Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2815 - A Rare Case of Pulmonary Sclerosing Pneumocytoma Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Mohammed Abusuliman, MD
Henry Ford Health
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammed Abusuliman, MD1, Amr Abusuliman, MD2, Nazeh Saad, BS3, Sheema Rehman, DO4, Ahmed M. Ibrahim, MD5, Taher Jamali, MD4, Omar Shamaa, MD1, Syed-Mohammed Jafri, MD1, Mazen Elatrache, MD6
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2Tanta University, Qutour, Al Gharbiyah, Egypt; 3Wayne State University School of Medicine, Dearborn Heights, MI; 4Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI; 5Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ypsilanti, MI; 6Henry Ford Health, Dearborn, MI
Introduction: Pulmonary sclerosing pneumocytoma (PSP), formerly known as pulmonary sclerosing hemangioma, is a rare benign lung tumor with malignant potential. It mostly affects middle- aged women of Asian descent and is usually incidentally found, as most patients do not exhibit obvious medical symptoms. Cytological and immunohistochemical analysis is essential for definitive diagnosis of PSP. Analysis is typically performed on biopsy specimen obtained via image-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) and endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA). We present a case of a middle-aged woman diagnosed with PSP via Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-guided FNA of a pulmonary nodule. To our knowledge, there are no reports of cases of PSP diagnosed with EUS-FNA.
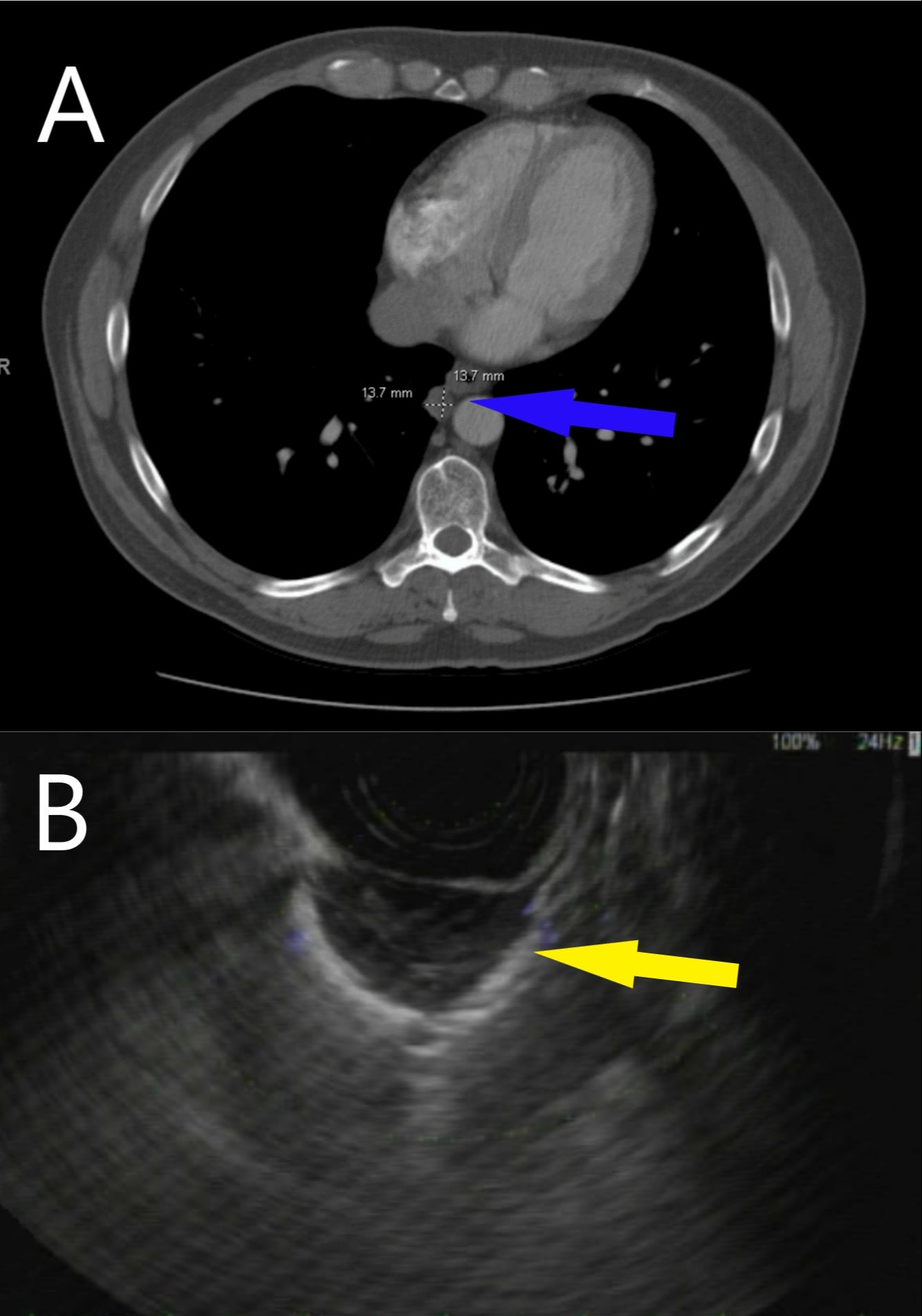
Case Description/Methods: A 54-year-old white woman, who is an ex-smoker with a family history of lung cancer, presented with right clavicle swelling after shoulder injury. A chest x-ray incidentally revealed a soft tissue mass seen on the lateral view just anterior to the xiphoid. Cross-sectional imaging of the chest showed a 14 mm para-mediastinal nodule extending to the mediastinal pleura in the medial basal segment of the right lower lobe in close proximity to the distal esophagus (Figure 1). . Due to proximity to the esophagus, this area was felt to be accessible with EUS. Endosonographic examination revealed a 17 mm by 10 mm extramural well-defined hypoechoic lesion with a microcystic component outside the distal esophageal wall and abutting it.
