Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4377 - Efficacy of Risankizumab Maintenance Therapy by Clinical Remission and Endoscopic Improvement Status in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Post Hoc Analysis of the COMMAND Phase 3 Study
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Remo Panaccione, MD
University of Calgary
Calgary, AB, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Remo Panaccione, MD1, Peter Bossuyt, 2, Irina Blumenstein, MD, PhD3, Luc Biedermann, MD4, Joana Torres, MD, PhD5, Ramona Vladea, MSc, PhD6, Ling Cheng, PhD6, Yafei Zhang, PhD6, Jasmina Kalabic, MD7, Karen Chien, PhD6, Pierre Morisset, MD6, Gareth Parkes, MD, PhD8
1University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada; 2Imelda GI Clinical Research Center, Imelda General Hospital, Bonheiden, Antwerpen, Belgium; 3Goethe University Hospital, Frankfurt, Hamburg, Germany; 4Universitäts Spital Zürich, Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland; 5Hospital da Luz, Hospital Beatriz Angelo, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Lisboa, Portugal; 6AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL; 7AbbVie Inc., Ludwigshafen, Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany; 8Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, England, United Kingdom
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB), an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody targeting p19, demonstrated efficacy vs placebo (PBO) and was well tolerated in the INSPIRE induction1 and COMMAND maintenance2 studies in patients (pts) with ulcerative colitis (UC). It is critical to understand if pts achieving outcomes (ie, clinical remission [CR] or endoscopic improvement [EI]) at the end of induction are better able to achieve long-term outcomes during maintenance. Here, we report endoscopic and histological outcomes by CR or EI status after 12 weeks (wks) of induction through 52wks of maintenance.
