Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1744 - Combined Effect of Obeticholic Acid and Bezafibrate in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Inadequate Response or Intolerance to Ursodeoxycholic Acid: 6-Month Results From a Phase 2 Trial
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Meha Ballard, RN, MSN
Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Morristown, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Meha Ballard, RN, MSN1, David E. Jones, PhD2, Alexandre Louvet, MD, PhD3, Christophe Corpechot, MD4, Vaclav Hejda, MD, PhD5, Heng Zou, 1, Antonio Civitarese, PhD6, Alejandra Villamil, MD7, Frederick Nevens, MD, PhD8
1Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Morristown, NJ; 2Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, England, United Kingdom; 3University Hospital, Lille, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France; 4Reference Centre for Inflammatory Biliary Diseases and Auto-Immune Hepatitis, Saint-Antoine Hospital, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; 5University Hospital, Pilsen, Plzensky kraj, Czech Republic; 6Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc., Morristown, NJ; 7Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina; 8University Hospital KU Leuven, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium
Introduction: Obeticholic acid (OCA) and bezafibrate (BZF) have each improved serum biomarkers of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)–related liver damage. We assessed the effects of OCA + BZF vs BZF alone on serum biomarker levels and safety/tolerability in patients (pts) with PBC who had inadequate response or intolerance to ursodeoxycholic acid.
Methods: This double-blind (DB) phase 2 trial randomized pts 1:1:1:1 to once-daily oral BZF 200 mg (B200) immediate release (IR), BZF 400 mg (B400) sustained release (SR), OCA 5 mg titrated to 10 mg at week 4 + BZF 200 mg IR (OCA/B200 IR), or OCA 5 mg titrated to 10 mg at week 4 + BZF 400 mg SR (OCA/B400 SR) in a 12-week DB treatment (tx) period. Pts continued their original tx assignment for an additional 12 weeks before transitioning to the planned phase 3 dose in a 96-week open-label long-term safety extension (LTSE). Here, we present data from month 6 (12-week DB tx period + DB follow-up period). Change from baseline and normalization rate of alkaline phosphatase (ALP; ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN]) and total bilirubin (TB; ≤ 0.6 x ULN) were assessed. Biochemical remission was defined as ≥ 40% reduction in ALP or ALP ≤ ULN; gamma-glutamyl transferase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase ≤ ULN; and TB ≤ 0.6 x ULN. GLOBE and UK-PBC scores estimated the risk of death and liver transplantation. Safety was assessed by tx-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
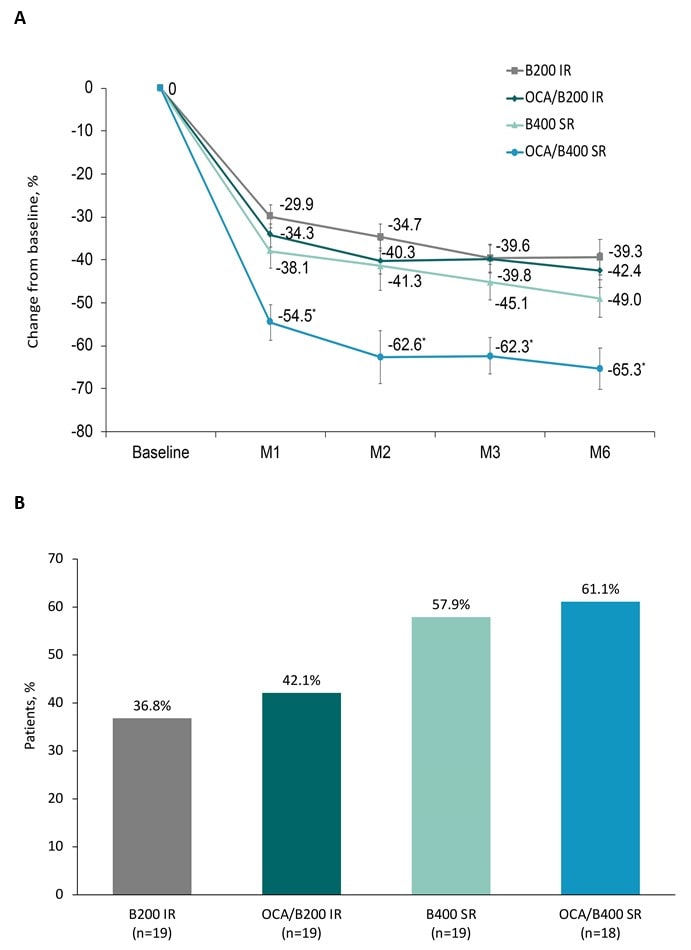
Results: The DB tx period included 75 pts; 66 pts continued to the LTSE. OCA/B400 SR demonstrated a 65.3% reduction in ALP and 27.6% reduction in TB; 61.1% of pts in this cohort achieved ALP ≤ ULN and 83.3% achieved TB ≤ 0.6 x ULN (Figure 1). OCA/B400 SR induced biochemical remission in 66.7% of pts and induced the greatest change in GLOBE (–0.7) and UK-PBC (–1.1) scores. TEAEs were generally balanced across cohorts. In the OCA/B400 SR cohort, 1 pt discontinued due to a serious TEAE of pruritus. The rate of new events of pruritus with OCA/B400 SR was low (11.1%). OCA/B400 SR demonstrated the greatest percentage reductions in total (19.6%) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (18.7%).
Discussion: OCA + BZF is generally well tolerated and has therapeutic potential to normalize serum biomarkers associated with improved transplant-free and decompensation-free survival. Low rates of pruritus were observed with OCA/B400 SR, which were substantially lower than those with OCA in the phase 3 POISE study. The data support phase 3 development of the SR formulation of BZF with low doses of OCA.
