Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2570 - Real World Experience With Microbiota Treatment for the Prevention of Recurrent Clostridioides difficile Infection
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- TR
Timothy E. Ritter, MD
GI Alliance
Southlake, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Timothy E. Ritter, MD1, Jonathan A. Rosenberg, MD2, Richard L. Hengel, MD, FIDSA3, Sujatha Krishnan, MD4, Kathy A. Baker, APRN5, Lucinda J. Van Anglen, BS, PharmD6, Kelly E. Hanna, PharmD6, Amy Guo, PhD7, Mielad Moosapanah, PharmD8, Sanghyuk Seo, PharmD, MS7, Kevin W. Garey, PharmD, MS9
1GI Alliance, Southlake, TX; 2GI Alliance of Illinois, Highland Park, IL; 3Atlanta ID Group, Atlanta, GA; 4DFW Infectious Diseases, PLLC, Frisco, TX; 5Harris College of Nursing & Health Sciences, Fort Worth, TX; 6Healix Infusion Therapy, LLC, Sugar Land, TX; 7Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Parsippany, NJ; 8Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Parsippany, NJ; 9University of Houston College of Pharmacy, Houston, TX
Introduction: Fecal microbiota, live-jslm (RBL) was approved in November 2022 as the first microbiome-based product for the prevention of recurrence of Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI). This pre-packaged, rectally administered microbiota product has shown effectiveness in clinical trials, but data is limited in the real-world setting. Our aim is to report outcomes of RBL treated patients in a population reflective of real world practice.
