Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1759 - EUS-Guided Needle-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (nCLE) for Dysplasia Classification in IPMNs: Assessment of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms to Reduce Interobserver Variability
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ahmed RM Abdelbaki, MBBCh
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Li Ziwei, 2, Wei-Lun chao, PhD2, Stacey Culp, PhD3, Phil Hart, MD1, Jordan Burlen, MD1, Samer Eldika, MD4, Helga Bertani, 5, Yunlu Feng, 6, Geri keane, MBBS7, Tara Keihanian, MD8, Antonio Ladd, MD9, Pradermchai Kongkam, 10, Sarah Leblanc, 11, Anjuli Luthra, MD12, Jorge D. Machicado, MD13, Shaffer Mok, MD12, Thiruvengadam Muniraj, MD14, Bertrand Napoléon, 15, Damien Tan, 16, Kavel H. Visrodia, MD17, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH; 3Ohio State University, Columbus, OH; 4Stanford Health Care, Palo Alto, CA; 5Baggiovara Hospital, Modena, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; 6Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China; 7Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Washington, WA; 8Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 9University of California Davis, Albuquerque, NM; 10King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Buriram, Thailand; 11Cochin Hospital, Paris, Bourgogne, France; 12Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL; 13University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, MI; 14Yale New Haven Health, New Haven, CT; 15Hôpital Privé Jean Mermoz, Lyon, Bretagne, France; 16Singapore General Hospital, Central Region, Singapore; 17New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Introduction: EUS-nCLE enables real-time in vivo visualization of papillae for risk stratification of IPMNs, but interobserver agreement (IOA) is a limitation. We have developed a fully functional nCLE-based AI algorithm to detect high-grade dysplasia/invasive adenocarcinoma (HGD-IC) in branch duct (BD)-IPMNs. We compared the performance of nCLE-based dysplasia classification of BD-IPMNs between an expert panel of EUS-nCLE users and an improved nCLE-AI algorithm.
Methods: We selected consecutive IPMNs with definitive diagnoses from prospective studies (2015-2023) evaluating EUS-guided nCLE for the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts.
IOA study: An international panel of 16 blinded interventional endoscopists reviewed full-length, unedited nCLE videos to classify dysplasia.
AI assessment: A fully functional two-stage AI model was used: Stage 1 selected high-yield frames, and Stage 2 extracted nCLE features for risk stratification.
Comparisons: The diagnostic parameters of the observers and the nCLE-AI algorithm were compared to the Kyoto guidelines’ high-risk criteria (HRC).
Results: Among 60 IPMNs (HGD-IC: 23), the mean size was 3.43±1.00 cm and mean age of subjects was 68.2±9.0 years. In the observer group (n=16; 960 classifications), the mean sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of HGD-IC were 58%, 59%, and 59%, respectively (Table 1). The interobserver agreement (IOA) was ‘fair’; κ=0.29 (95%CI: 0.27–0.32).
For the fully functional nCLE-AI algorithm, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for detecting HGD-IC were 78%, 70%, and 73%, respectively. To detect HGD-IC, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of Kyoto-HRC was 57%, 95%, and 80%, respectively (Table 1).
Discussion: The issue of suboptimal interobserver agreement among experts in classifying HGD-IC using nCLE imaging is resolved by introducing an nCLE-AI algorithm that does not rely on human interpretation. In this cohort, the nCLE-AI demonstrated superior sensitivity compared to the Kyoto-HRC for IPMN dysplasia classification while maintaining similar accuracy. Given the inherent ability of AI to improve with larger datasets, the algorithm's (nCLE-AI) accuracy and the validation of these findings would benefit from further refinement using extensive, real-time imaging data.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Li Ziwei, 2, Wei-Lun chao, PhD2, Stacey Culp, PhD3, Phil Hart, MD1, Jordan Burlen, MD1, Samer Eldika, MD4, Helga Bertani, 5, Yunlu Feng, 6, Geri keane, MBBS7, Tara Keihanian, MD8, Antonio Ladd, MD9, Pradermchai Kongkam, 10, Sarah Leblanc, 11, Anjuli Luthra, MD12, Jorge D. Machicado, MD13, Shaffer Mok, MD12, Thiruvengadam Muniraj, MD14, Bertrand Napoléon, 15, Damien Tan, 16, Kavel H. Visrodia, MD17, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1. P1759 - EUS-Guided Needle-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (nCLE) for Dysplasia Classification in IPMNs: Assessment of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms to Reduce Interobserver Variability, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH; 3Ohio State University, Columbus, OH; 4Stanford Health Care, Palo Alto, CA; 5Baggiovara Hospital, Modena, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; 6Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China; 7Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Washington, WA; 8Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 9University of California Davis, Albuquerque, NM; 10King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Buriram, Thailand; 11Cochin Hospital, Paris, Bourgogne, France; 12Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL; 13University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, MI; 14Yale New Haven Health, New Haven, CT; 15Hôpital Privé Jean Mermoz, Lyon, Bretagne, France; 16Singapore General Hospital, Central Region, Singapore; 17New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Introduction: EUS-nCLE enables real-time in vivo visualization of papillae for risk stratification of IPMNs, but interobserver agreement (IOA) is a limitation. We have developed a fully functional nCLE-based AI algorithm to detect high-grade dysplasia/invasive adenocarcinoma (HGD-IC) in branch duct (BD)-IPMNs. We compared the performance of nCLE-based dysplasia classification of BD-IPMNs between an expert panel of EUS-nCLE users and an improved nCLE-AI algorithm.
Methods: We selected consecutive IPMNs with definitive diagnoses from prospective studies (2015-2023) evaluating EUS-guided nCLE for the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts.
