Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2573 - Comparative Effectiveness of Bile Acid Sequestrants and Antibiotics in the Management of Pouchitis: A Matched Cohort Study From the United States
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Jana G. Al Hashash, MD, MSc, FACG
Associate Professor
Mayo Clinic
Jacksonville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Michael Camilleri, MD, MACG2, Abdulla Massad, MD3, Francis A. Farraye, MD, MSc4, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc4
1University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 4Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Bile acid sequestrants (BAS) are an emerging option for treatment of pouchitis. There is paucity of evidence regarding the effectiveness of BAS compared to standard treatment with antibiotics. We aimed to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of BAS monotherapy, antibiotic monotherapy, and combination therapy (BAS and antibiotics) in the treatment of pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) for ulcerative colitis (UC).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the US-Collaborative TriNetX database to identify patients ≥18 years with acute pouchitis and UC. Treatment groups were divided into: BAS (cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol), antibiotics (ciprofloxacin and/or metronidazole), and combination therapy of both BAS and antibiotics. Primary outcomes were failure of initial therapy (early relapse or nonresponse) and the development of recurrent pouchitis in the first 12 months after an initial episode of pouchitis. Using 1:1 propensity score matching, we adjusted for age, sex, race, smoking, obesity, primary sclerosing cholangitis and previous exposure to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors between the cohorts.
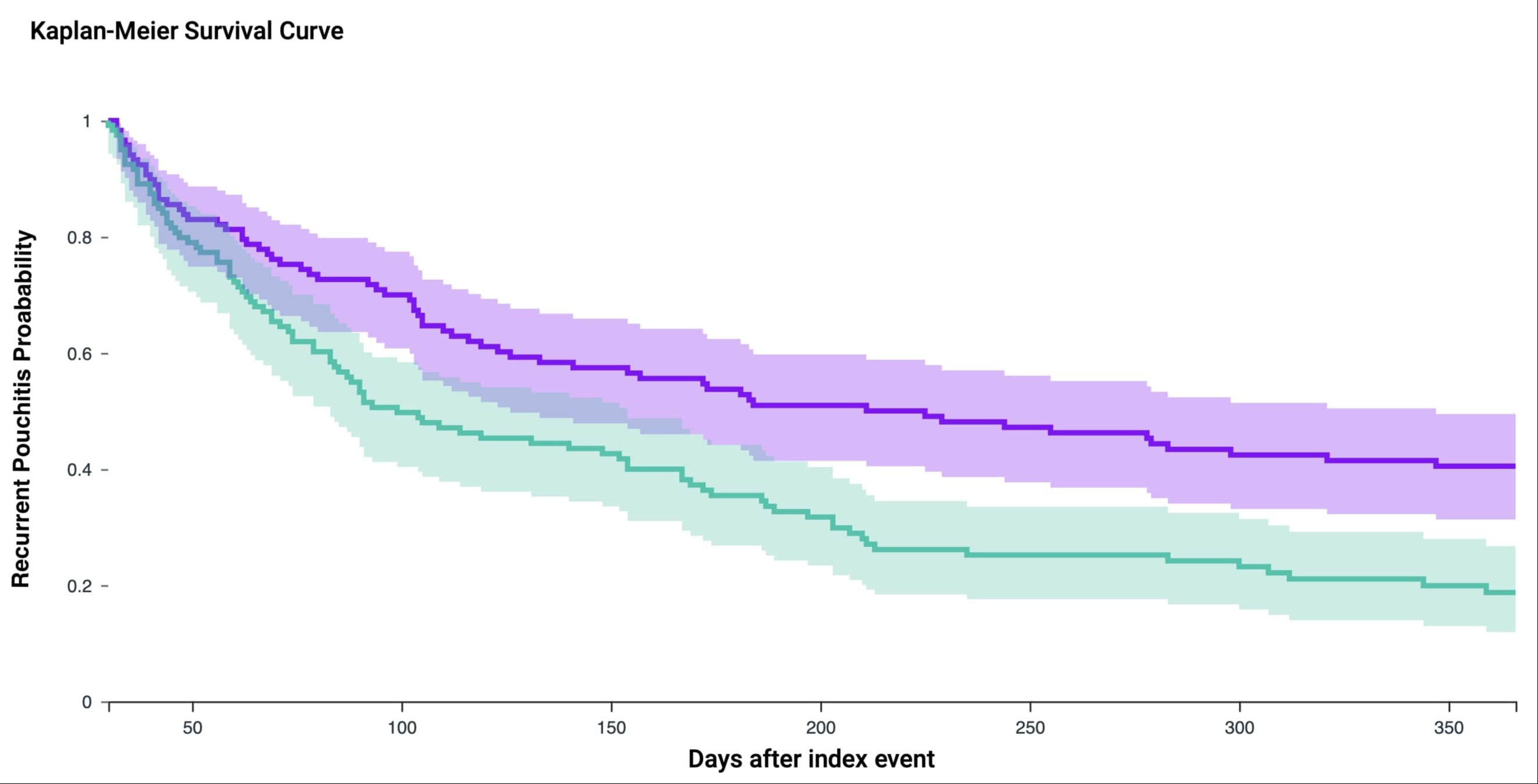
Results: Our analysis included 1064 patients (mean age 35.8±15 years, female 44%) of who 677 (64%) developed recurrent pouchitis. After adjusting for confounders, there was no significant difference in the odds of early relapse or nonresponse with BAS compared with antibiotic monotherapy (aOR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.42-1.54) or combination therapy (aOR: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.38-1.57) (Table 1). When compared with patients treated with antibiotics, patients treated with BAS had a statistically significant lower recurrent pouchitis rate (aOR: 0.39; 95% CI: 0.23-0.68). Using Logrank test model to compare the time to development of recurrent pouchitis, patients treated with BAS (225 days) had a statistically significant longer time to recurrent pouchitis (p< 0.001) when compared to antibiotics (99 days) (Figure 1).