Methods: This single-arm, US-based, retrospective, multicenter study included patients ≥18 years with rCDI who received RBL in physician offices from Feb 2023 to May 2024. Centralized electronic health records were reviewed for patient demographics, comorbidities, rCDI history, risk factors, RBL therapy characteristics and other related treatments. Recurrence was defined as any occurrence of diarrhea with 3 liquid bowel movements or more within 24 hours and was assessed at 8 weeks and 6 months post-RBL administration. Treatment success was defined as absence of recurrence.
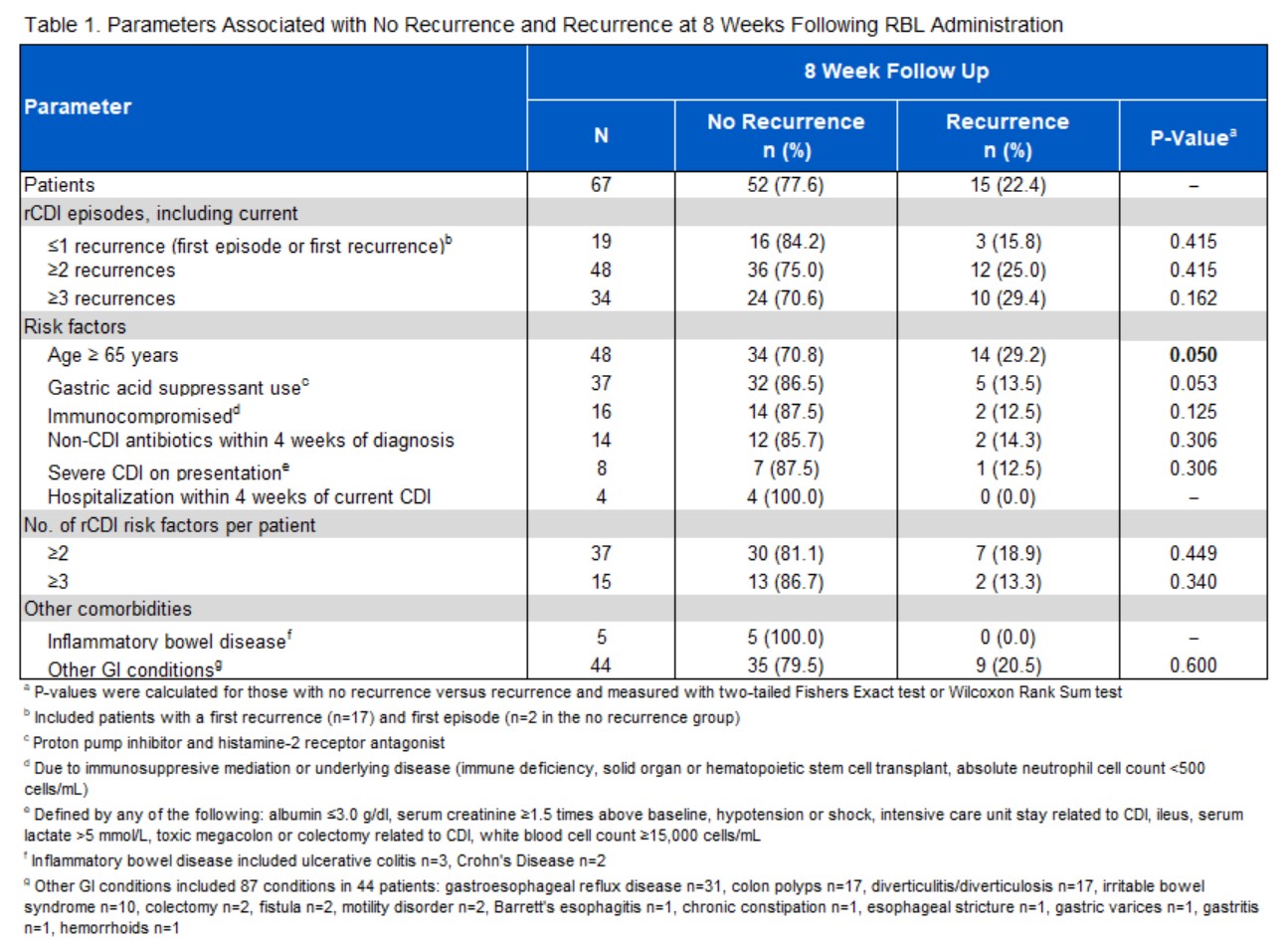
Results: 67 rCDI patients received RBL, with a median age of 74 years, IQR (63.0-81.5) and 47% female. The population was highly comorbid with a median Charlson comorbidity score of 4 (IQR 3.0-6.5). Over half (50.7%) had ≥3 recurrences of CDI, 48 (71.6%) were ≥65 years of age and 37 (55.2%) were on gastric acid suppressants. 5 (7.5%) patients had IBD, 2 with Crohn’s disease and 3 with ulcerative colitis. 44 (65.7%) patients had other gastrointestinal diseases. All patients received standard of care antibiotics prior to RBL, with fidaxomicin being most predominant in 39 (58.2%). There were no adverse events reported with administration of RBL. Treatment success rates at 8 weeks are noted in Table 1. The overall 8-week treatment success rate was 77.6%. Although not statistically significant, those with ≤1 recurrence of CDI had treatment success of 84.2%. Age ≥65 years was associated with a significantly higher incidence of recurrence. Of 30 patients with 6-month follow-up, 26 (86.7%) maintained a sustained response. Notably, there were no recurrences in patients with IBD at 8 weeks and at 6 months.
Discussion: This real-world study demonstrated the effectiveness of RBL at 8 weeks and 6 months. Although the sample was small, successful use of RBL in patients with gastrointestinal conditions shows promise, including in IBD. RBL is a safe and effective treatment for the prevention of recurrent C. difficile infections.