Methods: Clinical responders per Adapted Mayo score (AMS) to RZB induction were randomized 1:1:1 in COMMAND to subcutaneous (SC) RZB 180 mg (RZB180), 360 mg (RZB360), or PBO (RZB withdrawal) for 52wks. Overall induction responders in the primary efficacy population included all randomized pts who received ≥1 dose of study drug in the maintenance period after receiving RZB 600 mg, 1200 mg, or 1800 mg intravenous (IV) induction for 12wks. RZB 1200 mg (RZB1200) induction responders included clinical responders to 12wks of RZB1200 IV. Achievement of EI, endoscopic remission (ER), or histological-endoscopic mucosal healing (HEMI) at wk52 were evaluated according to status (yes/no) of CR per AMS or EI at maintenance wk0.
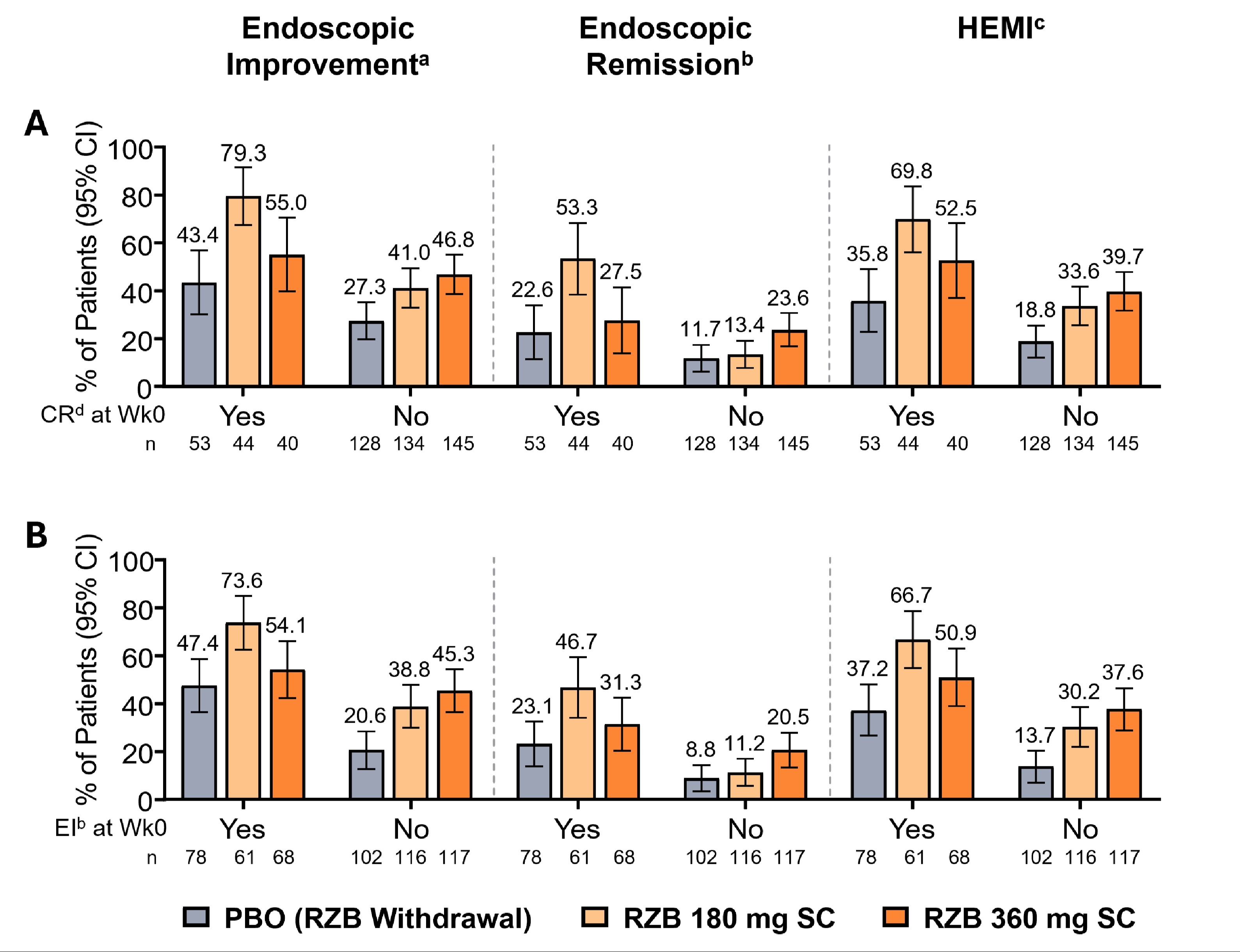
Results: Demographics and disease characteristics were balanced at induction baseline. Among overall induction responders with CR or EI at maintenance wk0, more pts treated with RZB vs PBO achieved EI, ER, or HEMI at wk52 (Figure 1A-B). Among RZB1200 induction responders with CR at maintenance wk0, more pts treated with RZB180 and RZB360 vs PBO achieved EI (80.5% and 66.7% vs 46.7%), ER (55.1% and 33.3% vs 23.3%), or HEMI (72.3% and 66.7% vs 40.0%) at wk52. RZB1200 induction responders with EI at maintenance wk0 achieved EI (74.8% and 59.4% vs 51.2%), ER (48.1% and 36.8% vs 23.3%), or HEMI (68.9% and 56.6% vs 39.5%) at wk52. The rates of each outcome were higher with RZB360 vs RZB180 in pts with inadequate disease activity (without CR or EI) at maintenance wk0.
Discussion: Regardless of CR or EI status after induction, RZB was more effective vs PBO in achieving EI, ER, and HEMI at maintenance wk52. In pts with UC who did not achieve CR or EI after induction, RZB360 demonstrated higher rates of improvement in endoscopic outcomes compared to RZB180 at maintenance wk52.
