Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
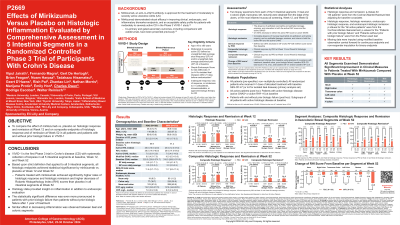
P2669 - Effects of Mirikizumab versus Placebo on Histologic Inflammation Evaluated by Comprehensive Assessment in 5 Intestinal Segments in a Randomized, Controlled Phase 3 Trial of Participants With Crohn’s Disease
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- CO
Charles C. C. Owen, Jr., MD, MBA
Eli Lilly and Company
Arlington, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Vipul Jairath, MBChB1, Fernando Magro, 2, Gert De Hertogh, 3, Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Noam Harpaz, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD5, Geert R. D'Haens, MD, PhD6, Rish Pai, MD, PhD7, Zhantao Lin, PhD8, Nathan Morris, 8, Marijana Protic, 8, Emily Hon, 8, Charles C. Owen, MD, MBA8, Rodrigo Escobar, 8, Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD9
1Western University, London, ON, Canada; 2Centro Hospitalar São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 3Laboratory of Translational Cell and Tissue Research, Leuven, Brabant Wallon, Belgium; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai, NY; 5Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 6Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Limburg, Netherlands; 7Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; 8Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN; 9Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Wien, Austria
Introduction: Histologic inflammation persists in up to one quarter of patients with Crohn’s Disease (CD) despite endoscopic mucosal healing. Responsiveness of histologic inflammation to treatment is an evolving outcome measure in CD. Mirikizumab (MIRI) increased histologic response (H-Res) and remission (H-Rem) relative to placebo (PBO) in the Phase 2 SERENITY trial.
Methods: We compared the effect of MIRI on H-Res and H-Rem at week (W)12 and W52 to PBO by composite endpoints of response (clinical response by Patient-Reported Outcome [PRO] at W12 and W52 H-Res) and of remission (clinical response by PRO at W12 and W52 H-Rem) at W52. The overall population of patients with moderate-to-severe active CD, patients without prior biologic failure (non-BF), and patients with prior BF were assessed, using data from the Phase 3 VIVID-1 trial. Two biopsy specimens from each of 5 intestinal segments (1 ileal and 4 colonic) were obtained from the edge of the ulcers, or the most inflamed mucosa from randomized patients at screening, W12, and W52. Criteria for H-Res: absence of epithelial neutrophils and epithelial damage, erosions, and ulceration or ≥50% decrease in either the sum of the 5 segments of Robarts Histopathology Index or the Global Histologic Disease Activity Score. H-Rem: complete absence of mucosal neutrophils (in epithelium and lamina propria), and no epithelial damage, erosions, and ulcers; these criteria had to be met in all biopsy specimens. Clinical response by PRO: ≥30% decrease in stool frequency and/or abdominal pain with neither score worse than baseline. H-Res, H-Rem, composite H-Res, and composite H-Rem in all patients were prespecified, non-multiplicity-controlled endpoints. Analyses in non-BF and BF patients were post hoc.
Results: At W12: treatment with MIRI resulted in nominally statistically significantly higher rates of H-Res in all three patient groups, differences between MIRI vs PBO were nominally significant in achieving H-Rem in all patients and in non-BF and BF patients. For W52: composite H-Res differences between MIRI vs PBO were nominally statistically significant in all patient groups, composite H-Rem differences were nominally statistically significant between MIRI vs PBO in all patients, in non-BF patients, and in BF patients (Table).
