Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2219 - Characteristics of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis on Concomitant Advanced Immune Therapies
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- EW
Evan Wilder, MD
Scripps Clinic
San Diego, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Evan Wilder, MD1, Tara Alleyasin, MD2, Christopher Yuki, MD2, Leah Puglisi, MS3, Rebekah Belasco, MS3, Sam Mouwakeh, 3, Mazer Ally, MD2, Fouad Moawad, MD2, Quan Nhu, MD, PhD2
1Scripps Clinic, San Diego, CA; 2Scripps Clinic, La Jolla, CA; 3Scripps Research, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the esophagus which can be associated with other immune-mediated diseases. It remains unclear if treatment for these immune-mediated conditions would have a therapeutic role in EoE as well. The aim of this study was to perform a descriptive analysis on an EoE cohort with concomitant immune-mediated diseases.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of EoE patients at our institution on biologics or small molecule therapies from 2017 to 2023.
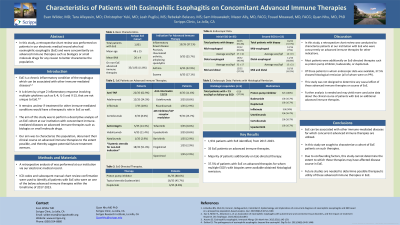
Results: We identified 1931 patients with EoE (mean age was 48 ± 15 years, 63% male, 89% Caucasian with a mean BMI of 26 ± 4). Of these patients, 35 (1.8%) were on non-EoE biologics or small molecules (Table 1). The indications for treatment included: 37.1% (13/35) had inflammatory bowel disease; 25.7% had rheumatological disease (psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis); 23% (8/35) had asthma.
Overall, the prevalence of EoE patients on advanced immune therapy was 1.8%. 63% (22/35) were on an anti-TNF therapy. 14% (5/35) were on anti-integrin therapy. 26% were on small molecule therapies (Table 1). Of the 35 patients, 89% were on PPI, 51% were on systemic steroids for non-EoE indications, 46% were on topical steroids, and 9% were on dupilumab.
Among patients for whom endoscopic data was available, 32/35 (91.4%) had esophageal biopsies. 65.6% (21/32) had mid esophageal biopsies; 46.9% (15/32) had distal biopsies, and 37.5% (12/32) had both. The average eosinophil count was 27 ± 16/hpf in the mid esophagus and 32 ± 17/hpf in the distal esophagus. 11.4% (4/32) of patients had < 15 eos/hpf on initial EGD for which data was available.
62.9% (22/35) of patients had data available from a second EGD. 72.7% (16/22) had biopsies (75% mid esophagus; 68.8% distal esophagus; 62.5% both segments). The average eosinophil count was 14 ± 15/hpf (mid) and 15 ± 21/hpf (distal). 37.5% (6/16) had < 15 eos/hpf on follow-up EGD. The 6 histologic responders received PPI (6/6), budesonide (1/6), dupilumab (1/6), prednisone (3/6), ustekinumab (1/6), infliximab (3/6), certolizumab (1/6), and upadacitinib (1/6).
Discussion: EoE can be associated with other immune-mediated diseases for which concurrent advanced immune therapies are utilized. In this study, we sought to characterize this EoE cohort on concomitant immune therapies. Future studies are needed to determine possible therapeutic utility of these advanced immune therapies in EoE.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Evan Wilder, MD1, Tara Alleyasin, MD2, Christopher Yuki, MD2, Leah Puglisi, MS3, Rebekah Belasco, MS3, Sam Mouwakeh, 3, Mazer Ally, MD2, Fouad Moawad, MD2, Quan Nhu, MD, PhD2. P2219 - Characteristics of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis on Concomitant Advanced Immune Therapies, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Scripps Clinic, San Diego, CA; 2Scripps Clinic, La Jolla, CA; 3Scripps Research, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the esophagus which can be associated with other immune-mediated diseases. It remains unclear if treatment for these immune-mediated conditions would have a therapeutic role in EoE as well. The aim of this study was to perform a descriptive analysis on an EoE cohort with concomitant immune-mediated diseases.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of EoE patients at our institution on biologics or small molecule therapies from 2017 to 2023.
Results: We identified 1931 patients with EoE (mean age was 48 ± 15 years, 63% male, 89% Caucasian with a mean BMI of 26 ± 4). Of these patients, 35 (1.8%) were on non-EoE biologics or small molecules (Table 1). The indications for treatment included: 37.1% (13/35) had inflammatory bowel disease; 25.7% had rheumatological disease (psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis); 23% (8/35) had asthma.
Overall, the prevalence of EoE patients on advanced immune therapy was 1.8%. 63% (22/35) were on an anti-TNF therapy. 14% (5/35) were on anti-integrin therapy. 26% were on small molecule therapies (Table 1). Of the 35 patients, 89% were on PPI, 51% were on systemic steroids for non-EoE indications, 46% were on topical steroids, and 9% were on dupilumab.
Among patients for whom endoscopic data was available, 32/35 (91.4%) had esophageal biopsies. 65.6% (21/32) had mid esophageal biopsies; 46.9% (15/32) had distal biopsies, and 37.5% (12/32) had both. The average eosinophil count was 27 ± 16/hpf in the mid esophagus and 32 ± 17/hpf in the distal esophagus. 11.4% (4/32) of patients had < 15 eos/hpf on initial EGD for which data was available.
62.9% (22/35) of patients had data available from a second EGD. 72.7% (16/22) had biopsies (75% mid esophagus; 68.8% distal esophagus; 62.5% both segments). The average eosinophil count was 14 ± 15/hpf (mid) and 15 ± 21/hpf (distal). 37.5% (6/16) had < 15 eos/hpf on follow-up EGD. The 6 histologic responders received PPI (6/6), budesonide (1/6), dupilumab (1/6), prednisone (3/6), ustekinumab (1/6), infliximab (3/6), certolizumab (1/6), and upadacitinib (1/6).
Discussion: EoE can be associated with other immune-mediated diseases for which concurrent advanced immune therapies are utilized. In this study, we sought to characterize this EoE cohort on concomitant immune therapies. Future studies are needed to determine possible therapeutic utility of these advanced immune therapies in EoE.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Evan Wilder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tara Alleyasin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Yuki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leah Puglisi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rebekah Belasco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sam Mouwakeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazer Ally: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Consultant.
Fouad Moawad: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Speakers Bureau.
Quan Nhu: Regeneron – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Evan Wilder, MD1, Tara Alleyasin, MD2, Christopher Yuki, MD2, Leah Puglisi, MS3, Rebekah Belasco, MS3, Sam Mouwakeh, 3, Mazer Ally, MD2, Fouad Moawad, MD2, Quan Nhu, MD, PhD2. P2219 - Characteristics of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis on Concomitant Advanced Immune Therapies, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
