Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2211 - An Observational Retrospective Cohort Study using PPI, Aspirin, Pyridoxine, and Folic Acid therapy for Non-Dysplastic Barrett’s Esophagus
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

GianPaolo Piccione, DO
Richmond University Medical Center
Staten Island, NY
Presenting Author(s)
GianPaolo Piccione, DO, James Ducey, MD, Inderbir Padda, MD, Paul Karroum, MD, Prassanna Wickremensinghe, MD, Svetoslav Badarov, MD
Richmond University Medical Center, Staten Island, NY
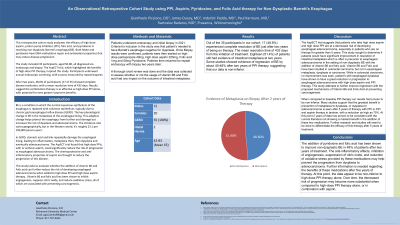
Introduction: This retrospective cohort study aims to evaluate the efficacy of high-dose aspirin, high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI), folic acid therapy, and pyridoxine in the resolution of non-dysplastic Barrett's esophagus. Both folate and pyridoxine have shown to have DNA methylation repair and anti-oxidant properties to minimize the progression of Barret’s esophagus.
Methods: Our study includes 35 participants, comprising both males and females aged 50-80 years. Participants in this study were treated with high-dose aspirin, high-dose PPI, folic acid and pyridoxine in the diagnosis of Barrett’s was confirmed on endoscopy and biopsy. The ASPECT trial, was used as the benchmark and inspiration for this study given the similar treatment modalities used. The ASPECT trial demonstrated the potential benefit of high-dose PPI therapy, with or without aspirin, in the management of Barrett's esophagus. Patient’s underwent screening endoscopy annually to survey for improvement or progression of the disease. Success with treatment was based on repeat biopsy results.
Results: Out of the 35 participants in our cohort, 17 (48.6%) experienced complete resolution of Barrett's esophagus, with a mean resolution time of 433 days from the initiation of treatment. These results are particularly promising as the study progresses, with more substantial data emerging after five years of continuous therapy. Notably, our findings after two years of treatment show non-inferiority to high-dose PPI therapy alone, as reported in the ASPECT
Discussion: The ongoing study indicates that the combination of high-dose aspirin, high-dose PPI, folic acid and pyridoxine may be an effective treatment strategy for Barrett's esophagus. The interim results after two years suggest comparable efficacy to high-dose PPI and aspirin, with the potential for even greater benefit over a more extended period. Continued follow-up and data collection will further elucidate the long-term effectiveness and safety of this therapeutic regimen.
Disclosures:
GianPaolo Piccione, DO, James Ducey, MD, Inderbir Padda, MD, Paul Karroum, MD, Prassanna Wickremensinghe, MD, Svetoslav Badarov, MD. P2211 - An Observational Retrospective Cohort Study using PPI, Aspirin, Pyridoxine, and Folic Acid therapy for Non-Dysplastic Barrett’s Esophagus, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Richmond University Medical Center, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: This retrospective cohort study aims to evaluate the efficacy of high-dose aspirin, high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI), folic acid therapy, and pyridoxine in the resolution of non-dysplastic Barrett's esophagus. Both folate and pyridoxine have shown to have DNA methylation repair and anti-oxidant properties to minimize the progression of Barret’s esophagus.
Methods: Our study includes 35 participants, comprising both males and females aged 50-80 years. Participants in this study were treated with high-dose aspirin, high-dose PPI, folic acid and pyridoxine in the diagnosis of Barrett’s was confirmed on endoscopy and biopsy. The ASPECT trial, was used as the benchmark and inspiration for this study given the similar treatment modalities used. The ASPECT trial demonstrated the potential benefit of high-dose PPI therapy, with or without aspirin, in the management of Barrett's esophagus. Patient’s underwent screening endoscopy annually to survey for improvement or progression of the disease. Success with treatment was based on repeat biopsy results.
Results: Out of the 35 participants in our cohort, 17 (48.6%) experienced complete resolution of Barrett's esophagus, with a mean resolution time of 433 days from the initiation of treatment. These results are particularly promising as the study progresses, with more substantial data emerging after five years of continuous therapy. Notably, our findings after two years of treatment show non-inferiority to high-dose PPI therapy alone, as reported in the ASPECT
Discussion: The ongoing study indicates that the combination of high-dose aspirin, high-dose PPI, folic acid and pyridoxine may be an effective treatment strategy for Barrett's esophagus. The interim results after two years suggest comparable efficacy to high-dose PPI and aspirin, with the potential for even greater benefit over a more extended period. Continued follow-up and data collection will further elucidate the long-term effectiveness and safety of this therapeutic regimen.
Disclosures:
GianPaolo Piccione indicated no relevant financial relationships.
James Ducey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Inderbir Padda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Karroum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prassanna Wickremensinghe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Svetoslav Badarov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
GianPaolo Piccione, DO, James Ducey, MD, Inderbir Padda, MD, Paul Karroum, MD, Prassanna Wickremensinghe, MD, Svetoslav Badarov, MD. P2211 - An Observational Retrospective Cohort Study using PPI, Aspirin, Pyridoxine, and Folic Acid therapy for Non-Dysplastic Barrett’s Esophagus, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
