Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2883 - Sarcopenia and Cirrhosis: Outcomes and Trends Over Five Years -- A Nationwide Retrospective Analysis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS
Brooklyn Hospital Center
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS1, Manasa Ginjupalli, MBBS, MD2, Chaula Desai, MD1, Vikash Kumar, MD3, Vidhi Maini, 4, Sweta Lohani, MBBS, MD1, Suriya Baskar, MD1, Saigopal R. Gujjula, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)5, Rasha H. Saleh, MD1, Matthew Peachey, MD1, Jeeva Jaganathan, MD1, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD6, Camelia Ciobanu, MD1, Amr Dokmak, MD1, Praneeth Bandaru, MBBS, MD1, Vijay Reddy Gayam, MD7, Arnold N. Forlemu, MD, MPH8, Denzil Etienne, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD, FACG1
1Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2The Brooklyn Hospital Center, New York, NY; 3Creighton University School of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; 4Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brroklyn, NY; 5Brooklyn Hospital Center, Houston, TX; 6The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 7University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 8Brooklyn Hospital Center, Athens, GA
Introduction: Liver cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to impaired liver function1. Sarcopenia, defined as the loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, is a common complication in patients with cirrhosis and is proposed to be an independent predictor of outcomes in cirrhosis2. We aimed to investigate the outcomes associated with sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients over the years using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using the NIS Database for the years 2016-2020. Inpatient admissions with a diagnosis of cirrhosis were identified each year using ICD-10 codes in STATA-17. The association between sarcopenia and primary and secondary outcomes was studied. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test, while continuous variables were compared using the t-test. Multivariable regression analyses were performed, adjusting for demographics, hospital level characteristics and relevant comorbidities including obesity, smoking status, opioid use, dyslipidemia, hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, testosterone deficiency, and malnutrition.
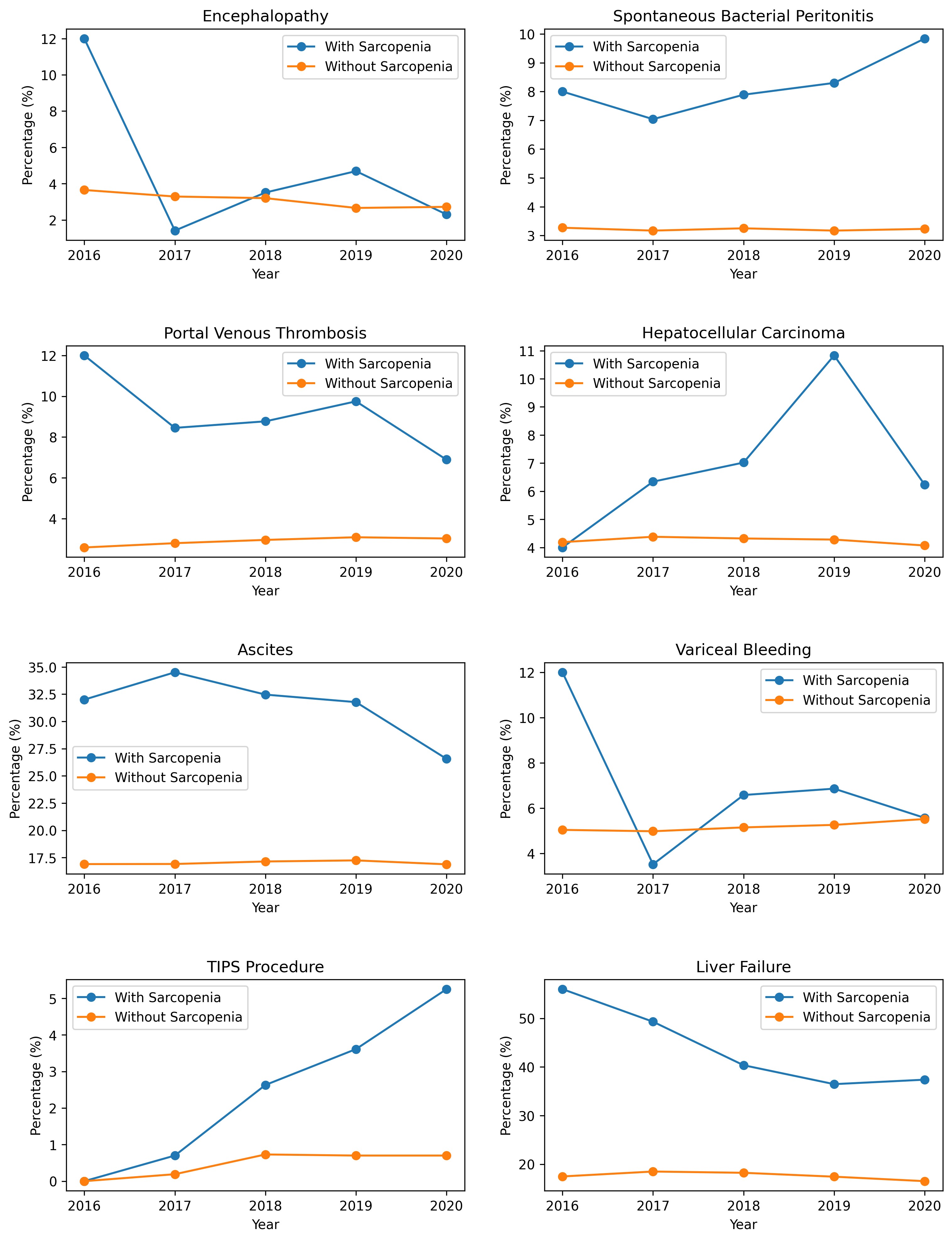
Results: A total of 3,738,364 inpatient admissions for adults with cirrhosis were identified, of which 4,885 had sarcopenia (Mean age 58.24yrs; 37.67% Females, 62.3% Males). Multivariate regression analysis of patients with cirrhosis showed sarcopenic patients had higher odds of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (Odds Ratio (OR) 1.66, 95% CI 1.31-2.10), portal vein thrombosis (OR 1.94, 95% CI 1.54-2.44), hepatocellular carcinoma (OR 1.38, 95% CI 1.06-1.78), ascites (OR 1.8, 95% CI 1.54-2.10), transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement (OR 3.87, 95% CI 2.56-5.84), and liver failure (OR 2.39, 95% CI 2.01-2.84) compared to non-sarcopenic patients. There was non-significant association with encephalopathy (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.55-1.15) and variceal bleeding (OR 1.08, 95% CI 0.83-1.40). Trends of each outcome studied in each year are shown in Figure 1.
