Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2827 - A Case of Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed Through an EUS Guided Biopsy of a Splenic Lesion
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ibukunoluwa E. Oshobu, MD
University of Missouri Health Care
Columbia, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Ibukunoluwa E. Oshobu, MD1, Mohammad Abudalou, MBBS1, Ahmed Swi, MBBS2, Ghassan Hammoud, MD1
1University of Missouri Health Care, Columbia, MO; 2University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) represents a rapidly evolving field, providing a diverse range of diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. One such application is the sampling of splenic lesions to achieve accurate diagnoses. We report a case of EUS-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) of a splenic lesion seen incidentally on MRI, which led to an accurate diagnosis of metastatic small cell carcinoma of the lung.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old male with a medical history of cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C presented to the hepatology clinic for routing hepatocellular carcinoma screening. His cirrhosis is complicated with esophageal varices and portal hypertensive gastropathy. He also has a 49-year smoking history. .
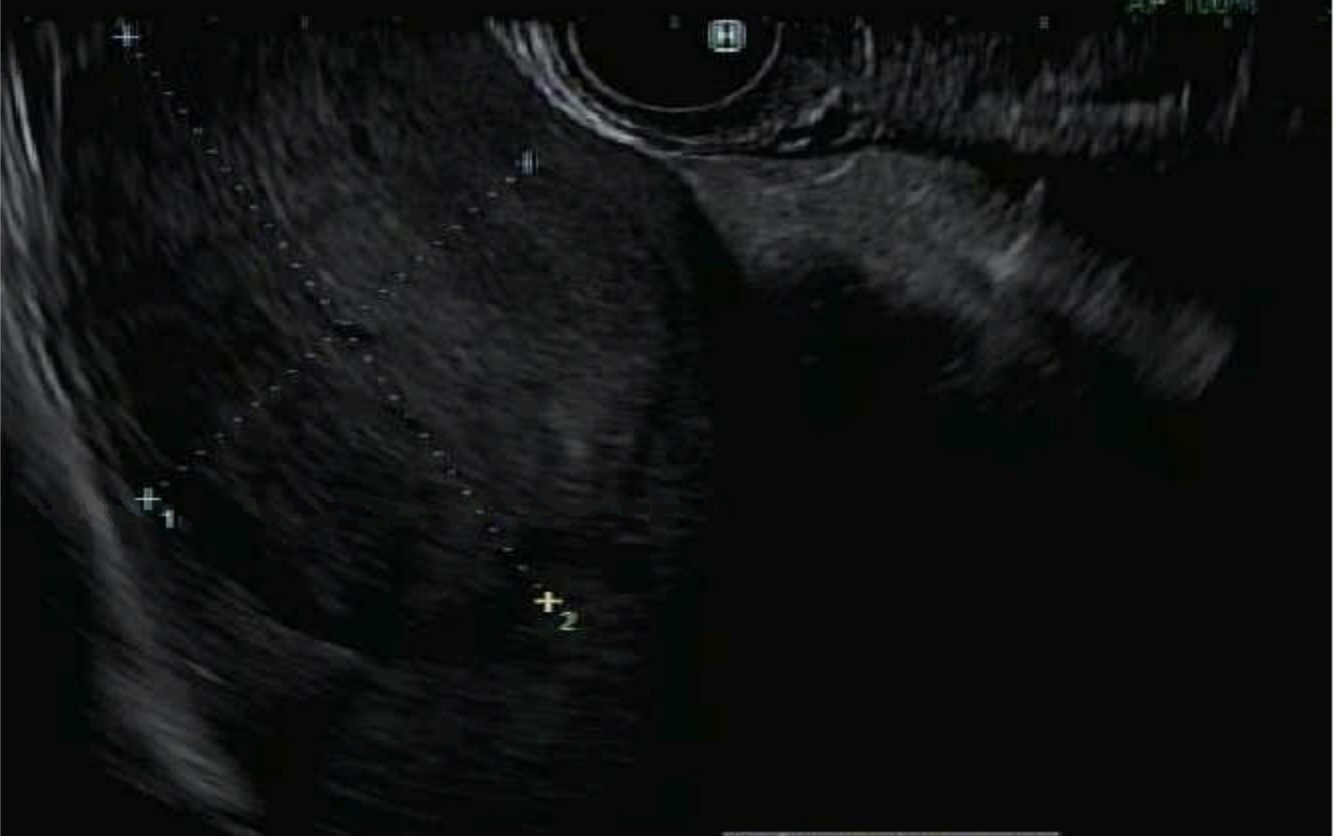
MRI of his abdomen showed a new indeterminate lesion in the spleen measuring 3.3cm x 3.1 cm in diameter, which had increased in size from prior MRI (< 1 cm)study two years ago. A lobulated mass was also seen in the left anterior abdominal wall, measuring 2.7cm x 2.7cm in diameter. He underwent an IR ultrasound-guided biopsy of the left abdominal wall mass revealing neuroendocrine tumor on pathology. Follow up EUS showed a hypoechoic heterogenous splenic lesion measured 41.3mm x 29mm in diameter. EUS-FNA of the new splenic mass was performed using a 22-gauge needle through the gastric body. The final pathology revealed positive for small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
To examine for distant metastasis, a CT scan of the chest was done and revealed multiple pulmonary nodules. A CT-guided biopsy of the lung nodule revealed small-cell neuroendocrine lung cancer.
