Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1748 - Nationwide Burden and Trend of Gallbladder and Biliary Disease Attributable to High BMI in the Last 3 Decades: Secondary Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

George Mathew Mukalil, MD
Central Michigan University
Saginaw, MI
Presenting Author(s)
George Mathew Mukalil, MD1, Akhilesh Sharma, MBBS2, Asmita Gera, MBBS3, Abobakr Saleh, MBBS4, Amit Banerjee, MBBS5, Shadi Abuhashem, MD6, Bhargav Koyani, MD7, Pragathi Munnangi, MBBS8, Rani Ratheesh, MD9, Lalitkumar Patel, MBBS10, Gunjan Kochhar, MBBS11, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS12, Tanvi Koduru, BS13, Himanshu Koyani, MBBS, MS14
1Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI; 2Adesh Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Bathinda, Punjab, India; 3Tianjin Medical University, Tianijin, Tianjin, China; 4Kasr Alainy Medical School, Cairo University, Cairo, Al Bahr al Ahmar, Egypt; 5Stanley Medical College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 6Alquds University, Gaza, Palestinian Territories; 7Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, Evanston, IL; 8N.R.I Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 9Dr. MGR Medical University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 10Suburban Medical Center, Schaumburg, IL; 11Punjab Institute of Medical Sciences, Jalandhar, Punjab, India; 12Gujarat Adani Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 13Bergen Community College, Paramus, NJ; 14Sterling Hospital, Rajkot, Gujarat, India
Introduction: The global obesity epidemic has profound implications for public health, with an estimated 650 million adults classified as obese worldwide as per World Health Organization (WHO) 2021 data. The global rise in obesity rates correlates with increased morbidity from various non-communicable diseases. Despite this growing recognition, comprehensive analyses quantifying the burden of gallbladder and biliary diseases (GBD) attributable to high body-mass index (BMI) across different global regions remain sparse.
