Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0015 - Per-Oral Pancreatoscopy Guided Laser Lithotripsy (POP-LL) vs Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy (ESWL) For Main Pancreatic Duct Stones: A Cost-effectiveness Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Sneh Sonaiya, MD
University of Nevada
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Sneh Sonaiya, MD1, Aastha V. Bharwad, MD2, Charmy Parikh, MD3, Raj H. Patel, MD4, Nikhil Bush, MD5
1University of Nevada, Las Vegas, NV; 2University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 3Mercy Catholic Medical Center, Darby, PA; 4St. Mary Medical Center, Bensalem, PA; 5Jersey City Medical Center, Auburn Hills, MI
Introduction: Pancreatic duct stone (PDS) is a common complication of chronic pancreatitis (CP) and develops in approximately 50%-90% of CP patients, leading to ductal hypertension and severe pain (1-2). ESWL is a standardized treatment option for CP patients with main PDS size >5mm and has a complete ductal clearance of 70.69% (95% CI, 68.97–72.38) (3). However, ESWL has limited efficacy with larger impacted stones, high density, or radiolucent stones. POP through Electrohydraulic Lithotripsy (EHL) or Laser Lithotripsy (LL) enables targeted therapy for PDS and some studies have indicated a complete ductal clearance rate of 80-90% with POP-LL (4-6). This study aims to compare the cost-effectiveness of POP-LL with ESWL for refractory main PDS in patients with CP.
Methods: An incremental cost-effectiveness analysis was performed comparing POP-LL vs ESWL for refractory main PDS in patients with CP using a Markov decision tree model including parameters from the review of available literature. The POP-LL and ESWL costs were derived through CPT codes and average institutional reimbursements for Johns Hopkins Medicine. Effectiveness was determined as post-procedural complete ductal clearance. Due to limited data on the Quality of Life (QoL) for ESWL or POP-LL procedures, estimates of utility were used for cost-effectiveness calculations. Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER) was determined for the base patient with CP and main PDS size >5mm. Analysis was performed using TreeAge Pro Healthcare 2024.
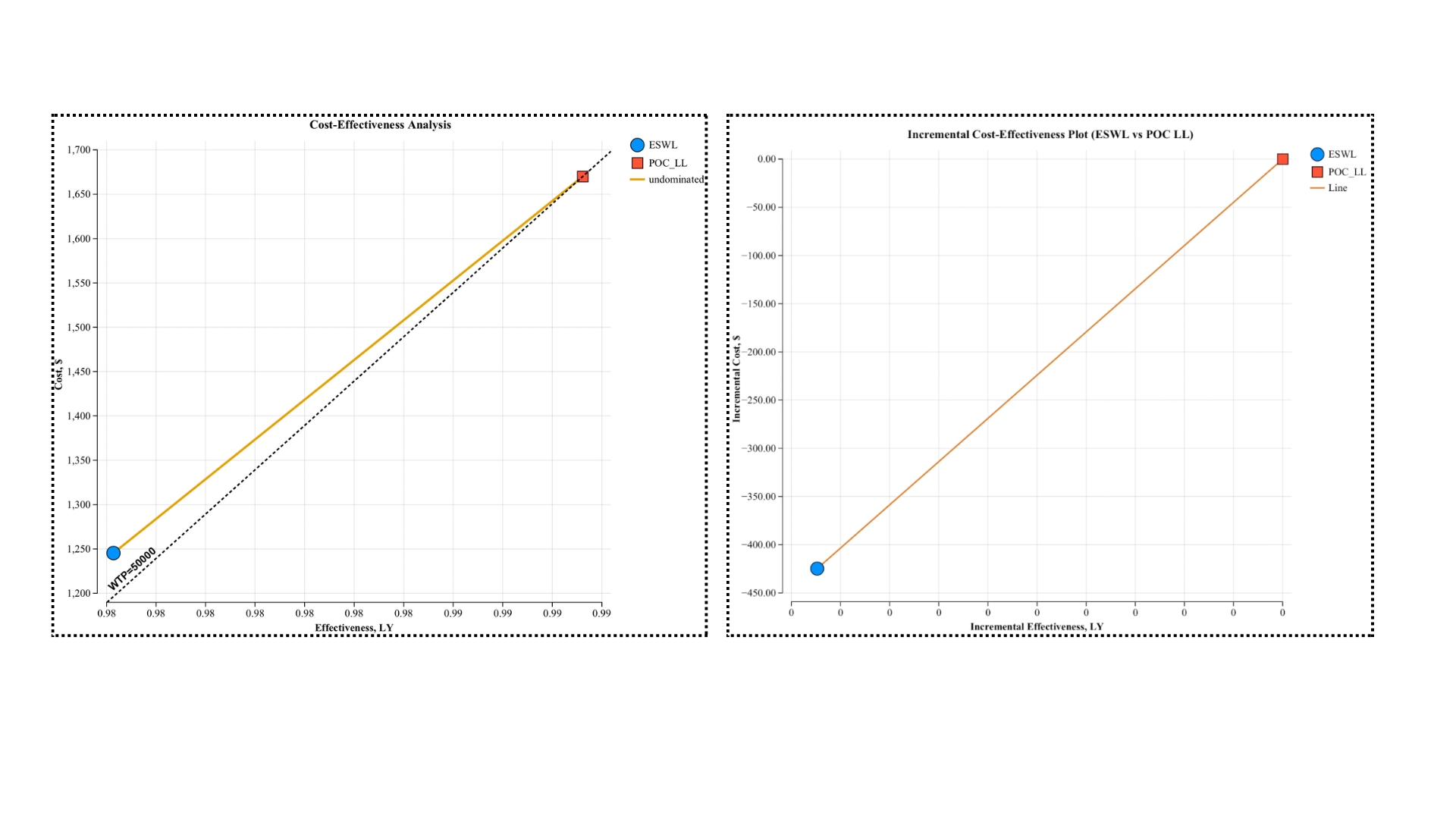
Results: POP-LL is associated with higher upfront costs compared to ESWL ($1,567 vs $963). POP-LL The technical success rate for POP-LL was higher compared to ESWL for main PDS of size >5mm (89.30% vs 70.69%). Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER) for ESWL vs POP-LL was $45323.13 per QALY. Considering the commonly accepted willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $50K per QALY, POP-LL is more cost-effective than ESWL for CP and main PDS size >5mm, and POP-LL is associated with a Net Monetary Benefit (NMB) of 47,749.
Discussion: Our analysis suggests a potentially favorable cost-effectiveness of POP-LL compared to ESWL, depending on the cost and reimbursement of POP-LL and ESWL in a given setting, and the patient’s willingness to pay.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Sneh Sonaiya, MD1, Aastha V. Bharwad, MD2, Charmy Parikh, MD3, Raj H. Patel, MD4, Nikhil Bush, MD5. P0015 - Per-Oral Pancreatoscopy Guided Laser Lithotripsy (POP-LL) vs Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy (ESWL) For Main Pancreatic Duct Stones: A Cost-effectiveness Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Nevada, Las Vegas, NV; 2University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 3Mercy Catholic Medical Center, Darby, PA; 4St. Mary Medical Center, Bensalem, PA; 5Jersey City Medical Center, Auburn Hills, MI