Discussion: MIRI achieved nominally significantly higher rates of H-Res and H-Rem compared to PBO in all patients at W12 and W52. The statistical difference was more pronounced in the BF population after 1 year of treatment.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Vipul Jairath, MBChB1, Fernando Magro, 2, Gert De Hertogh, 3, Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Noam Harpaz, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD5, Geert R. D'Haens, MD, PhD6, Rish Pai, MD, PhD7, Zhantao Lin, PhD8, Nathan Morris, 8, Marijana Protic, 8, Emily Hon, 8, Charles C. Owen, MD, MBA8, Rodrigo Escobar, 8, Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD9. P2669 - Effects of Mirikizumab versus Placebo on Histologic Inflammation Evaluated by Comprehensive Assessment in 5 Intestinal Segments in a Randomized, Controlled Phase 3 Trial of Participants With Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Western University, London, ON, Canada; 2Centro Hospitalar São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 3Laboratory of Translational Cell and Tissue Research, Leuven, Brabant Wallon, Belgium; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai, NY; 5Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 6Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Limburg, Netherlands; 7Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; 8Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN; 9Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Wien, Austria
Introduction: Histologic inflammation persists in up to one quarter of patients with Crohn’s Disease (CD) despite endoscopic mucosal healing. Responsiveness of histologic inflammation to treatment is an evolving outcome measure in CD. Mirikizumab (MIRI) increased histologic response (H-Res) and remission (H-Rem) relative to placebo (PBO) in the Phase 2 SERENITY trial.
Methods: We compared the effect of MIRI on H-Res and H-Rem at week (W)12 and W52 to PBO by composite endpoints of response (clinical response by Patient-Reported Outcome [PRO] at W12 and W52 H-Res) and of remission (clinical response by PRO at W12 and W52 H-Rem) at W52. The overall population of patients with moderate-to-severe active CD, patients without prior biologic failure (non-BF), and patients with prior BF were assessed, using data from the Phase 3 VIVID-1 trial. Two biopsy specimens from each of 5 intestinal segments (1 ileal and 4 colonic) were obtained from the edge of the ulcers, or the most inflamed mucosa from randomized patients at screening, W12, and W52. Criteria for H-Res: absence of epithelial neutrophils and epithelial damage, erosions, and ulceration or ≥50% decrease in either the sum of the 5 segments of Robarts Histopathology Index or the Global Histologic Disease Activity Score. H-Rem: complete absence of mucosal neutrophils (in epithelium and lamina propria), and no epithelial damage, erosions, and ulcers; these criteria had to be met in all biopsy specimens. Clinical response by PRO: ≥30% decrease in stool frequency and/or abdominal pain with neither score worse than baseline. H-Res, H-Rem, composite H-Res, and composite H-Rem in all patients were prespecified, non-multiplicity-controlled endpoints. Analyses in non-BF and BF patients were post hoc.
Results: At W12: treatment with MIRI resulted in nominally statistically significantly higher rates of H-Res in all three patient groups, differences between MIRI vs PBO were nominally significant in achieving H-Rem in all patients and in non-BF and BF patients. For W52: composite H-Res differences between MIRI vs PBO were nominally statistically significant in all patient groups, composite H-Rem differences were nominally statistically significant between MIRI vs PBO in all patients, in non-BF patients, and in BF patients (Table).
Discussion: MIRI achieved nominally significantly higher rates of H-Res and H-Rem compared to PBO in all patients at W12 and W52. The statistical difference was more pronounced in the BF population after 1 year of treatment.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Vipul Jairath: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Consultant, Employee, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Asahi Kasei Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Asieris Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Avoro Capital – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Endpoint Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Enthera – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Flagship Pioneering – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Galapagos NV – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Genentech – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Gilde Healthcare – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Innomar – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAMP – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. London Health Sciences Centre – Employee. Merck – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Metacrine – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Mylan – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pandion Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pendopharm – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus Therapeutics and Diagnostics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Roivant – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. SCOPE – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Second Genome – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Shire – Speakers Bureau. Sorriso Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Synedgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. TD Securities – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Teva – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Topivert – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Vividion Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Fernando Magro: AbbVie – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Biogen – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Dr. Falk Pharma – Received honoraria. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Hospira – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Laboratórios Vitória – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Merck Sharp & Dohme – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Vifor Pharma – Received honoraria, Speakers Bureau.
