Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1845 - A Case of Food Reflux Recurrent Cholangitis in a Patient With a Duodenal Deformity in the Setting of a Newly Diagnosed Distal Cholangiocarcinoma.
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ren C. Bryant, DO
University of Kentucky College of Medicine
Lexington, KY
Presenting Author(s)
Ren C. Bryant, DO1, Ujas Patel, MD2, Houssam Mardini, MD1
1University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, KY; 2University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY
Introduction: Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare malignancy that occurs within three defined regions of the biliary system; intrahepatic, perihilar, and the distal bile duct. Distal cholangiocarcinoma (dCCA) has a poor prognosis and a higher rate of recurrence [3] Some causes of acute cholangitis include choledocholithiasis, benign and malignant biliary stricture, and parasites. Structural deformity in the duodenum from malignant dCCA with resultant slow food passage causing food reflux into common bile duct (CBD) is a rare etiology of acute cholangitis. We highlight a case here of a patient with such deformity needing frequent ERCP for stent exchanges before definitive surgery for his duodenal deformity from malignant invasion.
Case Description/Methods: This is a case of a 60-year-old male presenting with classic symptoms for acute cholangitis; fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain. The patient underwent Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and was found to have CBD dilation and pericholecystic fluid without evidence of gallstones. The patient continued to have recurrent cholangitis with multiple ERCP’s with negative biopsies and even to have klebsiella bacteremia. Following this the patient underwent 4 additional ERCP’s with stent exchange and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy with improvement of biliary strictures. The patient would again present with symptoms of acute cholangitis and was found to have a distal structure. The biopsy was positive for dCCA. This was causing food reflux into the CBD due to the anatomical variant. Lab test showed an elevation of carbohydrate antigen 19-9(CA 19-9) at that time. Patient would undergo neoadjuvent immunotherapy with surgical intervention for treatment.
Discussion: Distal cholangiocarcinoma comprises around 20-30% of biliary cholangiocarcinoma with the most common cholangiocarcinoma is found proximal. In our patient, the food reflux was coming from a deformity in the 3rd part of the duodenum from malignant invasion creating an anatomical variant that predisposed him to recurrent cholangitis. While ERCP is a great tool to use for the evaluation of malignant strictures, ERCP guided interventions for indeterminate biliary strictures has a sensitivity of 45% for brushings, 48% for biopsies, and 59% for the combination. Per our literary review, there is a lack of literature for food reflux related cholangitis, and it is important to consider it on the differential for cholangiocarcinoma patients with acute cholangitis.
Disclosures:
Ren C. Bryant, DO1, Ujas Patel, MD2, Houssam Mardini, MD1. P1845 - A Case of Food Reflux Recurrent Cholangitis in a Patient With a Duodenal Deformity in the Setting of a Newly Diagnosed Distal Cholangiocarcinoma., ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, KY; 2University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY
Introduction: Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare malignancy that occurs within three defined regions of the biliary system; intrahepatic, perihilar, and the distal bile duct. Distal cholangiocarcinoma (dCCA) has a poor prognosis and a higher rate of recurrence [3] Some causes of acute cholangitis include choledocholithiasis, benign and malignant biliary stricture, and parasites. Structural deformity in the duodenum from malignant dCCA with resultant slow food passage causing food reflux into common bile duct (CBD) is a rare etiology of acute cholangitis. We highlight a case here of a patient with such deformity needing frequent ERCP for stent exchanges before definitive surgery for his duodenal deformity from malignant invasion.
Case Description/Methods: This is a case of a 60-year-old male presenting with classic symptoms for acute cholangitis; fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain. The patient underwent Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and was found to have CBD dilation and pericholecystic fluid without evidence of gallstones. The patient continued to have recurrent cholangitis with multiple ERCP’s with negative biopsies and even to have klebsiella bacteremia. Following this the patient underwent 4 additional ERCP’s with stent exchange and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy with improvement of biliary strictures. The patient would again present with symptoms of acute cholangitis and was found to have a distal structure. The biopsy was positive for dCCA. This was causing food reflux into the CBD due to the anatomical variant. Lab test showed an elevation of carbohydrate antigen 19-9(CA 19-9) at that time. Patient would undergo neoadjuvent immunotherapy with surgical intervention for treatment.
Discussion: Distal cholangiocarcinoma comprises around 20-30% of biliary cholangiocarcinoma with the most common cholangiocarcinoma is found proximal. In our patient, the food reflux was coming from a deformity in the 3rd part of the duodenum from malignant invasion creating an anatomical variant that predisposed him to recurrent cholangitis. While ERCP is a great tool to use for the evaluation of malignant strictures, ERCP guided interventions for indeterminate biliary strictures has a sensitivity of 45% for brushings, 48% for biopsies, and 59% for the combination. Per our literary review, there is a lack of literature for food reflux related cholangitis, and it is important to consider it on the differential for cholangiocarcinoma patients with acute cholangitis.

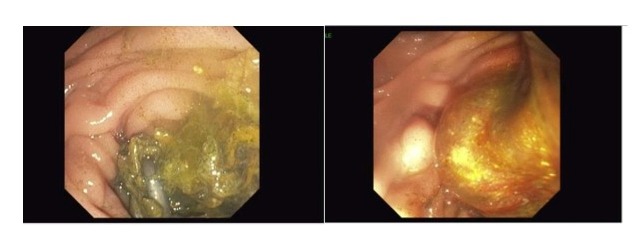
Figure: Left-multiple double pigtail stents at the ampulla with significant occlusion from food debris, Right- ERCP with balloon sweep of CBD resulting in expression of food particles from the duct.
Disclosures:
Ren Bryant indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ujas Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Houssam Mardini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ren C. Bryant, DO1, Ujas Patel, MD2, Houssam Mardini, MD1. P1845 - A Case of Food Reflux Recurrent Cholangitis in a Patient With a Duodenal Deformity in the Setting of a Newly Diagnosed Distal Cholangiocarcinoma., ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
