Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0160 - Seronegative IgG4 Cholangiopathy: A Diagnostic Challenge Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Navila Sharif, MD
Emory University School of Medicine
Atlanta, GA
Presenting Author(s)
Navila Sharif, MD, Arezou Khosroshahi, MD, Ravi Vora, MD
Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: IgG4 related cholangiopathy (IRC) is a newer entity with a variety of symptoms, and often multi organ involvement, making it a difficult diagnosis. Histology, staining and serum IgG4 levels are typically used for diagnosis. In this case report, we describe a unique case of IgG4 cholangiopathy with negative serology in a patient initially suspected to have cholangiocarcinoma.
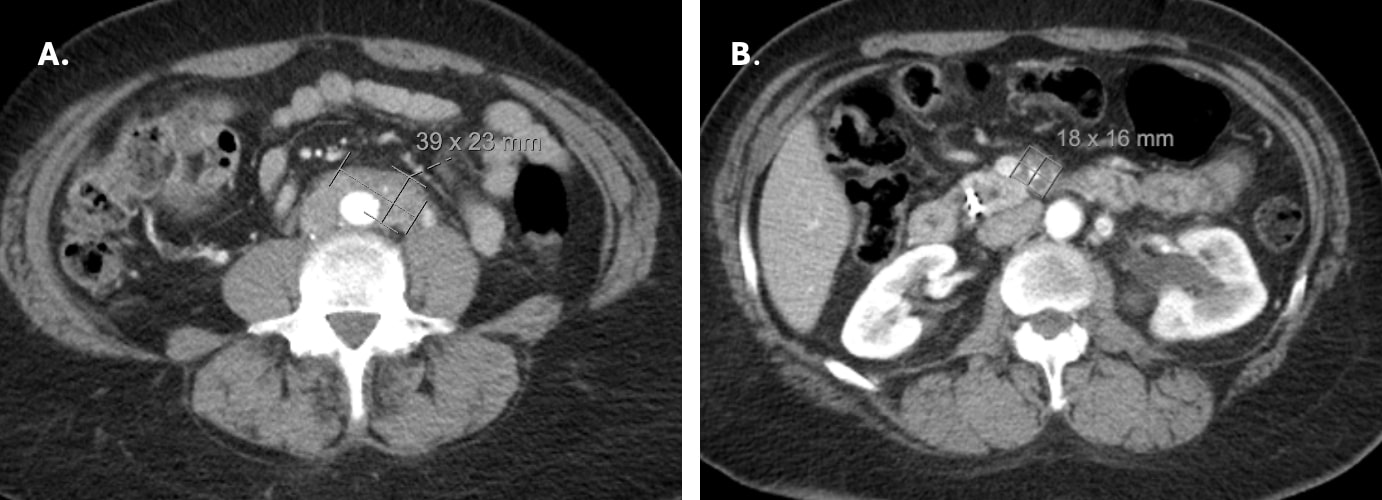
Case Description/Methods: A 65-year-old woman with history of cholecystectomy and choledocholithiasis complicated by recurrent pancreatitis status-post multiple endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with stent exchanges presented with fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, and unintentional weight loss. Labs on admission were remarkable for total bilirubin 16.8, ALP 405, AST 187, ALT 204. CT abdomen and pelvis demonstrated new enhancing soft tissue mass encircling the proximal superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and inferior mesenteric artery (IMA), concerning for malignancy. MRI was also concerning for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. She underwent ERCP with brushings, which was inconclusive on fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis. Repeat ERCP with spyglass and brushings for cytology was negative for cholangiocarcinoma. Serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) was in normal range. Serum IgG4 level was not elevated but due to concern for autoimmune etiology, the patient was started on corticosteroids, with clinical response and normalization of bilirubin levels. She now follows with hepatology and rheumatology outpatient, for a presumed diagnosis of IgG4 related disease.
Discussion: IgG4 related cholangiopathy is a rare but now increasingly described subset of IgG4-related disease. Classification criteria includes histopathology, immunostaining, serum IgG4 level, as well as chest and abdominal findings. While serum IgG4 level generally guides diagnosis, this case illustrates the importance of considering IRC if clinical suspicion is high with negative serology, after careful and thorough workup for malignancy. The features of other organ involvement including retroperitoneal fibrosis, aortitis, pancreatic atrophy suggestive of autoimmune pancreatitis pointed towards a systemic disease. Diagnostic accuracy between cholangiocarcinoma and IgG4 disease is crucial as the two conditions have vastly different treatments, from surgical resection and liver transplant evaluation on one end, to corticosteroid therapy which can lead to normalization of laboratory data and imaging.
Disclosures:
Navila Sharif, MD, Arezou Khosroshahi, MD, Ravi Vora, MD. P0160 - Seronegative IgG4 Cholangiopathy: A Diagnostic Challenge Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: IgG4 related cholangiopathy (IRC) is a newer entity with a variety of symptoms, and often multi organ involvement, making it a difficult diagnosis. Histology, staining and serum IgG4 levels are typically used for diagnosis. In this case report, we describe a unique case of IgG4 cholangiopathy with negative serology in a patient initially suspected to have cholangiocarcinoma.
Case Description/Methods: A 65-year-old woman with history of cholecystectomy and choledocholithiasis complicated by recurrent pancreatitis status-post multiple endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with stent exchanges presented with fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, and unintentional weight loss. Labs on admission were remarkable for total bilirubin 16.8, ALP 405, AST 187, ALT 204. CT abdomen and pelvis demonstrated new enhancing soft tissue mass encircling the proximal superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and inferior mesenteric artery (IMA), concerning for malignancy. MRI was also concerning for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. She underwent ERCP with brushings, which was inconclusive on fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis. Repeat ERCP with spyglass and brushings for cytology was negative for cholangiocarcinoma. Serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) was in normal range. Serum IgG4 level was not elevated but due to concern for autoimmune etiology, the patient was started on corticosteroids, with clinical response and normalization of bilirubin levels. She now follows with hepatology and rheumatology outpatient, for a presumed diagnosis of IgG4 related disease.
Discussion: IgG4 related cholangiopathy is a rare but now increasingly described subset of IgG4-related disease. Classification criteria includes histopathology, immunostaining, serum IgG4 level, as well as chest and abdominal findings. While serum IgG4 level generally guides diagnosis, this case illustrates the importance of considering IRC if clinical suspicion is high with negative serology, after careful and thorough workup for malignancy. The features of other organ involvement including retroperitoneal fibrosis, aortitis, pancreatic atrophy suggestive of autoimmune pancreatitis pointed towards a systemic disease. Diagnostic accuracy between cholangiocarcinoma and IgG4 disease is crucial as the two conditions have vastly different treatments, from surgical resection and liver transplant evaluation on one end, to corticosteroid therapy which can lead to normalization of laboratory data and imaging.

Figure: CT abdomen and pelvis demonstrating a new enhancing soft tissue mass surrounding the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery (A) and proximal superior mesenteric artery (B)
Disclosures:
Navila Sharif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arezou Khosroshahi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ravi Vora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navila Sharif, MD, Arezou Khosroshahi, MD, Ravi Vora, MD. P0160 - Seronegative IgG4 Cholangiopathy: A Diagnostic Challenge Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