Disclosures:
Timothy E. Ritter, MD1, Jonathan A. Rosenberg, MD2, Richard L. Hengel, MD, FIDSA3, Sujatha Krishnan, MD4, Kathy A. Baker, APRN5, Lucinda J. Van Anglen, BS, PharmD6, Kelly E. Hanna, PharmD6, Amy Guo, PhD7, Mielad Moosapanah, PharmD8, Sanghyuk Seo, PharmD, MS7, Kevin W. Garey, PharmD, MS9. P2570 - Real World Experience With Microbiota Treatment for the Prevention of Recurrent <i>Clostridioides difficile</i> Infection, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1GI Alliance, Southlake, TX; 2GI Alliance of Illinois, Highland Park, IL; 3Atlanta ID Group, Atlanta, GA; 4DFW Infectious Diseases, PLLC, Frisco, TX; 5Harris College of Nursing & Health Sciences, Fort Worth, TX; 6Healix Infusion Therapy, LLC, Sugar Land, TX; 7Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Parsippany, NJ; 8Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Parsippany, NJ; 9University of Houston College of Pharmacy, Houston, TX
Introduction: Fecal microbiota, live-jslm (RBL) was approved in November 2022 as the first microbiome-based product for the prevention of recurrence of Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI). This pre-packaged, rectally administered microbiota product has shown effectiveness in clinical trials, but data is limited in the real-world setting. Our aim is to report outcomes of RBL treated patients in a population reflective of real world practice.
Methods: This single-arm, US-based, retrospective, multicenter study included patients ≥18 years with rCDI who received RBL in physician offices from Feb 2023 to May 2024. Centralized electronic health records were reviewed for patient demographics, comorbidities, rCDI history, risk factors, RBL therapy characteristics and other related treatments. Recurrence was defined as any occurrence of diarrhea with 3 liquid bowel movements or more within 24 hours and was assessed at 8 weeks and 6 months post-RBL administration. Treatment success was defined as absence of recurrence.
Results: 67 rCDI patients received RBL, with a median age of 74 years, IQR (63.0-81.5) and 47% female. The population was highly comorbid with a median Charlson comorbidity score of 4 (IQR 3.0-6.5). Over half (50.7%) had ≥3 recurrences of CDI, 48 (71.6%) were ≥65 years of age and 37 (55.2%) were on gastric acid suppressants. 5 (7.5%) patients had IBD, 2 with Crohn’s disease and 3 with ulcerative colitis. 44 (65.7%) patients had other gastrointestinal diseases. All patients received standard of care antibiotics prior to RBL, with fidaxomicin being most predominant in 39 (58.2%). There were no adverse events reported with administration of RBL. Treatment success rates at 8 weeks are noted in Table 1. The overall 8-week treatment success rate was 77.6%. Although not statistically significant, those with ≤1 recurrence of CDI had treatment success of 84.2%. Age ≥65 years was associated with a significantly higher incidence of recurrence. Of 30 patients with 6-month follow-up, 26 (86.7%) maintained a sustained response. Notably, there were no recurrences in patients with IBD at 8 weeks and at 6 months.
Discussion: This real-world study demonstrated the effectiveness of RBL at 8 weeks and 6 months. Although the sample was small, successful use of RBL in patients with gastrointestinal conditions shows promise, including in IBD. RBL is a safe and effective treatment for the prevention of recurrent C. difficile infections.

Figure: Table 1.
Disclosures:
Timothy Ritter: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Eli Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Ferring/Rebiotix – has served on a Data Adjudication Committee. Genentech (Roche) – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Intercept – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Iterative Scopes – Advisory Committee/Board Member, holds shares in Iterative Scopes. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Nestlé/Seres – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau.
Jonathan Rosenberg: Aimmune – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Ferr – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Richard Hengel: Gilead – Grant/Research Support.
Sujatha Krishnan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathy Baker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lucinda Van Anglen: Cumberland Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Novartis Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support.
Kelly Hanna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amy Guo: Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – Employee.
Mielad Moosapanah: Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Employee.
Sanghyuk Seo: Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – Employee.
Kevin Garey: Acurx – Grant/Research Support.
Timothy E. Ritter, MD1, Jonathan A. Rosenberg, MD2, Richard L. Hengel, MD, FIDSA3, Sujatha Krishnan, MD4, Kathy A. Baker, APRN5, Lucinda J. Van Anglen, BS, PharmD6, Kelly E. Hanna, PharmD6, Amy Guo, PhD7, Mielad Moosapanah, PharmD8, Sanghyuk Seo, PharmD, MS7, Kevin W. Garey, PharmD, MS9. P2570 - Real World Experience With Microbiota Treatment for the Prevention of Recurrent <i>Clostridioides difficile</i> Infection, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
