Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2884 - Bariatric Surgery Associated With Improved Outcomes in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample Database (2016-2020)
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS
Brooklyn Hospital Center
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS1, Chaula Desai, MD1, Suriya Baskar, MD1, Manasa Ginjupalli, MBBS, MD2, Vikash Kumar, MD3, Sweta Lohani, MBBS, MD1, Saigopal R. Gujjula, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)4, Jeeva Jaganathan, MD1, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD5, Camelia Ciobanu, MD1, Amr Dokmak, MD1, Praneeth Bandaru, MBBS, MD1, Vijay Reddy Gayam, MD6, Arnold N. Forlemu, MD, MPH7, Denzil Etienne, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD, FACG1
1Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2The Brooklyn Hospital Center, New York, NY; 3Creighton University School of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; 4Brooklyn Hospital Center, Houston, TX; 5The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 6University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 7Brooklyn Hospital Center, Athens, GA
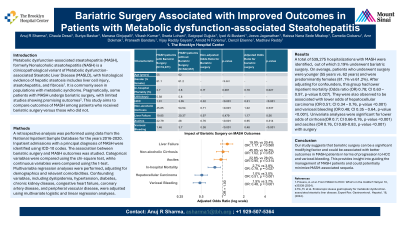
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), formerly Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a clinicopathological variant of Metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), with histological evidence of hepatic steatosis includes liver cell injury, steatohepatitis, and fibrosis. It is commonly seen in populations with metabolic syndrome. Pragmatically, some patients with MASH undergo bariatric surgery. This study aims to compare outcomes of MASH among patients who received bariatric surgery versus those who did not.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using data from the National Inpatient Sample Database for the years 2016-2020. Inpatient admissions with a principal diagnosis of MASH were identified using ICD-10 codes. The association between bariatric surgery and MASH outcomes was studied. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test, while continuous variables were compared using the t-test. Multivariable regression analyses were performed, adjusting for demographics and relevant comorbidities. Confounding variables, including dyslipidemia, hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and peripheral vascular disease, were adjusted using multivariate logistic and linear regression analyses.
Results: A total of 539,275 hospitalizations with MASH were identified, out of which 3.19% underwent bariatric surgery. On average, patients who underwent surgery were younger (55 years vs. 62 years) and were predominantly females (81.1% vs 61.2%). After adjusting for confounders, this group had lower inpatient mortality (Odds ratio (OR) 0.78; CI 0.63 – 0.97, p-value 0.027). They were also observed to be associated with lower odds of hepatocellular carcinoma (OR 0.51; CI 0.34 – 0.76, p-value < 0.001) and variceal bleeding (OR 0.48; CI 0.35 – 0.64, p-value < 0.001). Univariate analyses were significant for lower odds of cirrhosis(OR 0.7; CI 0.66-0.76, p-value < 0.001) and ascites (OR 0.76, CI 0.69-0.83, p-value < 0.001) with surgery
Discussion: Our study suggests that bariatric surgery can be a significant modifying factor and could be associated with better outcomes in MASH patients. This provides insight into guiding the management of MASH patients and could potentially minimize MASH-associated sequela.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS1, Chaula Desai, MD1, Suriya Baskar, MD1, Manasa Ginjupalli, MBBS, MD2, Vikash Kumar, MD3, Sweta Lohani, MBBS, MD1, Saigopal R. Gujjula, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)4, Jeeva Jaganathan, MD1, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD5, Camelia Ciobanu, MD1, Amr Dokmak, MD1, Praneeth Bandaru, MBBS, MD1, Vijay Reddy Gayam, MD6, Arnold N. Forlemu, MD, MPH7, Denzil Etienne, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD, FACG1. P2884 - Bariatric Surgery Associated With Improved Outcomes in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample Database (2016-2020), ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2The Brooklyn Hospital Center, New York, NY; 3Creighton University School of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; 4Brooklyn Hospital Center, Houston, TX; 5The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 6University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 7Brooklyn Hospital Center, Athens, GA
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), formerly Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a clinicopathological variant of Metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), with histological evidence of hepatic steatosis includes liver cell injury, steatohepatitis, and fibrosis. It is commonly seen in populations with metabolic syndrome. Pragmatically, some patients with MASH undergo bariatric surgery. This study aims to compare outcomes of MASH among patients who received bariatric surgery versus those who did not.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using data from the National Inpatient Sample Database for the years 2016-2020. Inpatient admissions with a principal diagnosis of MASH were identified using ICD-10 codes. The association between bariatric surgery and MASH outcomes was studied. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test, while continuous variables were compared using the t-test. Multivariable regression analyses were performed, adjusting for demographics and relevant comorbidities. Confounding variables, including dyslipidemia, hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and peripheral vascular disease, were adjusted using multivariate logistic and linear regression analyses.
Results: A total of 539,275 hospitalizations with MASH were identified, out of which 3.19% underwent bariatric surgery. On average, patients who underwent surgery were younger (55 years vs. 62 years) and were predominantly females (81.1% vs 61.2%). After adjusting for confounders, this group had lower inpatient mortality (Odds ratio (OR) 0.78; CI 0.63 – 0.97, p-value 0.027). They were also observed to be associated with lower odds of hepatocellular carcinoma (OR 0.51; CI 0.34 – 0.76, p-value < 0.001) and variceal bleeding (OR 0.48; CI 0.35 – 0.64, p-value < 0.001). Univariate analyses were significant for lower odds of cirrhosis(OR 0.7; CI 0.66-0.76, p-value < 0.001) and ascites (OR 0.76, CI 0.69-0.83, p-value < 0.001) with surgery
Discussion: Our study suggests that bariatric surgery can be a significant modifying factor and could be associated with better outcomes in MASH patients. This provides insight into guiding the management of MASH patients and could potentially minimize MASH-associated sequela.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Anuj Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chaula Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suriya Baskar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manasa Ginjupalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sweta Lohani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saigopal Gujjula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iyad Al-bustami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeeva Jaganathan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Camelia Ciobanu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amr Dokmak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Praneeth Bandaru indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijay Reddy Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arnold Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denzil Etienne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhavi Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anuj R. Sharma, MBBS1, Chaula Desai, MD1, Suriya Baskar, MD1, Manasa Ginjupalli, MBBS, MD2, Vikash Kumar, MD3, Sweta Lohani, MBBS, MD1, Saigopal R. Gujjula, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)4, Jeeva Jaganathan, MD1, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD5, Camelia Ciobanu, MD1, Amr Dokmak, MD1, Praneeth Bandaru, MBBS, MD1, Vijay Reddy Gayam, MD6, Arnold N. Forlemu, MD, MPH7, Denzil Etienne, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD, FACG1. P2884 - Bariatric Surgery Associated With Improved Outcomes in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample Database (2016-2020), ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