References:
1. Louis E et al. Am J Gastroenterol 2023;118(10S):S624–S625
2. Louis E et al. J Crohn’s Colitis 2024;18(Suppl_1):i10–i12
Disclosures:
Remo Panaccione, MD1, Peter Bossuyt, 2, Irina Blumenstein, MD, PhD3, Luc Biedermann, MD4, Joana Torres, MD, PhD5, Ramona Vladea, MSc, PhD6, Ling Cheng, PhD6, Yafei Zhang, PhD6, Jasmina Kalabic, MD7, Karen Chien, PhD6, Pierre Morisset, MD6, Gareth Parkes, MD, PhD8. P4377 - Efficacy of Risankizumab Maintenance Therapy by Clinical Remission and Endoscopic Improvement Status in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Post Hoc Analysis of the COMMAND Phase 3 Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada; 2Imelda GI Clinical Research Center, Imelda General Hospital, Bonheiden, Antwerpen, Belgium; 3Goethe University Hospital, Frankfurt, Hamburg, Germany; 4Universitäts Spital Zürich, Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland; 5Hospital da Luz, Hospital Beatriz Angelo, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Lisboa, Portugal; 6AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL; 7AbbVie Inc., Ludwigshafen, Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany; 8Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, England, United Kingdom
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB), an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody targeting p19, demonstrated efficacy vs placebo (PBO) and was well tolerated in the INSPIRE induction1 and COMMAND maintenance2 studies in patients (pts) with ulcerative colitis (UC). It is critical to understand if pts achieving outcomes (ie, clinical remission [CR] or endoscopic improvement [EI]) at the end of induction are better able to achieve long-term outcomes during maintenance. Here, we report endoscopic and histological outcomes by CR or EI status after 12 weeks (wks) of induction through 52wks of maintenance.
Methods: Clinical responders per Adapted Mayo score (AMS) to RZB induction were randomized 1:1:1 in COMMAND to subcutaneous (SC) RZB 180 mg (RZB180), 360 mg (RZB360), or PBO (RZB withdrawal) for 52wks. Overall induction responders in the primary efficacy population included all randomized pts who received ≥1 dose of study drug in the maintenance period after receiving RZB 600 mg, 1200 mg, or 1800 mg intravenous (IV) induction for 12wks. RZB 1200 mg (RZB1200) induction responders included clinical responders to 12wks of RZB1200 IV. Achievement of EI, endoscopic remission (ER), or histological-endoscopic mucosal healing (HEMI) at wk52 were evaluated according to status (yes/no) of CR per AMS or EI at maintenance wk0.
Results: Demographics and disease characteristics were balanced at induction baseline. Among overall induction responders with CR or EI at maintenance wk0, more pts treated with RZB vs PBO achieved EI, ER, or HEMI at wk52 (Figure 1A-B). Among RZB1200 induction responders with CR at maintenance wk0, more pts treated with RZB180 and RZB360 vs PBO achieved EI (80.5% and 66.7% vs 46.7%), ER (55.1% and 33.3% vs 23.3%), or HEMI (72.3% and 66.7% vs 40.0%) at wk52. RZB1200 induction responders with EI at maintenance wk0 achieved EI (74.8% and 59.4% vs 51.2%), ER (48.1% and 36.8% vs 23.3%), or HEMI (68.9% and 56.6% vs 39.5%) at wk52. The rates of each outcome were higher with RZB360 vs RZB180 in pts with inadequate disease activity (without CR or EI) at maintenance wk0.
Discussion: Regardless of CR or EI status after induction, RZB was more effective vs PBO in achieving EI, ER, and HEMI at maintenance wk52. In pts with UC who did not achieve CR or EI after induction, RZB360 demonstrated higher rates of improvement in endoscopic outcomes compared to RZB180 at maintenance wk52.
References:
1. Louis E et al. Am J Gastroenterol 2023;118(10S):S624–S625
2. Louis E et al. J Crohn’s Colitis 2024;18(Suppl_1):i10–i12

Figure: Figure 1. Summary of Key Secondary Endpoints at Week 52 According to Clinical Remission per Adapted Mayo Score or Endoscopic Improvement Status at Week 0 in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active UC.
Status (yes/no) of A) CR per Adapted Mayo score or B) EI at maintenance week 0.
Overall induction responder in the primary efficacy population includes all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study drug in the 52-week maintenance period after receiving RZB 600 mg IV, RZB 1200 mg IV, or RZB 1800 mg IV for 12 weeks in the induction study.
Results for categorical endpoints are based on nonresponder imputation incorporating multiple imputation to handle missing data due to logistic restrictions (COVID-19 or the geo-political conflict in Ukraine and surrounding impacted regions) (NRI-MI).
(a) EI is defined as an endoscopy subscore ≤ 1 without friability.
(b) ER is defined as an endoscopy subscore = 0.