Disclosures:
Meha Ballard, RN, MSN1, David E. Jones, PhD2, Alexandre Louvet, MD, PhD3, Christophe Corpechot, MD4, Vaclav Hejda, MD, PhD5, Heng Zou, 1, Antonio Civitarese, PhD6, Alejandra Villamil, MD7, Frederick Nevens, MD, PhD8. P1744 - Combined Effect of Obeticholic Acid and Bezafibrate in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Inadequate Response or Intolerance to Ursodeoxycholic Acid: 6-Month Results From a Phase 2 Trial, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Morristown, NJ; 2Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, England, United Kingdom; 3University Hospital, Lille, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France; 4Reference Centre for Inflammatory Biliary Diseases and Auto-Immune Hepatitis, Saint-Antoine Hospital, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; 5University Hospital, Pilsen, Plzensky kraj, Czech Republic; 6Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc., Morristown, NJ; 7Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina; 8University Hospital KU Leuven, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium
Introduction: Obeticholic acid (OCA) and bezafibrate (BZF) have each improved serum biomarkers of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)–related liver damage. We assessed the effects of OCA + BZF vs BZF alone on serum biomarker levels and safety/tolerability in patients (pts) with PBC who had inadequate response or intolerance to ursodeoxycholic acid.
Methods: This double-blind (DB) phase 2 trial randomized pts 1:1:1:1 to once-daily oral BZF 200 mg (B200) immediate release (IR), BZF 400 mg (B400) sustained release (SR), OCA 5 mg titrated to 10 mg at week 4 + BZF 200 mg IR (OCA/B200 IR), or OCA 5 mg titrated to 10 mg at week 4 + BZF 400 mg SR (OCA/B400 SR) in a 12-week DB treatment (tx) period. Pts continued their original tx assignment for an additional 12 weeks before transitioning to the planned phase 3 dose in a 96-week open-label long-term safety extension (LTSE). Here, we present data from month 6 (12-week DB tx period + DB follow-up period). Change from baseline and normalization rate of alkaline phosphatase (ALP; ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN]) and total bilirubin (TB; ≤ 0.6 x ULN) were assessed. Biochemical remission was defined as ≥ 40% reduction in ALP or ALP ≤ ULN; gamma-glutamyl transferase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase ≤ ULN; and TB ≤ 0.6 x ULN. GLOBE and UK-PBC scores estimated the risk of death and liver transplantation. Safety was assessed by tx-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
Results: The DB tx period included 75 pts; 66 pts continued to the LTSE. OCA/B400 SR demonstrated a 65.3% reduction in ALP and 27.6% reduction in TB; 61.1% of pts in this cohort achieved ALP ≤ ULN and 83.3% achieved TB ≤ 0.6 x ULN (Figure 1). OCA/B400 SR induced biochemical remission in 66.7% of pts and induced the greatest change in GLOBE (–0.7) and UK-PBC (–1.1) scores. TEAEs were generally balanced across cohorts. In the OCA/B400 SR cohort, 1 pt discontinued due to a serious TEAE of pruritus. The rate of new events of pruritus with OCA/B400 SR was low (11.1%). OCA/B400 SR demonstrated the greatest percentage reductions in total (19.6%) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (18.7%).
Discussion: OCA + BZF is generally well tolerated and has therapeutic potential to normalize serum biomarkers associated with improved transplant-free and decompensation-free survival. Low rates of pruritus were observed with OCA/B400 SR, which were substantially lower than those with OCA in the phase 3 POISE study. The data support phase 3 development of the SR formulation of BZF with low doses of OCA.

Figure: Figure 1. Percentage change in ALP from baseline to month 6 (A) and proportion of patients who achieved normalization of ALP at month 6 (B)
*p<0.05 for OCA/B400 SR vs B400 SR.
Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; B200, bezafibrate 200 mg; B400, bezafibrate 400 mg; IR, immediate release; M, month; OCA, obeticholic acid; SR, sustained release.
*p<0.05 for OCA/B400 SR vs B400 SR.
Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; B200, bezafibrate 200 mg; B400, bezafibrate 400 mg; IR, immediate release; M, month; OCA, obeticholic acid; SR, sustained release.
Disclosures:
Meha Ballard: Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee.
David Jones: Abbott – Consultant, speaker fees. Advanz – Consultant. Falk – speaker fees. GSK – Consultant, speaker fees. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker fees. Ipsen – speaker fees.
Alexandre Louvet: Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Ipsen – Consultant. Tillotts Pharma AG – Speaker.
Christophe Corpechot: CymaBay, a Gilead Sciences Company – Consultant. Ipsen – Consultant.
Vaclav Hejda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heng Zou: Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee.
Antonio Civitarese: Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee.
Alejandra Villamil: CymaBay – Consultant. Genfit – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. GSK – Consultant, Consulting fees. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Speaker. Mirum – Consultant. Novartis – Consultant, Consulting fees. Zydus Therapeutics – Consultant.
Frederick Nevens: AbbVie – Consultant. Cellaïon – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Twin Pharma – Consultant.
Meha Ballard, RN, MSN1, David E. Jones, PhD2, Alexandre Louvet, MD, PhD3, Christophe Corpechot, MD4, Vaclav Hejda, MD, PhD5, Heng Zou, 1, Antonio Civitarese, PhD6, Alejandra Villamil, MD7, Frederick Nevens, MD, PhD8. P1744 - Combined Effect of Obeticholic Acid and Bezafibrate in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Inadequate Response or Intolerance to Ursodeoxycholic Acid: 6-Month Results From a Phase 2 Trial, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
