Monday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P2119 - Next Generation mt-sDNA Has the Best Balance Between the Benefit and Burden of the Age- and Interval-Recommended CRC Screening Among Stool- and Blood-Based Tests
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD
Exact Sciences
Lake Forest, IL
Presenting Author(s)
John B. Kisiel, MD1, Derek W. Ebner, MD1, A. Mark Fendrick, MD2, Chris Estes, MPH3, Vahab Vahdat, PhD3, A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD4, Paul Limburg, MD, MPH5
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI; 3Exact Sciences, Madison, WI; 4Exact Sciences, Lake Forest, IL; 5Exact Sciences, Rochester, MN
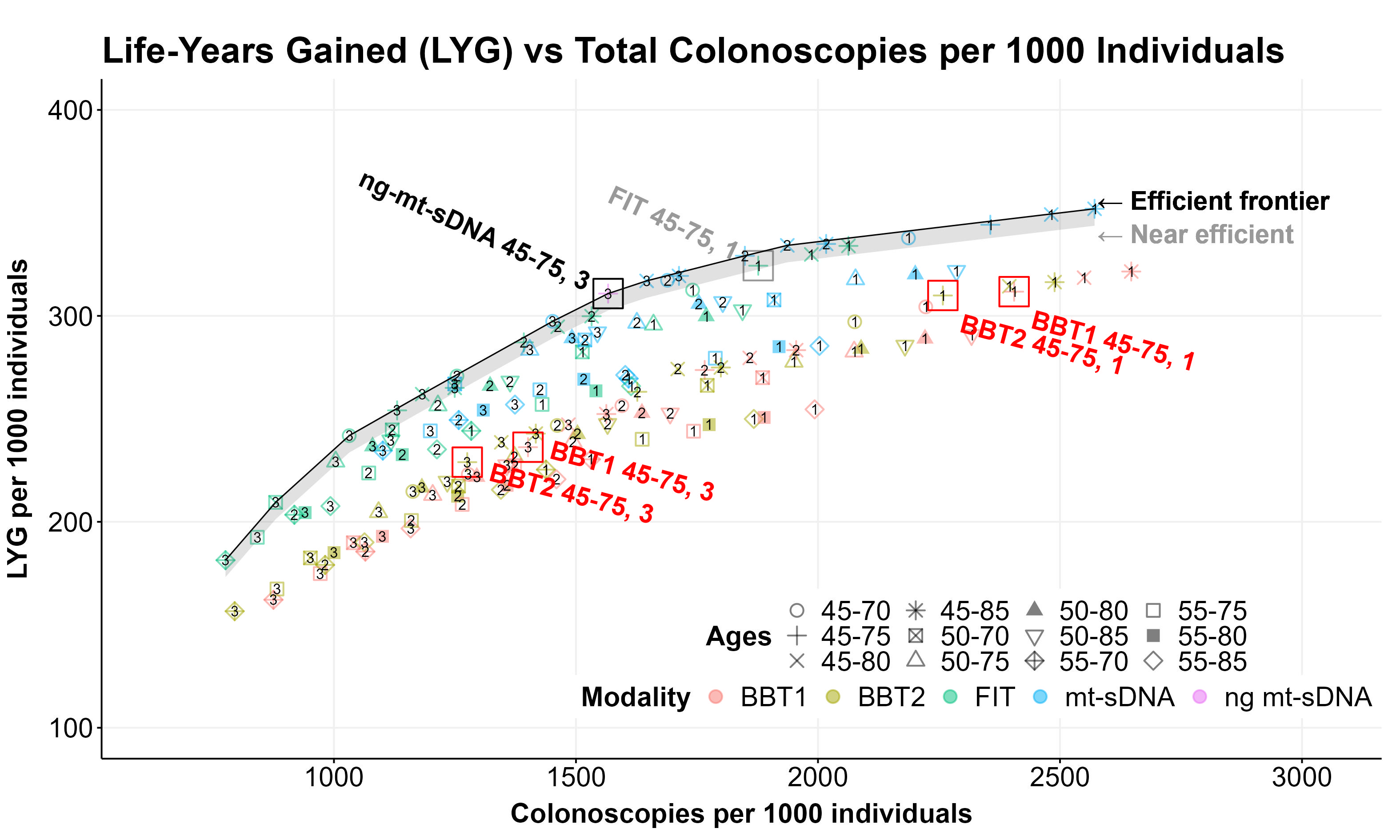
Introduction: Average-risk colorectal cancer (CRC) screening guidelines include multiple options, including the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and multi-target stool DNA (mt-sDNA) test. Recent clinical studies have reported data for emerging blood-based CRC screening tests (ECLIPSE and PREMPT CRC studies), as well as a next-generation mt-sDNA test (ng-mt-sDNA; BLUE-C study). To predict and compare the effectiveness of these tests, we conducted a microsimulation modeling study to generate an efficiency frontier, assessing the benefit-to-burden ratio of screening strategies using life-years gained (LYG) and total colonoscopies (COL) as proxies for benefit and burden, respectively.
Methods: Screening with stool- or blood-based tests at 1-, 2-, or 3-year intervals was simulated for average-risk adults using the validated CRC-AIM model with varied screening start ages (45, 50, or 55 years) and end ages (70, 75, 80, and 85 years). CRC screening sensitivity and specificity inputs were derived from the BLUE-C (FIT, ng-mt-sDNA test), ECLIPSE (BBT1) and PREEMPT CRC (BBT2) studies. To estimate the maximum benefits and burden achievable, adherence to initial screening and follow-up COL after a positive screening test were modeled at 100%. LYG and total lifetime COL per 1000 individuals for each strategy were plotted to generate the efficient frontier. Per established definitions,1 efficient strategies were on the efficient frontier and near-efficient strategies were within 3 days of LYG per person of the efficient frontier.
