Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P1976 - Looking Beyond the Surface: An Exceedingly Rare Presentation of Metastatic Cutaneous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- AB
Ali Bilal, MD
University of Texas Medical Branch
Galveston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Ali Bilal, MD1, Kevin Pham, DO1, Jacqueline Ochoa, MPH2, Chance Winters, BS3, Aisha Cantu, BS3, Brinda Chellappan, MD1, Patrick Sweet, DO1, Leah Low, MD1
1University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 2University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy School of Medicine, Galveston, TX; 3John Sealy School of Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Introduction: A literature review shows cutaneous metastases of colorectal cancer are uncommon, manifesting in about 4-6 percent of patients. We report a patient who presented with metastatic cancer of unknown primary but was also incidentally found to have a scalp lesion. While it was initially presumed to be a common skin cancer, biopsy revealed it to be a cutaneous metastasis of colonic adenocarcinoma.
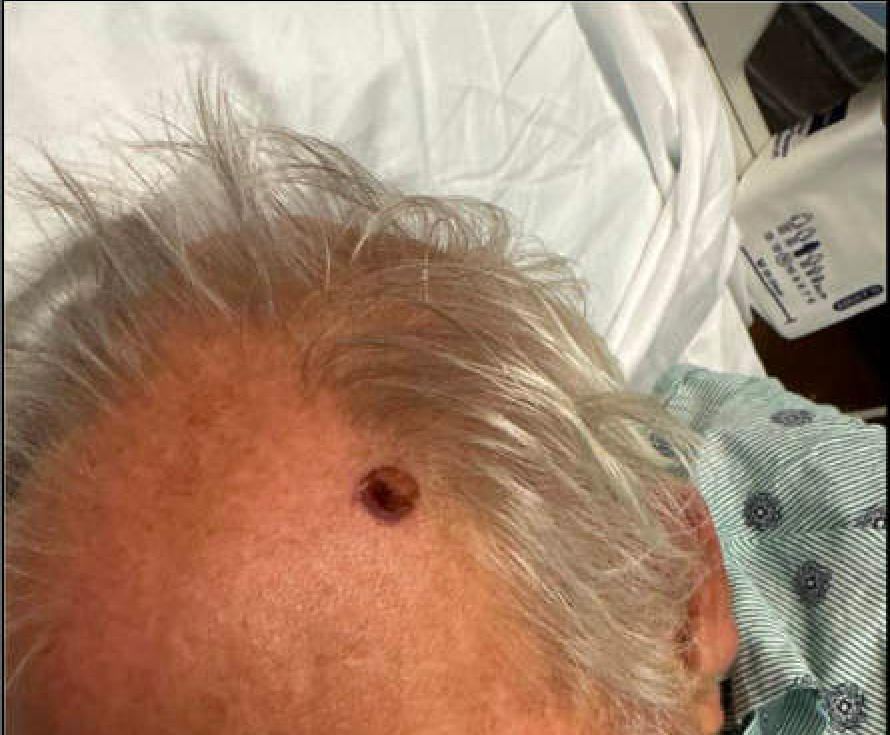
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old male with a history of prostate cancer status post complete prostatectomy presented with a three-week history of worsening lower back pain, bilateral lower extremity weakness, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Exam also showed a 1.3 cm by 1.2 cm nodule on the left frontal scalp. Imaging revealed L2, L4, and L5 compression fractures with retropulsion. A CT abdomen/pelvis revealed metastatic tumor burden. With the initial diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma, the patient underwent a skin biopsy. Preliminary pathology showed cutaneous metastasis of adenocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining, which was positive for CK20 and CDX2 and negative for NKX3.1 and CK7, confirmed the skin lesion to be a cutaneous metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Due to extensive tumor burden and clinical deterioration, the patient elected for hospice care.
Discussion: In females, the most common primary cancers with cutaneous metastasis are breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and melanoma. In males, these include lung cancer, melanoma, and colorectal cancer. Given that cutaneous metastases tend to affect sites near the primary tumor, with colorectal lesions primarily localized to the abdomen, our case highlights the need for clinicians to thoroughly evaluate any suspicious skin lesions in patients, particularly those with a prior history of malignancy. Furthermore, because the diagnosis of metastatic cutaneous findings is associated with an average survival rate of 18 months and cutaneous manifestations can occur two years after diagnosis of the primary tumor, screening techniques and the expansion of contemporary literature emphasize the importance of early detection. Therefore, early identification of these lesions is crucial for accurate diagnosis, proper management, and improved prognosis.
Disclosures:
Ali Bilal, MD1, Kevin Pham, DO1, Jacqueline Ochoa, MPH2, Chance Winters, BS3, Aisha Cantu, BS3, Brinda Chellappan, MD1, Patrick Sweet, DO1, Leah Low, MD1. P1976 - Looking Beyond the Surface: An Exceedingly Rare Presentation of Metastatic Cutaneous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Ali Bilal, MD1, Kevin Pham, DO1, Jacqueline Ochoa, MPH2, Chance Winters, BS3, Aisha Cantu, BS3, Brinda Chellappan, MD1, Patrick Sweet, DO1, Leah Low, MD1
1University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 2University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy School of Medicine, Galveston, TX; 3John Sealy School of Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Introduction: A literature review shows cutaneous metastases of colorectal cancer are uncommon, manifesting in about 4-6 percent of patients. We report a patient who presented with metastatic cancer of unknown primary but was also incidentally found to have a scalp lesion. While it was initially presumed to be a common skin cancer, biopsy revealed it to be a cutaneous metastasis of colonic adenocarcinoma.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old male with a history of prostate cancer status post complete prostatectomy presented with a three-week history of worsening lower back pain, bilateral lower extremity weakness, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Exam also showed a 1.3 cm by 1.2 cm nodule on the left frontal scalp. Imaging revealed L2, L4, and L5 compression fractures with retropulsion. A CT abdomen/pelvis revealed metastatic tumor burden. With the initial diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma, the patient underwent a skin biopsy. Preliminary pathology showed cutaneous metastasis of adenocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining, which was positive for CK20 and CDX2 and negative for NKX3.1 and CK7, confirmed the skin lesion to be a cutaneous metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Due to extensive tumor burden and clinical deterioration, the patient elected for hospice care.
Discussion: In females, the most common primary cancers with cutaneous metastasis are breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and melanoma. In males, these include lung cancer, melanoma, and colorectal cancer. Given that cutaneous metastases tend to affect sites near the primary tumor, with colorectal lesions primarily localized to the abdomen, our case highlights the need for clinicians to thoroughly evaluate any suspicious skin lesions in patients, particularly those with a prior history of malignancy. Furthermore, because the diagnosis of metastatic cutaneous findings is associated with an average survival rate of 18 months and cutaneous manifestations can occur two years after diagnosis of the primary tumor, screening techniques and the expansion of contemporary literature emphasize the importance of early detection. Therefore, early identification of these lesions is crucial for accurate diagnosis, proper management, and improved prognosis.

Figure: 1.3 cm by 1.2 cm erythematous nodule with collarette of scale and hemorrhagic crust on the left frontal scalp
Disclosures:
Ali Bilal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Pham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacqueline Ochoa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chance Winters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aisha Cantu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brinda Chellappan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patrick Sweet indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leah Low indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Bilal, MD1, Kevin Pham, DO1, Jacqueline Ochoa, MPH2, Chance Winters, BS3, Aisha Cantu, BS3, Brinda Chellappan, MD1, Patrick Sweet, DO1, Leah Low, MD1. P1976 - Looking Beyond the Surface: An Exceedingly Rare Presentation of Metastatic Cutaneous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