Discussion: In our case, EUS-FNA was able to capable of confirming a diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer to the spleen. Based on our literature search, the traditional method of obtaining splenic biopsy is via percutaneous ultrasound-guided biopsy. Studies have shown the safety and efficacy of EUS-FNA in making diagnosis of splenic lesions among patients. The adequacy and accuracy of EUS-FNA of the spleen in a study was 92.8% (95% CI, 86.3% -99.3%) and 88.2% (95% CI, 79.3%-97.1%), respectively.
Disclosures:
Ibukunoluwa E. Oshobu, MD1, Mohammad Abudalou, MBBS1, Ahmed Swi, MBBS2, Ghassan Hammoud, MD1. P2827 - A Case of Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed Through an EUS Guided Biopsy of a Splenic Lesion, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Missouri Health Care, Columbia, MO; 2University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) represents a rapidly evolving field, providing a diverse range of diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. One such application is the sampling of splenic lesions to achieve accurate diagnoses. We report a case of EUS-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) of a splenic lesion seen incidentally on MRI, which led to an accurate diagnosis of metastatic small cell carcinoma of the lung.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old male with a medical history of cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C presented to the hepatology clinic for routing hepatocellular carcinoma screening. His cirrhosis is complicated with esophageal varices and portal hypertensive gastropathy. He also has a 49-year smoking history. .
MRI of his abdomen showed a new indeterminate lesion in the spleen measuring 3.3cm x 3.1 cm in diameter, which had increased in size from prior MRI (< 1 cm)study two years ago. A lobulated mass was also seen in the left anterior abdominal wall, measuring 2.7cm x 2.7cm in diameter. He underwent an IR ultrasound-guided biopsy of the left abdominal wall mass revealing neuroendocrine tumor on pathology. Follow up EUS showed a hypoechoic heterogenous splenic lesion measured 41.3mm x 29mm in diameter. EUS-FNA of the new splenic mass was performed using a 22-gauge needle through the gastric body. The final pathology revealed positive for small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
To examine for distant metastasis, a CT scan of the chest was done and revealed multiple pulmonary nodules. A CT-guided biopsy of the lung nodule revealed small-cell neuroendocrine lung cancer.
Discussion: In our case, EUS-FNA was able to capable of confirming a diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer to the spleen. Based on our literature search, the traditional method of obtaining splenic biopsy is via percutaneous ultrasound-guided biopsy. Studies have shown the safety and efficacy of EUS-FNA in making diagnosis of splenic lesions among patients. The adequacy and accuracy of EUS-FNA of the spleen in a study was 92.8% (95% CI, 86.3% -99.3%) and 88.2% (95% CI, 79.3%-97.1%), respectively.

Figure: Splenic image on MRI
Disclosures:
Ibukunoluwa Oshobu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Abudalou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Swi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ghassan Hammoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ibukunoluwa E. Oshobu, MD1, Mohammad Abudalou, MBBS1, Ahmed Swi, MBBS2, Ghassan Hammoud, MD1. P2827 - A Case of Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed Through an EUS Guided Biopsy of a Splenic Lesion, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