1. Knudsen AB, et al. U.S. Colorectal Cancer Screening: An Updated Decision Analysis for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021.
Results: For the recommended screening age of 45-75 years, biennial and triennial ng-mt-sDNA were efficient whereas annual ng-mt-sDNA was near-efficient (Figure). FIT at any interval was near-efficient. The blood-based tests were not efficient or near-efficient at any combination of interval and age range.
Discussion: The ng-mt-sDNA test was the only efficient modality for screening over the guideline-recommended age interval of 45-75 years. Blood-based screening strategies were not efficient, implying consideration as second line options for average-risk CRC screening.
Disclosures:
John B. Kisiel, MD1, Derek W. Ebner, MD1, A. Mark Fendrick, MD2, Chris Estes, MPH3, Vahab Vahdat, PhD3, A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD4, Paul Limburg, MD, MPH5. P2119 - Next Generation mt-sDNA Has the Best Balance Between the Benefit and Burden of the Age- and Interval-Recommended CRC Screening Among Stool- and Blood-Based Tests, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI; 3Exact Sciences, Madison, WI; 4Exact Sciences, Lake Forest, IL; 5Exact Sciences, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Average-risk colorectal cancer (CRC) screening guidelines include multiple options, including the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and multi-target stool DNA (mt-sDNA) test. Recent clinical studies have reported data for emerging blood-based CRC screening tests (ECLIPSE and PREMPT CRC studies), as well as a next-generation mt-sDNA test (ng-mt-sDNA; BLUE-C study). To predict and compare the effectiveness of these tests, we conducted a microsimulation modeling study to generate an efficiency frontier, assessing the benefit-to-burden ratio of screening strategies using life-years gained (LYG) and total colonoscopies (COL) as proxies for benefit and burden, respectively.
Methods: Screening with stool- or blood-based tests at 1-, 2-, or 3-year intervals was simulated for average-risk adults using the validated CRC-AIM model with varied screening start ages (45, 50, or 55 years) and end ages (70, 75, 80, and 85 years). CRC screening sensitivity and specificity inputs were derived from the BLUE-C (FIT, ng-mt-sDNA test), ECLIPSE (BBT1) and PREEMPT CRC (BBT2) studies. To estimate the maximum benefits and burden achievable, adherence to initial screening and follow-up COL after a positive screening test were modeled at 100%. LYG and total lifetime COL per 1000 individuals for each strategy were plotted to generate the efficient frontier. Per established definitions,1 efficient strategies were on the efficient frontier and near-efficient strategies were within 3 days of LYG per person of the efficient frontier.
1. Knudsen AB, et al. U.S. Colorectal Cancer Screening: An Updated Decision Analysis for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021.
Results: For the recommended screening age of 45-75 years, biennial and triennial ng-mt-sDNA were efficient whereas annual ng-mt-sDNA was near-efficient (Figure). FIT at any interval was near-efficient. The blood-based tests were not efficient or near-efficient at any combination of interval and age range.
Discussion: The ng-mt-sDNA test was the only efficient modality for screening over the guideline-recommended age interval of 45-75 years. Blood-based screening strategies were not efficient, implying consideration as second line options for average-risk CRC screening.

Figure: Figure. Efficient frontier of CRC screening strategies. Strategies are considered efficient if on the line, near efficient if within gray bound, and not efficient otherwise.
Disclosures:
John Kisiel: Exact Sciences – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Intellectual Property/Patents, all paid to Mayo Clinic, Royalties.
Derek Ebner: Exact Sciences – Consultant, Independent Contractor.
A. Mark Fendrick: AbbVie – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. Arnold Ventures – Grant/Research Support. Centivo – Consultant. Community Oncology Association – Consultant. Covered California – Consultant. EmblemHealth – Consultant. Exact Sciences – Consultant. Freedman Health – Consultant. Gary and Mary West Health Policy Center – Grant/Research Support. GRAIL – Consultant. Harvard University – Consultant. Health & Wellness Innovations – Consultant. Health at Scale Technologies – Consultant. MedZed – Consultant. National Pharmaceutical Council – Grant/Research Support. Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute – Grant/Research Support. Penguin Pay – Consultant. Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America – Grant/Research Support. Risalto – Consultant. Sempre Health – Consultant. the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality – Grant/Research Support. the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services – Grant/Research Support. the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation – Grant/Research Support. the State of Michigan – Grant/Research Support. the State of Minnesota – Consultant. U.S. Department of Defense – Consultant. Virginia Center for Health Innovation – Consultant. Wellthy – Consultant. Zansors – Consultant.
Chris Estes: Exact Sciences – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Vahab Vahdat: Exact Sciences – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
A. Burak Ozbay: Exact Sciences – Employee, Stock Options.
Paul Limburg: Exact Sciences Corporation – Consultant, Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
John B. Kisiel, MD1, Derek W. Ebner, MD1, A. Mark Fendrick, MD2, Chris Estes, MPH3, Vahab Vahdat, PhD3, A. Burak Ozbay, MBA, PhD4, Paul Limburg, MD, MPH5. P2119 - Next Generation mt-sDNA Has the Best Balance Between the Benefit and Burden of the Age- and Interval-Recommended CRC Screening Among Stool- and Blood-Based Tests, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
