Monday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P2332 - Biofeedback Therapy is Effective in All Types of Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia: A Tertiary Care Centre Experience From India
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Ayush Agarwal, MBBS, MD
All India Institute of Medical Sciences
New Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Ayush Agarwal, MBBS, MD1, Abhijith Anil, MBBS, MD1, Rajkumar Bayye, MBBS, MD1, Ashish Agarwal, MBBS, MD, DM2, Ashish Chauhan, MBBS, MD, DM3, Saurabh Kedia, MBBS, MD, DM1, Vineet Ahuja, MBBS, MD, DM1, Govind Makharia, MD, DM1
1All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India; 3Indira Gandha Medical College and Hospital, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh, India
Introduction: Pelvic floor dyssynergia (PFD) is a common cause of chronic constipation in adults with significant impact on quality of life. Biofeedback therapy (BFT) is the recommended first-line therapy for treatment of PFD, but the data on its efficacy among different types of PFD and the predictors of its positive outcome in Indian population are limited. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effect of BFT on clinical and manometric parameters in different types of PFD, and to identify predictors of its positive response.
Methods: All consecutive adult patients with PFD undergoing BFT at a tertiary care center in New Delhi, India from April 2021 to February 2024, who completed 6 sessions of BFT were included in this retrospective cohort study. Anorectal manometry-based BFT was provided by a trained practitioner every week for 6 weeks with each session lasting 15 minutes. Demographic, clinical, and manometric parameters of the patients before and after BFT were evaluated. Primary outcome was the change in Cleveland clinic constipation score, and secondary outcomes were changes in clinical symptoms and manometric parameters in different types of PFD, and baseline predictors of positive response to BFT.
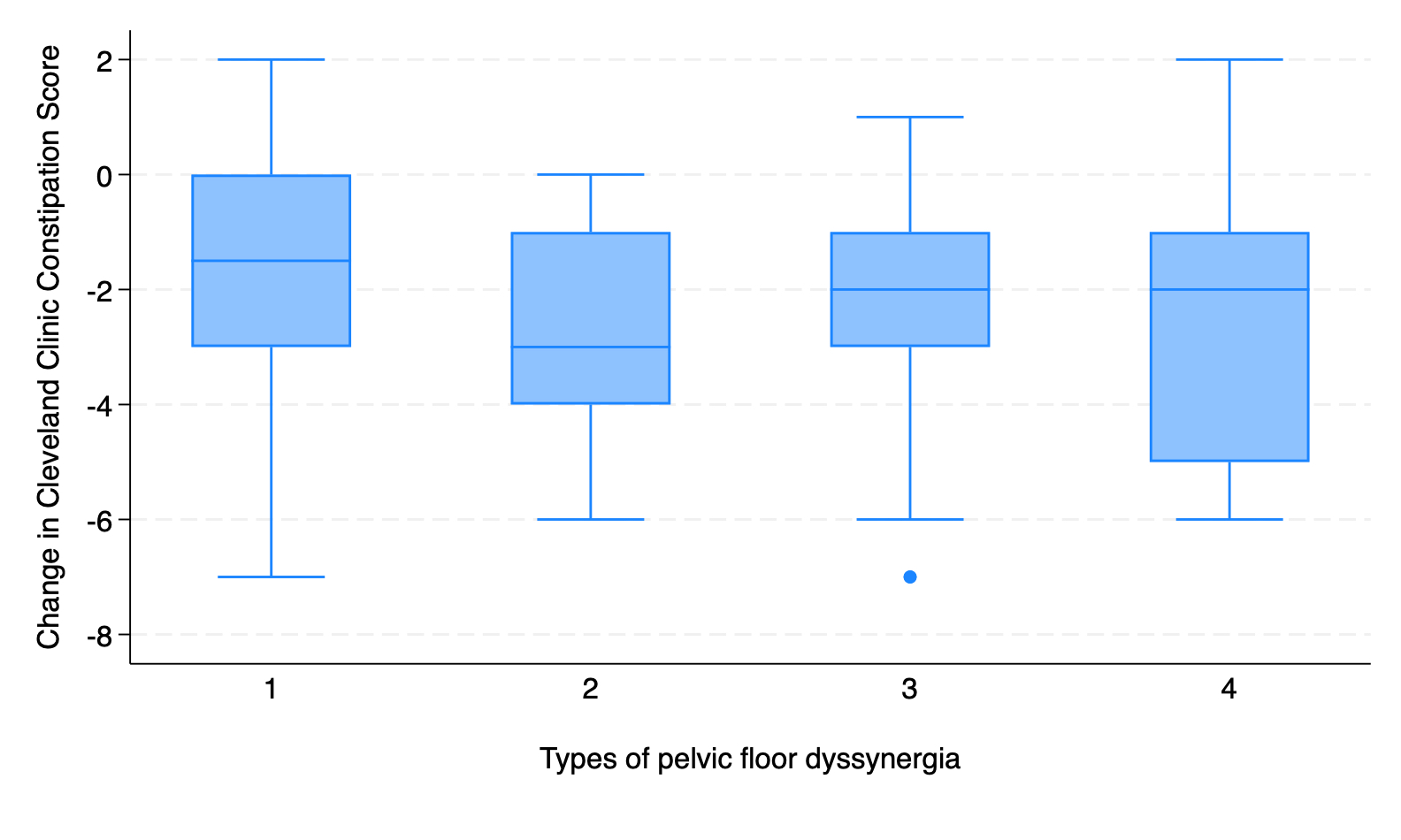
Results: Out of 240 patients who underwent BFT, 63 patients completed 6 sessions and were included: 41 (65.1%) were males with a median age of 39 years (IQR 27-55 years). According to Rao classification, type 3 (26, 41.2%) and type 1 PFD (22, 34.9%) were the most common, followed by type 4 (10, 15.9%) and type 2 (5, 7.9%) PFD. There was a significant improvement in Cleveland Clinic constipation score after biofeedback therapy (pre-therapy 7(4-8) to post-therapy 4 (2-6), p-value < 0.001). Improvement of ≥25% on the visual analog scale in overall symptoms was observed in 47 (74.6%) patients. There was a significant improvement in clinical symptoms (straining, bloating, urge, feeling of obstruction, unsuccessful attempts, manual evacuation) and manometric parameters (anal relaxation%). There was no significant difference in outcomes between different types of PFD according to Rao or Rome IV classification. No baseline clinical or manometric parameters significantly predicted a positive response to BFT.