Gert De Hertogh: Centocor Inc. – Fees for clinical trial activities (paid to his institution). Johnson & Johnson – Fees for clinical trial activities (paid to his institution).
Brian Feagan: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. AbolerIS – Consultant. AgomAB Therapeutics – Consultant. Allianthera – Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AnaptysBio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Applied Molecular Transport Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Arena Pharma – Consultant. Atomwise – Consultant. Avoro Capital Advisors – Consultant. Axio Research – Advisory Committee/Board Member. BioJamp – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boxer – Consultant. Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Celsius Therapeutics – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant, stock or other ownership interest. Cytoki – Consultant. Disc Medicine – Consultant. Duality – Consultant. EcoR1 Capital – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Ermium – Consultant. First Wave – Consultant. First Word Group – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Galen Atlantica – Consultant. Genentech/Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gossamer Pharma – Consultant, Stock Options. Hinge Bio – Consultant. Hot Spot Therapeutics – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Immunic Therapeutics – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAKAcademy – Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Japan Tobacco Inc. – Consultant. Kaleido Biosciences – Consultant. L.E.K. Consulting – Consultant. Landos Biopharma – Consultant. Leadiant – Consultant. Lenczner Slaght – Consultant, payment for expert testimony. LifeSci Capital – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Lument AB – Consultant. Millennium – Consultant. MiroBio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Morgan Lewis – Consultant, payment for expert testimony. Morphic Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Mylan – Consultant. OM Pharma – Consultant. Origo BioPharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Orphagen – Consultant. Pandion Therapeutics – Consultant. Pendopharm – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Play to Know AG – Consultant. Progenity – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Protagonist – Consultant. PTM Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rebiotix – Consultant. REDX – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Consultant. Silverback Therapeutics – Consultant. Surrozen Inc. – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Teva – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Thelium – Consultant. Tigenix – Consultant. Tillotts Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant. VHSquared Ltd – Consultant. Viatris – Consultant. Ysios – Consultant. Ysopia – Consultant. Zealand Pharma – Consultant.
Noam Harpaz: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Meyers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. PathAI Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi-Sankyo – Grant/Research Support. EA Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. JIMRO – Grant/Research Support. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support. Nippon Kayaku – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support. Takeda Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees.
Geert D'Haens: AbbVie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Agomab Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Allergan – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Alphabiomics – Advisor or Review Panel Member. AstraZeneca – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Immunic – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer Inc – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Seres – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Tillotts – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Ventyx – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Rish Pai: AbbVie – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant. Genentech – Consultant. PathAI – Consultant.
Zhantao Lin: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Nathan Morris: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Marijana Protic: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Emily Hon: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Charles C. Owen: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Rodrigo Escobar: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Walter Reinisch: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AOP Orphan – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Calyx – Consultant. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Ferring – Speakers Bureau. Galapagos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – Consultant. Index Pharma – Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Medahead – Consultant. Microbiotica – Consultant. MSD – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Speakers Bureau. Sandoz – Grant/Research Support. Sanofi – Grant/Research Support. Sobi – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Vipul Jairath, MBChB1, Fernando Magro, 2, Gert De Hertogh, 3, Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Noam Harpaz, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD5, Geert R. D'Haens, MD, PhD6, Rish Pai, MD, PhD7, Zhantao Lin, PhD8, Nathan Morris, 8, Marijana Protic, 8, Emily Hon, 8, Charles C. Owen, MD, MBA8, Rodrigo Escobar, 8, Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD9. P2669 - Effects of Mirikizumab versus Placebo on Histologic Inflammation Evaluated by Comprehensive Assessment in 5 Intestinal Segments in a Randomized, Controlled Phase 3 Trial of Participants With Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
