Survival was stratified by clinical stage (Figure). The mean improvement 14 days after a spray cryotherapy treatment in the QLQ-C30 was 1.67 (95% confidence limits (CI) 0.09-3.27). For each subsequent round of treatment, the QLQ-C30 at baseline worsened by 0.33 (95% CI 0.27-0.94). In an interaction model, the magnitude of improvement for each repeated treatment at fourteen days was essentially stable at 0.06 better per round (95% CI -0.31-0.42). Similar patterns were observed for all measures (Table).
Discussion: LNSCT treatment for palliation of esophageal cancer offered durable and repeatable symptom improvement in this cohort of patients. The observational design of this study is susceptible to bias due to the placebo effect and differential loss to follow-up. Repeated LNSCT treatments demonstrated repeatable palliation in patients with esophageal cancer, with a subset of patients with stage II-III cancer experiencing survival of > 2 years in the absence of other curative therapies.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH1, Swathi Eluri, MD, MSCR2, Vivek Kaul, MD3, Neil Sharma, MD4, Stuart Gordon, MD5, Toufic Kachaamy, MD6, George Smallfield, MD7, Jason Samarasena, MD8, Arvind Trindade, MD9, Field Willingham, MD, MPH10, Eugene Zolotarevsky, MD11, Jeremy Barber, MD11, Shivangi Kothari, MD3, Kenneth J. Chang, MD, FACG12, Petros Benias, MD9, Mathew McKinley, MD13, Arjun Juneja, BS1, Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH14. P0473 - Repeated Liquid Nitrogen Spray Cryotherapy Treatment Results in Sustained Palliation for Some Patients With Esophageal Cancer, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 3University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY; 4Peak Gastroenterology Associates, Colorado Springs, CO; 5Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH; 6City of Hope, Goodyear, AZ; 7Mitchell Endoscopy Center, Richmond, VA; 8University of California, Irvine, Orange, CA; 9Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY; 10Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 11Corewell Health, Grand Rapids, MI; 12University of California Irvine, Cerritos, CA; 13NYU Langone Health, Bethpage, NY; 14Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing, and Center for Gastrointestinal Biology and Disease, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC
Introduction: Esophageal stents and feeding tubes are traditional methods to palliate dysphagia in esophageal cancer but are limited by complications and diminished quality of life. Liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy offers an endoscopic treatment modality for palliation of esophageal cancer. While prior studies have described short-term improvement in dysphagia and other measures with LNSCT, we aimed to examine the long-term symptomatic outcomes of LNSCT treatment for esophageal cancer, and the durability and repeatability of any palliative benefits.
Methods: Data are from a prospective study of LNSCT in luminal esophageal cancer patients at 10 United States sites, 18-89 years old, not candidates for further therapy, naïve to LNSCT, and without esophageal stents at baseline. Patients completed the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life questionnaire (QLQ-C30), esophageal symptoms module (QLQ-OES18), and an ordinal dysphagia score. Symptom outcomes were assessed at baseline and 14 days after each treatment using small-sample-robust mixed linear regression models. We performed Kaplan-Meier survival analysis by clinical stage.
Results: Of 54 enrolled patients, 49 were treated and 48 with complete symptom indices were included for this analysis (5 squamous cell carcinoma and 43 adenocarcinoma), with a total of 261 treatments (average 5.4 per pt). Survival was stratified by clinical stage (Figure). The mean improvement 14 days after a spray cryotherapy treatment in the QLQ-C30 was 1.67 (95% confidence limits (CI) 0.09-3.27). For each subsequent round of treatment, the QLQ-C30 at baseline worsened by 0.33 (95% CI 0.27-0.94). In an interaction model, the magnitude of improvement for each repeated treatment at fourteen days was essentially stable at 0.06 better per round (95% CI -0.31-0.42). Similar patterns were observed for all measures (Table).
Discussion: LNSCT treatment for palliation of esophageal cancer offered durable and repeatable symptom improvement in this cohort of patients. The observational design of this study is susceptible to bias due to the placebo effect and differential loss to follow-up. Repeated LNSCT treatments demonstrated repeatable palliation in patients with esophageal cancer, with a subset of patients with stage II-III cancer experiencing survival of > 2 years in the absence of other curative therapies.

Figure: Survival estimates by American Joint Committee on Cancer 8th edition numeric clinical stage categories at first palliative liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy treatment with number remaining under observation.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Cary Cotton: Pentax – Grant/Research Support.
Swathi Eluri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vivek Kaul: ABBVIE – Consultant. CASTLE BIOSCIENCES – Consultant. CDX DIAGNOSTICS – Consultant. COOK MEDICAL – Consultant. EXACT SCIENCES – Consultant. IRONWOOD PHARMA – Consultant.
Neil Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stuart Gordon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Toufic Kachaamy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
George Smallfield indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Samarasena: Cook Medical – Consultant. Medtronic – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Neptune Medical – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Olympus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ovesco – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. SatisfAI – Stock-privately held company. Steris – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Arvind Trindade indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Field Willingham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eugene Zolotarevsky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeremy Barber: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Pentax – Consultant.
Shivangi Kothari: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Castle Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. olympus – Consultant.
Kenneth Chang: Cook Medical – Consultant. Creo Medical – Consultant. EndoGastric Solutions – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Medtronic – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Petros Benias indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mathew McKinley indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arjun Juneja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicholas Shaheen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH1, Swathi Eluri, MD, MSCR2, Vivek Kaul, MD3, Neil Sharma, MD4, Stuart Gordon, MD5, Toufic Kachaamy, MD6, George Smallfield, MD7, Jason Samarasena, MD8, Arvind Trindade, MD9, Field Willingham, MD, MPH10, Eugene Zolotarevsky, MD11, Jeremy Barber, MD11, Shivangi Kothari, MD3, Kenneth J. Chang, MD, FACG12, Petros Benias, MD9, Mathew McKinley, MD13, Arjun Juneja, BS1, Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH14. P0473 - Repeated Liquid Nitrogen Spray Cryotherapy Treatment Results in Sustained Palliation for Some Patients With Esophageal Cancer, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