Methods: Using Global Burden of Disease 2021 tool, We estimated deaths, years lived with disability (YLDs), years of life lost (YLL) by age, sex, year and location due to GBD attributable to HBMI in 204 Countries and territories from 1990-2021. Results were presented in absolute counts and age-standardized rate (per 100,000 person years).
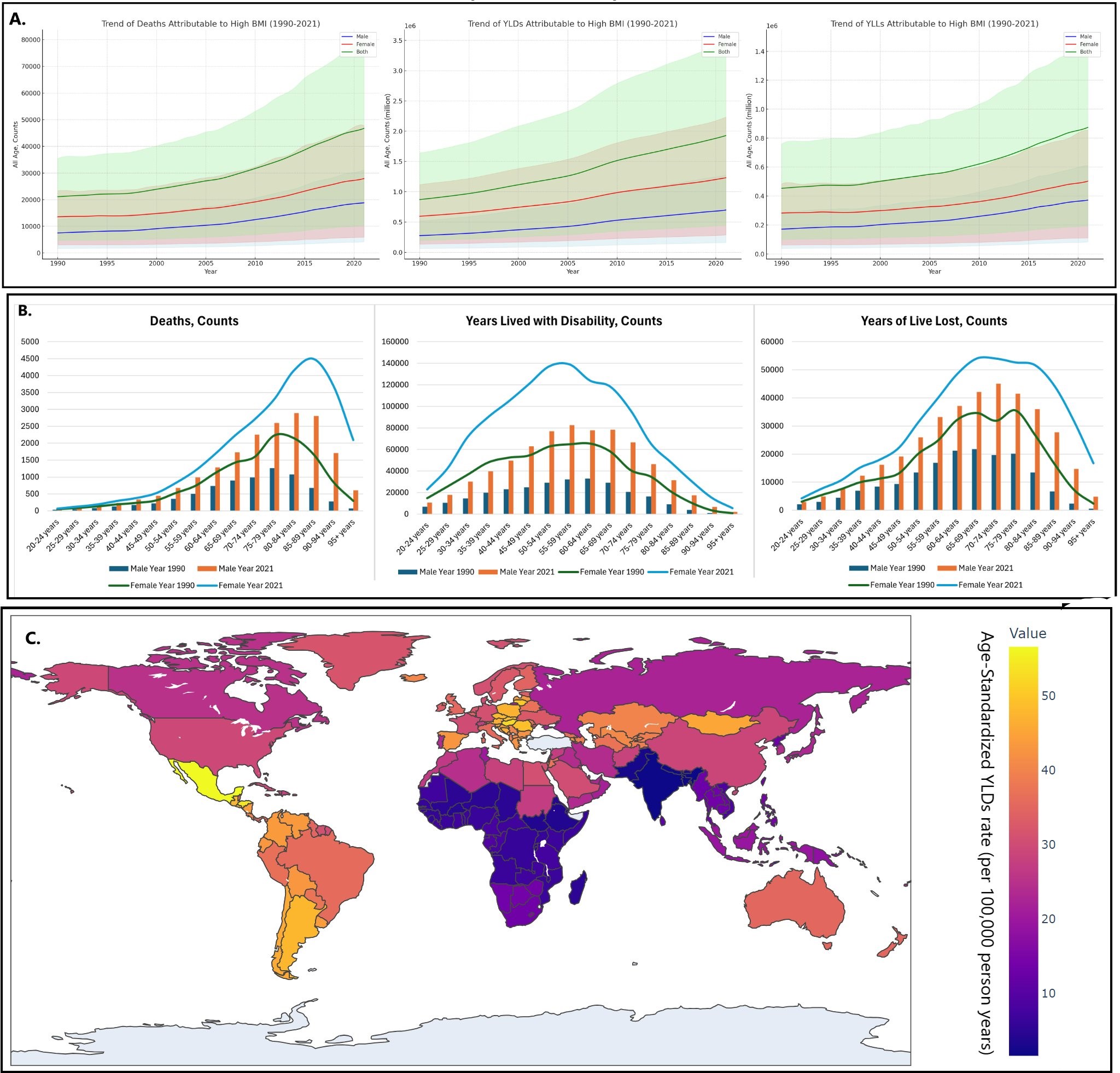
Results: The total number of deaths increased from 21,102 (95% Uncertainty Interval: 4,725-35,435) in 1990 to 46,715 (10,268-79,843) in 2021. Regionally, Central sub-Saharan Africa saw the largest increase in the total percentage change (TPC) in age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), with a 69% rise from 1999-2021. East Asia experienced the most significant rise in age-standardized YLDs rate (ASYLDR), with a 76% increase in TPC. Socio-demographically, the highest TPC in ASMR was observed in low Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) countries at 31%, followed by a 38% increase in ASYLDR in middle SDI countries. Nationally, Greece recorded the highest TPC in ASMR at 143%, followed by the United Kingdom at 125%. Age-wise, individuals aged 20-54 years accounted for 4,219 deaths, while those aged 55 and above accounted for 42,396 deaths in 2021. In terms of gender, males exhibited a higher increase in burden with a TPC in deaths of 150% compared to females at 105%, and in YLDs at 153% versus 107%, and YLLs at 117% versus 78% from 1990-2021.
Discussion: Deaths due to GBD attributable to HBMI accounted for 35.63% of all GBD related casualties in 2021. This rising burden underscores the urgent need for public health interventions and policymaker action. Preventative strategies are crucial, as they are more effective than treatment. The adoption of e-health and m-health initiatives is vital to educate the public and promote healthier lifestyle choices, helping to curb the increasing trend in HBMI-related health issues.