Discussion: Biofeedback therapy is effective in all types of PFD in the Indian population with no significant difference in response among various types of PFD.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ayush Agarwal, MBBS, MD1, Abhijith Anil, MBBS, MD1, Rajkumar Bayye, MBBS, MD1, Ashish Agarwal, MBBS, MD, DM2, Ashish Chauhan, MBBS, MD, DM3, Saurabh Kedia, MBBS, MD, DM1, Vineet Ahuja, MBBS, MD, DM1, Govind Makharia, MD, DM1. P2332 - Biofeedback Therapy is Effective in All Types of Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia: A Tertiary Care Centre Experience From India, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India; 3Indira Gandha Medical College and Hospital, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh, India
Introduction: Pelvic floor dyssynergia (PFD) is a common cause of chronic constipation in adults with significant impact on quality of life. Biofeedback therapy (BFT) is the recommended first-line therapy for treatment of PFD, but the data on its efficacy among different types of PFD and the predictors of its positive outcome in Indian population are limited. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effect of BFT on clinical and manometric parameters in different types of PFD, and to identify predictors of its positive response.
Methods: All consecutive adult patients with PFD undergoing BFT at a tertiary care center in New Delhi, India from April 2021 to February 2024, who completed 6 sessions of BFT were included in this retrospective cohort study. Anorectal manometry-based BFT was provided by a trained practitioner every week for 6 weeks with each session lasting 15 minutes. Demographic, clinical, and manometric parameters of the patients before and after BFT were evaluated. Primary outcome was the change in Cleveland clinic constipation score, and secondary outcomes were changes in clinical symptoms and manometric parameters in different types of PFD, and baseline predictors of positive response to BFT.
Results: Out of 240 patients who underwent BFT, 63 patients completed 6 sessions and were included: 41 (65.1%) were males with a median age of 39 years (IQR 27-55 years). According to Rao classification, type 3 (26, 41.2%) and type 1 PFD (22, 34.9%) were the most common, followed by type 4 (10, 15.9%) and type 2 (5, 7.9%) PFD. There was a significant improvement in Cleveland Clinic constipation score after biofeedback therapy (pre-therapy 7(4-8) to post-therapy 4 (2-6), p-value < 0.001). Improvement of ≥25% on the visual analog scale in overall symptoms was observed in 47 (74.6%) patients. There was a significant improvement in clinical symptoms (straining, bloating, urge, feeling of obstruction, unsuccessful attempts, manual evacuation) and manometric parameters (anal relaxation%). There was no significant difference in outcomes between different types of PFD according to Rao or Rome IV classification. No baseline clinical or manometric parameters significantly predicted a positive response to BFT.
Discussion: Biofeedback therapy is effective in all types of PFD in the Indian population with no significant difference in response among various types of PFD.

Figure: Effect of biofeedback therapy on Cleveland Clinic Constipation Score in different types of Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ayush Agarwal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhijith Anil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajkumar Bayye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashish Agarwal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashish Chauhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saurabh Kedia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vineet Ahuja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Govind Makharia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayush Agarwal, MBBS, MD1, Abhijith Anil, MBBS, MD1, Rajkumar Bayye, MBBS, MD1, Ashish Agarwal, MBBS, MD, DM2, Ashish Chauhan, MBBS, MD, DM3, Saurabh Kedia, MBBS, MD, DM1, Vineet Ahuja, MBBS, MD, DM1, Govind Makharia, MD, DM1. P2332 - Biofeedback Therapy is Effective in All Types of Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia: A Tertiary Care Centre Experience From India, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