IOA study: An international panel of 16 blinded interventional endoscopists reviewed full-length, unedited nCLE videos to classify dysplasia.
AI assessment: A fully functional two-stage AI model was used: Stage 1 selected high-yield frames, and Stage 2 extracted nCLE features for risk stratification.
Comparisons: The diagnostic parameters of the observers and the nCLE-AI algorithm were compared to the Kyoto guidelines’ high-risk criteria (HRC).
Results: Among 60 IPMNs (HGD-IC: 23), the mean size was 3.43±1.00 cm and mean age of subjects was 68.2±9.0 years. In the observer group (n=16; 960 classifications), the mean sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of HGD-IC were 58%, 59%, and 59%, respectively (Table 1). The interobserver agreement (IOA) was ‘fair’; κ=0.29 (95%CI: 0.27–0.32).
For the fully functional nCLE-AI algorithm, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for detecting HGD-IC were 78%, 70%, and 73%, respectively. To detect HGD-IC, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of Kyoto-HRC was 57%, 95%, and 80%, respectively (Table 1).
Discussion: The issue of suboptimal interobserver agreement among experts in classifying HGD-IC using nCLE imaging is resolved by introducing an nCLE-AI algorithm that does not rely on human interpretation. In this cohort, the nCLE-AI demonstrated superior sensitivity compared to the Kyoto-HRC for IPMN dysplasia classification while maintaining similar accuracy. Given the inherent ability of AI to improve with larger datasets, the algorithm's (nCLE-AI) accuracy and the validation of these findings would benefit from further refinement using extensive, real-time imaging data.

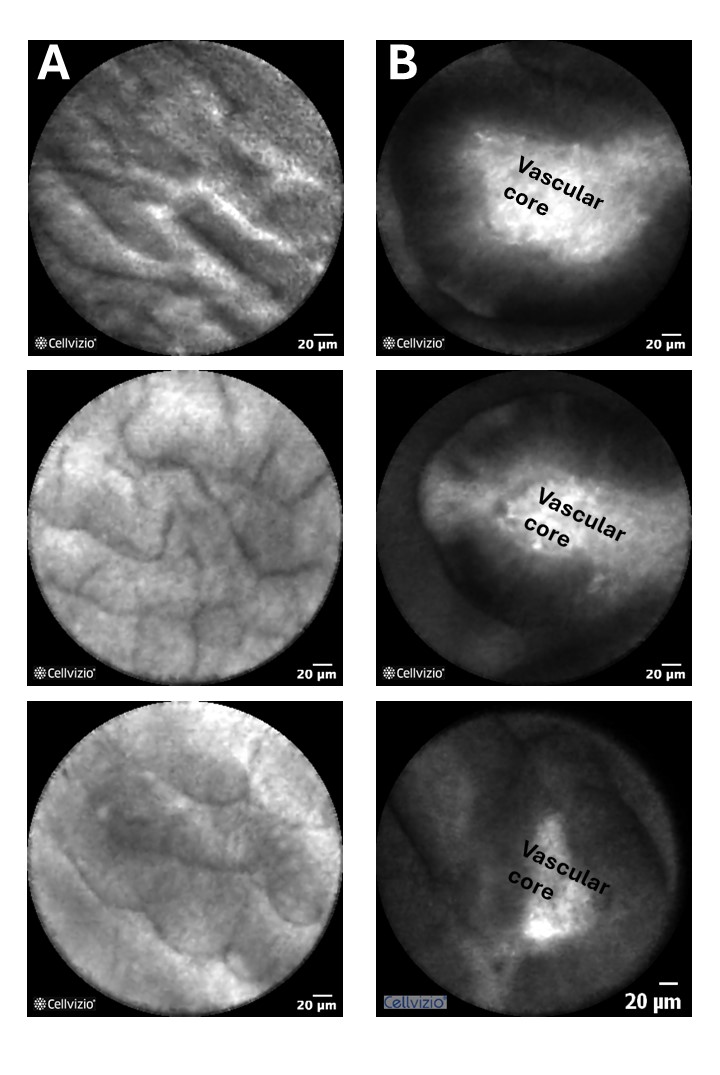
Figure: A) IPMN with low-grade dysplasia: nCLE showing thin, flat epithelium without nuclear or cellular stratification. (B) IPMN with high-grade dysplasia showing large papilla with thick and dark epithelium due to nuclear stratification.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ahmed Abdelbaki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Li Ziwei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wei-Lun chao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stacey Culp indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phil Hart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Burlen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samer Eldika indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Helga Bertani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yunlu Feng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Geri keane indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tara Keihanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antonio Ladd indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pradermchai Kongkam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Leblanc indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjuli Luthra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jorge Machicado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaffer Mok: C2/Pentax – Consultant. Steris – Consultant.
Thiruvengadam Muniraj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bertrand Napoléon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Damien Tan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kavel Visrodia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somashekar G Krishna: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Mauna Kea Technologies, and TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support. TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support.
Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Li Ziwei, 2, Wei-Lun chao, PhD2, Stacey Culp, PhD3, Phil Hart, MD1, Jordan Burlen, MD1, Samer Eldika, MD4, Helga Bertani, 5, Yunlu Feng, 6, Geri keane, MBBS7, Tara Keihanian, MD8, Antonio Ladd, MD9, Pradermchai Kongkam, 10, Sarah Leblanc, 11, Anjuli Luthra, MD12, Jorge D. Machicado, MD13, Shaffer Mok, MD12, Thiruvengadam Muniraj, MD14, Bertrand Napoléon, 15, Damien Tan, 16, Kavel H. Visrodia, MD17, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1. P1759 - EUS-Guided Needle-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (nCLE) for Dysplasia Classification in IPMNs: Assessment of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms to Reduce Interobserver Variability, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