Discussion: Using real-world evidence, our cohort study showed that, for treatment of pouchitis, BAS monotherapy was not significantly different from antibiotic monotherapy or combination therapy in terms of early relapse or nonresponse. However, BAS was associated with a significantly lower rate and a longer time to recurrent pouchitis compared to antibiotics. These findings suggest that BAS may offer a promising alternative for the management of pouchitis, warranting further prospective studies to confirm their efficacy and long-term outcomes.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Michael Camilleri, MD, MACG2, Abdulla Massad, MD3, Francis A. Farraye, MD, MSc4, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc4. P2573 - Comparative Effectiveness of Bile Acid Sequestrants and Antibiotics in the Management of Pouchitis: A Matched Cohort Study From the United States, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Michael Camilleri, MD, MACG2, Abdulla Massad, MD3, Francis A. Farraye, MD, MSc4, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc4
1University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 4Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Bile acid sequestrants (BAS) are an emerging option for treatment of pouchitis. There is paucity of evidence regarding the effectiveness of BAS compared to standard treatment with antibiotics. We aimed to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of BAS monotherapy, antibiotic monotherapy, and combination therapy (BAS and antibiotics) in the treatment of pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) for ulcerative colitis (UC).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the US-Collaborative TriNetX database to identify patients ≥18 years with acute pouchitis and UC. Treatment groups were divided into: BAS (cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol), antibiotics (ciprofloxacin and/or metronidazole), and combination therapy of both BAS and antibiotics. Primary outcomes were failure of initial therapy (early relapse or nonresponse) and the development of recurrent pouchitis in the first 12 months after an initial episode of pouchitis. Using 1:1 propensity score matching, we adjusted for age, sex, race, smoking, obesity, primary sclerosing cholangitis and previous exposure to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors between the cohorts.
Results: Our analysis included 1064 patients (mean age 35.8±15 years, female 44%) of who 677 (64%) developed recurrent pouchitis. After adjusting for confounders, there was no significant difference in the odds of early relapse or nonresponse with BAS compared with antibiotic monotherapy (aOR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.42-1.54) or combination therapy (aOR: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.38-1.57) (Table 1). When compared with patients treated with antibiotics, patients treated with BAS had a statistically significant lower recurrent pouchitis rate (aOR: 0.39; 95% CI: 0.23-0.68). Using Logrank test model to compare the time to development of recurrent pouchitis, patients treated with BAS (225 days) had a statistically significant longer time to recurrent pouchitis (p< 0.001) when compared to antibiotics (99 days) (Figure 1).
Discussion: Using real-world evidence, our cohort study showed that, for treatment of pouchitis, BAS monotherapy was not significantly different from antibiotic monotherapy or combination therapy in terms of early relapse or nonresponse. However, BAS was associated with a significantly lower rate and a longer time to recurrent pouchitis compared to antibiotics. These findings suggest that BAS may offer a promising alternative for the management of pouchitis, warranting further prospective studies to confirm their efficacy and long-term outcomes.

Figure: Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier curve comparing time to an episode of recurrent pouchitis among patients treated with bile acid sequestrants (purple) versus antibiotics (green) for an initial episode of pouchitis.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Saqr Alsakarneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Camilleri: Aclipse Therapeutics – Consultant. Aditum Bio – Consultant. Alfasigma – Consultant. APHAIA Pharma – Consultant. Bilayer Therapeutics – Stock Options. Biocodex – Grant/Research Support. BioKier – Consultant. Brightseed Bio – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Coloplast – Consultant. Cosmo Pharmceuticals – Consultant. Dignify Therapeutics – Stock Options. Enterin – Stock Options. Invea Therapeutics – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Medpace – Consultant. Monteresearch – Consultant. Neurogastrx – Consultant. NGM Biopharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support. Phenomix – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Stock Options. Renexxion – Consultant. SKYE Bioscience – Consultant. Sumitomo / Sunovion – Consultant. Synlogic – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Thelium Therapeutics – Stock Options. Vanda – Grant/Research Support.
Abdulla Massad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Francis Farraye: AbbVie – Consultant. Avalo Therapeutics – Consultant. Bausch – Advisor or Review Panel Member. BMS – Consultant. Braintree Labs – Consultant. DSMB for Lilly. – Sits on. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. GI Reviewers and IBD Educational Group – independent contractor. GSK, Iterative Health, Janssen, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Sandoz Immunology, Sebela and Viatris – Consultant.
Jana Hashash: Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant.
Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Michael Camilleri, MD, MACG2, Abdulla Massad, MD3, Francis A. Farraye, MD, MSc4, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc4. P2573 - Comparative Effectiveness of Bile Acid Sequestrants and Antibiotics in the Management of Pouchitis: A Matched Cohort Study From the United States, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

