Monday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P2334 - Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Constipation: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 Clinical Study Data Assessing Primary and Additional Endpoints by Race and Ethnicity, and by Age
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- BM
Baharak Moshiree, MD
Advocate Health Wake Forest Medical University
Charlotte, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Baharak Moshiree, MD1, Lin Chang, MD2, Mena Boules, MD3, Wendy Chen, PharmD4, James Wu, PhD3, Moming Li, PhD4, Paul Feuerstadt, MD5, Kyle Staller, MD, MPH6
1Advocate Health Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, NC; 2Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 3Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Boston, MA; 4AbbVie, Inc., North Chicago, IL; 5Yale School of Medicine, PACT Gastroenterology Center, Hamden, CT; 6Center for Neurointestinal Health, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) is a common gastrointestinal condition. Race-/ethnicity-related variations may influence its clinical presentation and treatment outcomes, yet published data differentiating CIC experience between these groups are limited. This post hoc analysis evaluated linaclotide (LIN) efficacy and safety in CIC patients by race and ethnicity, followed by age.
Methods: Pooled data from 4 Phase 3 randomized controlled studies (NCT00730015, NCT00765882, NCT02291679, NCT01642914) of patients who met modified Rome II/III CIC criteria and received placebo (PBO), LIN 72 µg or LIN 145 µg were stratified by race (white, Black, Asian, Other) and ethnicity (non-Hispanic, Hispanic), followed by age (< 65, ≥65 yrs). Statistical analyses assessed the complete spontaneous bowel movement (CSBM) overall responder rate (≥3 CSBM per week and ≥baseline+1 for ≥9/12 weeks; primary endpoint), 12-week change from baseline (CFB) in CIC symptoms and time to response across groups. Safety was also evaluated.
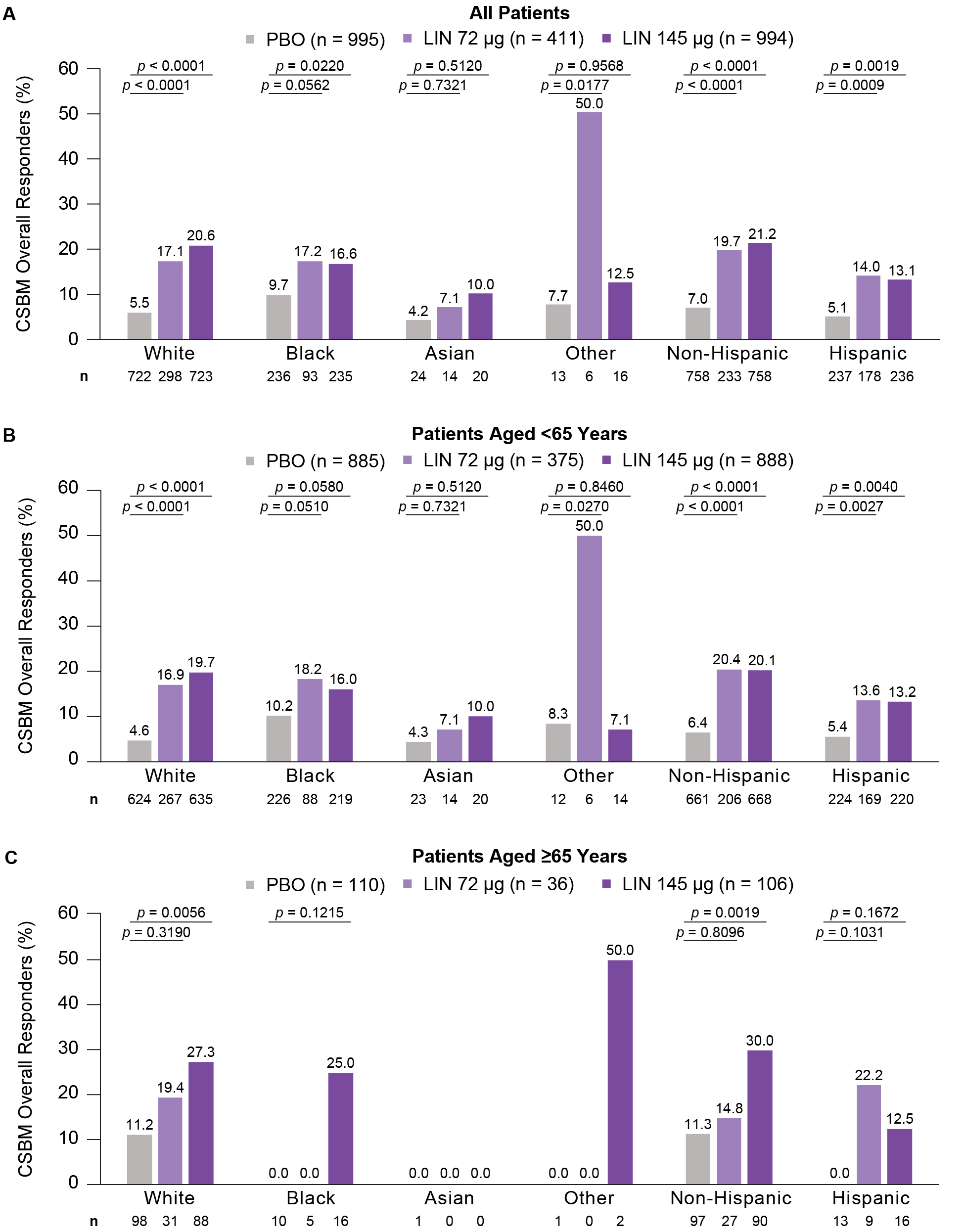
Results: Of the 2,400 CIC patients (83.3% female), there were 72.6% white (mean age: 47.9 yrs), 23.5% Black (45.0 yrs), 2.4% Asian (38.0 yrs) and 1.5% Other (42.1 yrs); 72.9% non-Hispanic (47.9 yrs) and 27.1% Hispanic (44.0 yrs). Within each race/ethnicity group, baseline bowel and abdominal symptoms were generally similar across treatment arms. The proportion of CSBM overall responders was higher for LIN than PBO across races/ethnicities, mostly irrespective of age (Figure 1). Similar trends in 12-week CFB in CIC symptoms were generally observed across races/ethnicities (Table 1). Overall, median time to improvement from baseline in CSBM weekly rate ≥1 was 3 