Introduction: Pancreatic duct stone (PDS) is a common complication of chronic pancreatitis (CP) and develops in approximately 50%-90% of CP patients, leading to ductal hypertension and severe pain (1-2). ESWL is a standardized treatment option for CP patients with main PDS size >5mm and has a complete ductal clearance of 70.69% (95% CI, 68.97–72.38) (3). However, ESWL has limited efficacy with larger impacted stones, high density, or radiolucent stones. POP through Electrohydraulic Lithotripsy (EHL) or Laser Lithotripsy (LL) enables targeted therapy for PDS and some studies have indicated a complete ductal clearance rate of 80-90% with POP-LL (4-6). This study aims to compare the cost-effectiveness of POP-LL with ESWL for refractory main PDS in patients with CP.
Methods: An incremental cost-effectiveness analysis was performed comparing POP-LL vs ESWL for refractory main PDS in patients with CP using a Markov decision tree model including parameters from the review of available literature. The POP-LL and ESWL costs were derived through CPT codes and average institutional reimbursements for Johns Hopkins Medicine. Effectiveness was determined as post-procedural complete ductal clearance. Due to limited data on the Quality of Life (QoL) for ESWL or POP-LL procedures, estimates of utility were used for cost-effectiveness calculations. Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER) was determined for the base patient with CP and main PDS size >5mm. Analysis was performed using TreeAge Pro Healthcare 2024.
Results: POP-LL is associated with higher upfront costs compared to ESWL ($1,567 vs $963). POP-LL The technical success rate for POP-LL was higher compared to ESWL for main PDS of size >5mm (89.30% vs 70.69%). Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER) for ESWL vs POP-LL was $45323.13 per QALY. Considering the commonly accepted willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $50K per QALY, POP-LL is more cost-effective than ESWL for CP and main PDS size >5mm, and POP-LL is associated with a Net Monetary Benefit (NMB) of 47,749.
Discussion: Our analysis suggests a potentially favorable cost-effectiveness of POP-LL compared to ESWL, depending on the cost and reimbursement of POP-LL and ESWL in a given setting, and the patient’s willingness to pay.

Figure: Cost-effectiveness analysis (POP-LL vs ESWL)
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Sneh Sonaiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aastha Bharwad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charmy Parikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikhil Bush indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sneh Sonaiya, MD1, Aastha V. Bharwad, MD2, Charmy Parikh, MD3, Raj H. Patel, MD4, Nikhil Bush, MD5. P0015 - Per-Oral Pancreatoscopy Guided Laser Lithotripsy (POP-LL) vs Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy (ESWL) For Main Pancreatic Duct Stones: A Cost-effectiveness Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