EUS-guided FNA of the lesion was performed. Histopathological examination revealed atypical alveolar type 2-like pneumocytes concerning for Sclerosing Pneumocytoma. The patient underwent wedge resection and is currently undergoing surveillance imaging.
Discussion: PSP is a rare, slow-growing benign lung tumor with malignant potential. Most patients are asymptomatic on presentation. Diagnosis is frequently incidental, and a definitive diagnosis requires histopathological examination. EUS-FNA can be a safe and minimally invasive tool to aid in the diagnosis of this rare condition when it is in close proximity to the gastrointestinal tract. Our case highlights the utility of EUS-FNA in diagnosis and management of unique mediastinal and lung lesions outside of the GI tract.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abusuliman, MD1, Amr Abusuliman, MD2, Nazeh Saad, BS3, Sheema Rehman, DO4, Ahmed M. Ibrahim, MD5, Taher Jamali, MD4, Omar Shamaa, MD1, Syed-Mohammed Jafri, MD1, Mazen Elatrache, MD6. P2815 - A Rare Case of Pulmonary Sclerosing Pneumocytoma Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS), ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2Tanta University, Qutour, Al Gharbiyah, Egypt; 3Wayne State University School of Medicine, Dearborn Heights, MI; 4Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI; 5Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ypsilanti, MI; 6Henry Ford Health, Dearborn, MI
Introduction: Pulmonary sclerosing pneumocytoma (PSP), formerly known as pulmonary sclerosing hemangioma, is a rare benign lung tumor with malignant potential. It mostly affects middle- aged women of Asian descent and is usually incidentally found, as most patients do not exhibit obvious medical symptoms. Cytological and immunohistochemical analysis is essential for definitive diagnosis of PSP. Analysis is typically performed on biopsy specimen obtained via image-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) and endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA). We present a case of a middle-aged woman diagnosed with PSP via Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-guided FNA of a pulmonary nodule. To our knowledge, there are no reports of cases of PSP diagnosed with EUS-FNA.
Case Description/Methods: A 54-year-old white woman, who is an ex-smoker with a family history of lung cancer, presented with right clavicle swelling after shoulder injury. A chest x-ray incidentally revealed a soft tissue mass seen on the lateral view just anterior to the xiphoid. Cross-sectional imaging of the chest showed a 14 mm para-mediastinal nodule extending to the mediastinal pleura in the medial basal segment of the right lower lobe in close proximity to the distal esophagus (Figure 1). . Due to proximity to the esophagus, this area was felt to be accessible with EUS. Endosonographic examination revealed a 17 mm by 10 mm extramural well-defined hypoechoic lesion with a microcystic component outside the distal esophageal wall and abutting it.
EUS-guided FNA of the lesion was performed. Histopathological examination revealed atypical alveolar type 2-like pneumocytes concerning for Sclerosing Pneumocytoma. The patient underwent wedge resection and is currently undergoing surveillance imaging.
Discussion: PSP is a rare, slow-growing benign lung tumor with malignant potential. Most patients are asymptomatic on presentation. Diagnosis is frequently incidental, and a definitive diagnosis requires histopathological examination. EUS-FNA can be a safe and minimally invasive tool to aid in the diagnosis of this rare condition when it is in close proximity to the gastrointestinal tract. Our case highlights the utility of EUS-FNA in diagnosis and management of unique mediastinal and lung lesions outside of the GI tract.

Figure: Figure 1 : CT chest showing the mediastinal lesion (Panel A, blue arrow). EUS image showing an extra mural hypoechoic lesion (Panel B, yellow arrow).
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abusuliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amr Abusuliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nazeh Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sheema Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Taher Jamali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Shamaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed-Mohammed Jafri: Gilead, Takeda, Abbvie, Intercept, VectivBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau.
Mazen Elatrache indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abusuliman, MD1, Amr Abusuliman, MD2, Nazeh Saad, BS3, Sheema Rehman, DO4, Ahmed M. Ibrahim, MD5, Taher Jamali, MD4, Omar Shamaa, MD1, Syed-Mohammed Jafri, MD1, Mazen Elatrache, MD6. P2815 - A Rare Case of Pulmonary Sclerosing Pneumocytoma Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS), ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