(c) HEMI is defined as an endoscopy subscore = 0 or 1 without friability and Geboes score ≤ 3.1.
(d) CR per Adapted Mayo score is defined as stool frequency score ≤ 1, and not greater than baseline, rectal bleeding score of 0, and endoscopy subscore ≤ 1.
CI, confidence interval; CR, clinical remission; EI, endoscopic improvement; ER, endoscopic remission; HEMI, Histological-Endoscopic Mucosal Improvement; IV, intravenous; pts, patients; RZB, risankizumab; SC, subcutaneous; UC, ulcerative colitis; wk, week.
Status (yes/no) of A) CR per Adapted Mayo score or B) EI at maintenance week 0.
Overall induction responder in the primary efficacy population includes all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study drug in the 52-week maintenance period after receiving RZB 600 mg IV, RZB 1200 mg IV, or RZB 1800 mg IV for 12 weeks in the induction study.
Results for categorical endpoints are based on nonresponder imputation incorporating multiple imputation to handle missing data due to logistic restrictions (COVID-19 or the geo-political conflict in Ukraine and surrounding impacted regions) (NRI-MI).
(a) EI is defined as an endoscopy subscore ≤ 1 without friability.
(b) ER is defined as an endoscopy subscore = 0.
(c) HEMI is defined as an endoscopy subscore = 0 or 1 without friability and Geboes score ≤ 3.1.
(d) CR per Adapted Mayo score is defined as stool frequency score ≤ 1, and not greater than baseline, rectal bleeding score of 0, and endoscopy subscore ≤ 1.
CI, confidence interval; CR, clinical remission; EI, endoscopic improvement; ER, endoscopic remission; HEMI, Histological-Endoscopic Mucosal Improvement; IV, intravenous; pts, patients; RZB, risankizumab; SC, subcutaneous; UC, ulcerative colitis; wk, week.
Disclosures:
Remo Panaccione: Élan – Consultant. Abbivax – Consultant. Abbott – Consultant. AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaking Fees. Alimentiv – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Biogen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Celltrion – Consultant. Cosmos Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eisai – Consultant. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAMP Bio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Mylan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Novartis – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Oppilan Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Organon – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Pandion Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pendopharm – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Progenity – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Satisfai Health – Consultant. Shire – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Sublimity Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Theravance – Consultant. Trellus – Consultant. UCB – Consultant. Ventyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Viatris – Consultant.
Peter Bossuyt: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Amgen – Grant/Research Support. Arena pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Benelux – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. CAG – Lecture fees. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. CiRC Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Dr. Falk Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. EPGS – Lecture fees. Galapagos NV – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. Globalport – Lecture fees. Hospira – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Materia Prima – Lecture fees. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Mundipharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Mylan – Grant/Research Support. Pentax – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support, Advisory board fees. PSI CRO – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Scope – Lecture fees. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. Tetrameros – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Viatris – Grant/Research Support.
Irina Blumenstein: AbbVie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Amgen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Arena – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Biogen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Celgene – Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Ferring – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Galapagos – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Mylan – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, Stock Options. Shire – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Luc Biedermann: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Calypso – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Esocap – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Falk – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member. MSD – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vifor – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Joana Torres: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Arena – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speaker Fees. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau.
Ramona Vladea: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Ling Cheng: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Yafei Zhang: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Jasmina Kalabic: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Karen Chien: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Pierre Morisset: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Gareth Parkes: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ampersand Health – Director, Stock Options. BMS – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Napp Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Sorriso Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Tillotts – Consultant.
Remo Panaccione, MD1, Peter Bossuyt, 2, Irina Blumenstein, MD, PhD3, Luc Biedermann, MD4, Joana Torres, MD, PhD5, Ramona Vladea, MSc, PhD6, Ling Cheng, PhD6, Yafei Zhang, PhD6, Jasmina Kalabic, MD7, Karen Chien, PhD6, Pierre Morisset, MD6, Gareth Parkes, MD, PhD8. P4377 - Efficacy of Risankizumab Maintenance Therapy by Clinical Remission and Endoscopic Improvement Status in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Post Hoc Analysis of the COMMAND Phase 3 Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