Discussion: Our analysis revealed sarcopenia is associated with higher odds of certain complications in hospitalized cirrhotic patients, which might lead to worse outcomes, longer hospital stays and healthcare expenditure. Further prospective studies are needed to confirm these associations and explore potential interventions targeting sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS1, Manasa Ginjupalli, MBBS, MD2, Chaula Desai, MD1, Vikash Kumar, MD3, Vidhi Maini, 4, Sweta Lohani, MBBS, MD1, Suriya Baskar, MD1, Saigopal R. Gujjula, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)5, Rasha H. Saleh, MD1, Matthew Peachey, MD1, Jeeva Jaganathan, MD1, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD6, Camelia Ciobanu, MD1, Amr Dokmak, MD1, Praneeth Bandaru, MBBS, MD1, Vijay Reddy Gayam, MD7, Arnold N. Forlemu, MD, MPH8, Denzil Etienne, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD, FACG1. P2883 - Sarcopenia and Cirrhosis: Outcomes and Trends Over Five Years -- A Nationwide Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2The Brooklyn Hospital Center, New York, NY; 3Creighton University School of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; 4Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brroklyn, NY; 5Brooklyn Hospital Center, Houston, TX; 6The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 7University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 8Brooklyn Hospital Center, Athens, GA
Introduction: Liver cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to impaired liver function1. Sarcopenia, defined as the loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, is a common complication in patients with cirrhosis and is proposed to be an independent predictor of outcomes in cirrhosis2. We aimed to investigate the outcomes associated with sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients over the years using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using the NIS Database for the years 2016-2020. Inpatient admissions with a diagnosis of cirrhosis were identified each year using ICD-10 codes in STATA-17. The association between sarcopenia and primary and secondary outcomes was studied. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test, while continuous variables were compared using the t-test. Multivariable regression analyses were performed, adjusting for demographics, hospital level characteristics and relevant comorbidities including obesity, smoking status, opioid use, dyslipidemia, hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, testosterone deficiency, and malnutrition.
Results: A total of 3,738,364 inpatient admissions for adults with cirrhosis were identified, of which 4,885 had sarcopenia (Mean age 58.24yrs; 37.67% Females, 62.3% Males). Multivariate regression analysis of patients with cirrhosis showed sarcopenic patients had higher odds of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (Odds Ratio (OR) 1.66, 95% CI 1.31-2.10), portal vein thrombosis (OR 1.94, 95% CI 1.54-2.44), hepatocellular carcinoma (OR 1.38, 95% CI 1.06-1.78), ascites (OR 1.8, 95% CI 1.54-2.10), transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement (OR 3.87, 95% CI 2.56-5.84), and liver failure (OR 2.39, 95% CI 2.01-2.84) compared to non-sarcopenic patients. There was non-significant association with encephalopathy (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.55-1.15) and variceal bleeding (OR 1.08, 95% CI 0.83-1.40). Trends of each outcome studied in each year are shown in Figure 1.
Discussion: Our analysis revealed sarcopenia is associated with higher odds of certain complications in hospitalized cirrhotic patients, which might lead to worse outcomes, longer hospital stays and healthcare expenditure. Further prospective studies are needed to confirm these associations and explore potential interventions targeting sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients.

Figure: Trends of outcomes in cirrhotic patients with and without sarcopenia over each year represented in percentage.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Anuj Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manasa Ginjupalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chaula Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vidhi Maini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sweta Lohani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suriya Baskar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saigopal Gujjula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iyad Al-bustami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rasha Saleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Peachey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeeva Jaganathan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Camelia Ciobanu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amr Dokmak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Praneeth Bandaru indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijay Reddy Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arnold Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denzil Etienne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhavi Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS1, Manasa Ginjupalli, MBBS, MD2, Chaula Desai, MD1, Vikash Kumar, MD3, Vidhi Maini, 4, Sweta Lohani, MBBS, MD1, Suriya Baskar, MD1, Saigopal R. Gujjula, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)5, Rasha H. Saleh, MD1, Matthew Peachey, MD1, Jeeva Jaganathan, MD1, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD6, Camelia Ciobanu, MD1, Amr Dokmak, MD1, Praneeth Bandaru, MBBS, MD1, Vijay Reddy Gayam, MD7, Arnold N. Forlemu, MD, MPH8, Denzil Etienne, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD, FACG1. P2883 - Sarcopenia and Cirrhosis: Outcomes and Trends Over Five Years -- A Nationwide Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