Disclosures:
George Mathew Mukalil, MD1, Akhilesh Sharma, MBBS2, Asmita Gera, MBBS3, Abobakr Saleh, MBBS4, Amit Banerjee, MBBS5, Shadi Abuhashem, MD6, Bhargav Koyani, MD7, Pragathi Munnangi, MBBS8, Rani Ratheesh, MD9, Lalitkumar Patel, MBBS10, Gunjan Kochhar, MBBS11, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS12, Tanvi Koduru, BS13, Himanshu Koyani, MBBS, MS14. P1748 - Nationwide Burden and Trend of Gallbladder and Biliary Disease Attributable to High BMI in the Last 3 Decades: Secondary Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI; 2Adesh Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Bathinda, Punjab, India; 3Tianjin Medical University, Tianijin, Tianjin, China; 4Kasr Alainy Medical School, Cairo University, Cairo, Al Bahr al Ahmar, Egypt; 5Stanley Medical College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 6Alquds University, Gaza, Palestinian Territories; 7Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, Evanston, IL; 8N.R.I Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 9Dr. MGR Medical University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 10Suburban Medical Center, Schaumburg, IL; 11Punjab Institute of Medical Sciences, Jalandhar, Punjab, India; 12Gujarat Adani Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 13Bergen Community College, Paramus, NJ; 14Sterling Hospital, Rajkot, Gujarat, India
Introduction: The global obesity epidemic has profound implications for public health, with an estimated 650 million adults classified as obese worldwide as per World Health Organization (WHO) 2021 data. The global rise in obesity rates correlates with increased morbidity from various non-communicable diseases. Despite this growing recognition, comprehensive analyses quantifying the burden of gallbladder and biliary diseases (GBD) attributable to high body-mass index (BMI) across different global regions remain sparse.
Methods: Using Global Burden of Disease 2021 tool, We estimated deaths, years lived with disability (YLDs), years of life lost (YLL) by age, sex, year and location due to GBD attributable to HBMI in 204 Countries and territories from 1990-2021. Results were presented in absolute counts and age-standardized rate (per 100,000 person years).
Results: The total number of deaths increased from 21,102 (95% Uncertainty Interval: 4,725-35,435) in 1990 to 46,715 (10,268-79,843) in 2021. Regionally, Central sub-Saharan Africa saw the largest increase in the total percentage change (TPC) in age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), with a 69% rise from 1999-2021. East Asia experienced the most significant rise in age-standardized YLDs rate (ASYLDR), with a 76% increase in TPC. Socio-demographically, the highest TPC in ASMR was observed in low Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) countries at 31%, followed by a 38% increase in ASYLDR in middle SDI countries. Nationally, Greece recorded the highest TPC in ASMR at 143%, followed by the United Kingdom at 125%. Age-wise, individuals aged 20-54 years accounted for 4,219 deaths, while those aged 55 and above accounted for 42,396 deaths in 2021. In terms of gender, males exhibited a higher increase in burden with a TPC in deaths of 150% compared to females at 105%, and in YLDs at 153% versus 107%, and YLLs at 117% versus 78% from 1990-2021.
Discussion: Deaths due to GBD attributable to HBMI accounted for 35.63% of all GBD related casualties in 2021. This rising burden underscores the urgent need for public health interventions and policymaker action. Preventative strategies are crucial, as they are more effective than treatment. The adoption of e-health and m-health initiatives is vital to educate the public and promote healthier lifestyle choices, helping to curb the increasing trend in HBMI-related health issues.

Figure: A: Global Trend of Gallbladder and Biliary Disease Attributable to High BMI in 204 Countries and Territories from 1990-2021, B: Age-Wise Distribution of Gallbladder and Biliary Disease Attributable to High BMI in 204 Countries and Territories in year 1990 and 2021, C: Age-Standardized YLDs Rate due to Gallbladder and Biliary Disease Attributable to High BMI in 204 Countries and Territories in 2021
Disclosures:
George Mathew Mukalil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akhilesh Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asmita Gera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abobakr Saleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amit Banerjee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shadi Abuhashem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhargav Koyani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pragathi Munnangi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rani Ratheesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lalitkumar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gunjan Kochhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hardik Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanvi Koduru indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Himanshu Koyani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
George Mathew Mukalil, MD1, Akhilesh Sharma, MBBS2, Asmita Gera, MBBS3, Abobakr Saleh, MBBS4, Amit Banerjee, MBBS5, Shadi Abuhashem, MD6, Bhargav Koyani, MD7, Pragathi Munnangi, MBBS8, Rani Ratheesh, MD9, Lalitkumar Patel, MBBS10, Gunjan Kochhar, MBBS11, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS12, Tanvi Koduru, BS13, Himanshu Koyani, MBBS, MS14. P1748 - Nationwide Burden and Trend of Gallbladder and Biliary Disease Attributable to High BMI in the Last 3 Decades: Secondary Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