weeks (LIN 72 µg) and 2 weeks (LIN 145 µg); in general, LIN reduced time to improvement vs PBO across races/ethnicities (Table 1). Diarrhea was the most common treatment-emergent adverse event in LIN-treated patients across races except Other (LIN 72 µg: White, 20.1%, Black, 18.3%, Asian, 7.1%, Other, 16.7%; LIN 145 µg: White, 18.9%, Black, 13.6%, Asian, 5.0%, Other, 6.3%) and across ethnicities (LIN 72 µg: Non-Hispanic, 28.3%, Hispanic, 7.3%; LIN 145 µg: Non-Hispanic, 19.0%, Hispanic, 11.4%), mostly irrespective of age.
Discussion: LIN improved CSBM responder rates and CIC symptoms, and had a similar safety profile, across most races/ethnicities and ages in CIC patients. Small sample sizes for Asian and Other groups (and some age subgroups) limit data interpretation and highlight the need to recruit more diverse populations in clinical studies.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Baharak Moshiree, MD1, Lin Chang, MD2, Mena Boules, MD3, Wendy Chen, PharmD4, James Wu, PhD3, Moming Li, PhD4, Paul Feuerstadt, MD5, Kyle Staller, MD, MPH6. P2334 - Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Constipation: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 Clinical Study Data Assessing Primary and Additional Endpoints by Race and Ethnicity, and by Age, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Advocate Health Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, NC; 2Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 3Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Boston, MA; 4AbbVie, Inc., North Chicago, IL; 5Yale School of Medicine, PACT Gastroenterology Center, Hamden, CT; 6Center for Neurointestinal Health, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) is a common gastrointestinal condition. Race-/ethnicity-related variations may influence its clinical presentation and treatment outcomes, yet published data differentiating CIC experience between these groups are limited. This post hoc analysis evaluated linaclotide (LIN) efficacy and safety in CIC patients by race and ethnicity, followed by age.
Methods: Pooled data from 4 Phase 3 randomized controlled studies (NCT00730015, NCT00765882, NCT02291679, NCT01642914) of patients who met modified Rome II/III CIC criteria and received placebo (PBO), LIN 72 µg or LIN 145 µg were stratified by race (white, Black, Asian, Other) and ethnicity (non-Hispanic, Hispanic), followed by age (< 65, ≥65 yrs). Statistical analyses assessed the complete spontaneous bowel movement (CSBM) overall responder rate (≥3 CSBM per week and ≥baseline+1 for ≥9/12 weeks; primary endpoint), 12-week change from baseline (CFB) in CIC symptoms and time to response across groups. Safety was also evaluated.
Results: Of the 2,400 CIC patients (83.3% female), there were 72.6% white (mean age: 47.9 yrs), 23.5% Black (45.0 yrs), 2.4% Asian (38.0 yrs) and 1.5% Other (42.1 yrs); 72.9% non-Hispanic (47.9 yrs) and 27.1% Hispanic (44.0 yrs). Within each race/ethnicity group, baseline bowel and abdominal symptoms were generally similar across treatment arms. The proportion of CSBM overall responders was higher for LIN than PBO across races/ethnicities, mostly irrespective of age (Figure 1). Similar trends in 12-week CFB in CIC symptoms were generally observed across races/ethnicities (Table 1). Overall, median time to improvement from baseline in CSBM weekly rate ≥1 was 3 weeks (LIN 72 µg) and 2 weeks (LIN 145 µg); in general, LIN reduced time to improvement vs PBO across races/ethnicities (Table 1). Diarrhea was the most common treatment-emergent adverse event in LIN-treated patients across races except Other (LIN 72 µg: White, 20.1%, Black, 18.3%, Asian, 7.1%, Other, 16.7%; LIN 145 µg: White, 18.9%, Black, 13.6%, Asian, 5.0%, Other, 6.3%) and across ethnicities (LIN 72 µg: Non-Hispanic, 28.3%, Hispanic, 7.3%; LIN 145 µg: Non-Hispanic, 19.0%, Hispanic, 11.4%), mostly irrespective of age.
Discussion: LIN improved CSBM responder rates and CIC symptoms, and had a similar safety profile, across most races/ethnicities and ages in CIC patients. Small sample sizes for Asian and Other groups (and some age subgroups) limit data interpretation and highlight the need to recruit more diverse populations in clinical studies.

Figure: Percentage of CSBM Overall Responders by A) Race and Ethnicity in All Patients, B) Race and Ethnicity in Patients Aged <65 Years and C) Race and Ethnicity in Patients Aged ≥65 Years.
n represents the number of patients with CSBM overall responder data available within each group. p-values are descriptive only and show the difference in responder rate obtained from Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel tests controlling for geographic region for pairwise comparisons of each LIN dose vs PBO. ‘Black’ includes patients who identified as Black or African American. ‘Other’ includes patients who identified as having more than one race or being American Indian or Alaskan Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, South American, Indian, Mexican, Puerto Rican, Creole, Italian/Leonese, Middle Eastern or Spanish. ‘Hispanic’ includes patients who identified as Hispanic or Latino. A CSBM overall responder was defined as a patient with ≥3 CSBMs per week and an increase of ≥1 CSBM per week from baseline for ≥9 of the 12 treatment-period weeks.
CSBM, complete spontaneous bowel movement; LIN, linaclotide; PBO, placebo.
n represents the number of patients with CSBM overall responder data available within each group. p-values are descriptive only and show the difference in responder rate obtained from Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel tests controlling for geographic region for pairwise comparisons of each LIN dose vs PBO. ‘Black’ includes patients who identified as Black or African American. ‘Other’ includes patients who identified as having more than one race or being American Indian or Alaskan Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, South American, Indian, Mexican, Puerto Rican, Creole, Italian/Leonese, Middle Eastern or Spanish. ‘Hispanic’ includes patients who identified as Hispanic or Latino. A CSBM overall responder was defined as a patient with ≥3 CSBMs per week and an increase of ≥1 CSBM per week from baseline for ≥9 of the 12 treatment-period weeks.
CSBM, complete spontaneous bowel movement; LIN, linaclotide; PBO, placebo.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Baharak Moshiree: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Allergan – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Alnylam Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Atmo Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Biora Therapeutics (formerly Progenity) – Advisory Committee/Board Member. CinDome Pharma – Grant/Research Support. CinPhloro Pharma – Grant/Research Support. Restalsis Health – Grant/Research Support. Salix Pharmaceuticals of Bausch Health – Grant/Research Support. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support.
Lin Chang: AbbVie – Speaker. AnX Robotica – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Atmo Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch Health – Consultant, Speaker. FoodMarble Digestive Health – Consultant, Stock Options. Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. ModifyHealth – Stock Options. Trellus Health – Consultant, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Vibrant Advisory Board – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Vibrant Gastro – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Mena Boules: Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Wendy Chen: AbbVie – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
James Wu: Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Moming Li: AbbVie – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Paul Feuerstadt: Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Probiotech – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Seres Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Kyle Staller: Anji Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Ardelyx – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. GI Supply – Consultant. Mahana Therapeutics – Consultant. Restalsis Health – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Salix – Consultant.
Baharak Moshiree, MD1, Lin Chang, MD2, Mena Boules, MD3, Wendy Chen, PharmD4, James Wu, PhD3, Moming Li, PhD4, Paul Feuerstadt, MD5, Kyle Staller, MD, MPH6. P2334 - Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Constipation: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 Clinical Study Data Assessing Primary and Additional Endpoints by Race and Ethnicity, and by Age, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
