Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4382 - The Efficacy of Mirikizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Muhammad YN Chaudhary, MBChB
Indiana University Southwest
Evansville, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB1, Mohammad Jawwad, MBBS2, Muhammad Ismail, MD3, Muhammad H N. Chaudhary, MBChB4, Umna Naveed, MBChB, MBA, MPH5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Ajeet Singh, MBBS7, Monazza Riaz, MBBS8, Abdul Arham, MD9, Oluwagbenga Serrano, MD, FACG10, Syed Abdul Basit, MD11
1Indiana University Southwest, Evansville, IN; 2Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3Indiana University Southwest, Cedar Rapids, IA; 4Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust, Stockport, England, United Kingdom; 5NHS, Liverpool, England, United Kingdom; 6Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 7Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Dow Medical College, Norwich, England, United Kingdom; 9Baystate Medical Center, Chicopee, MA; 10Good Samaritan Hospital, Vincennes, IN; 11Southern Hills Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is integral to intestinal homeostasis and inflammation, contributing significantly to the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This cytokine's proinflammatory roles have prompted the development of Mirikizumab (Omvoh®), a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody targeting IL-23p19. Our meta-analysis, the first of its kind, assesses the efficacy and safety of Mirikizumab in managing ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov, were used to conduct a systematic literature review of studies focusing on Mirikizumab’s effectiveness and safety. We extracted data regarding endoscopic, clinical and symptomatic remission. Dose-dependent response, adverse events, and overall efficacy when compared with placebo were also evaluated. Rstudio was used to pool outcome data under the common effects (CE) model. RevMan 5.4 calculated rush risk ratios (RR) and mean differences (MDs) within a random-effects model.
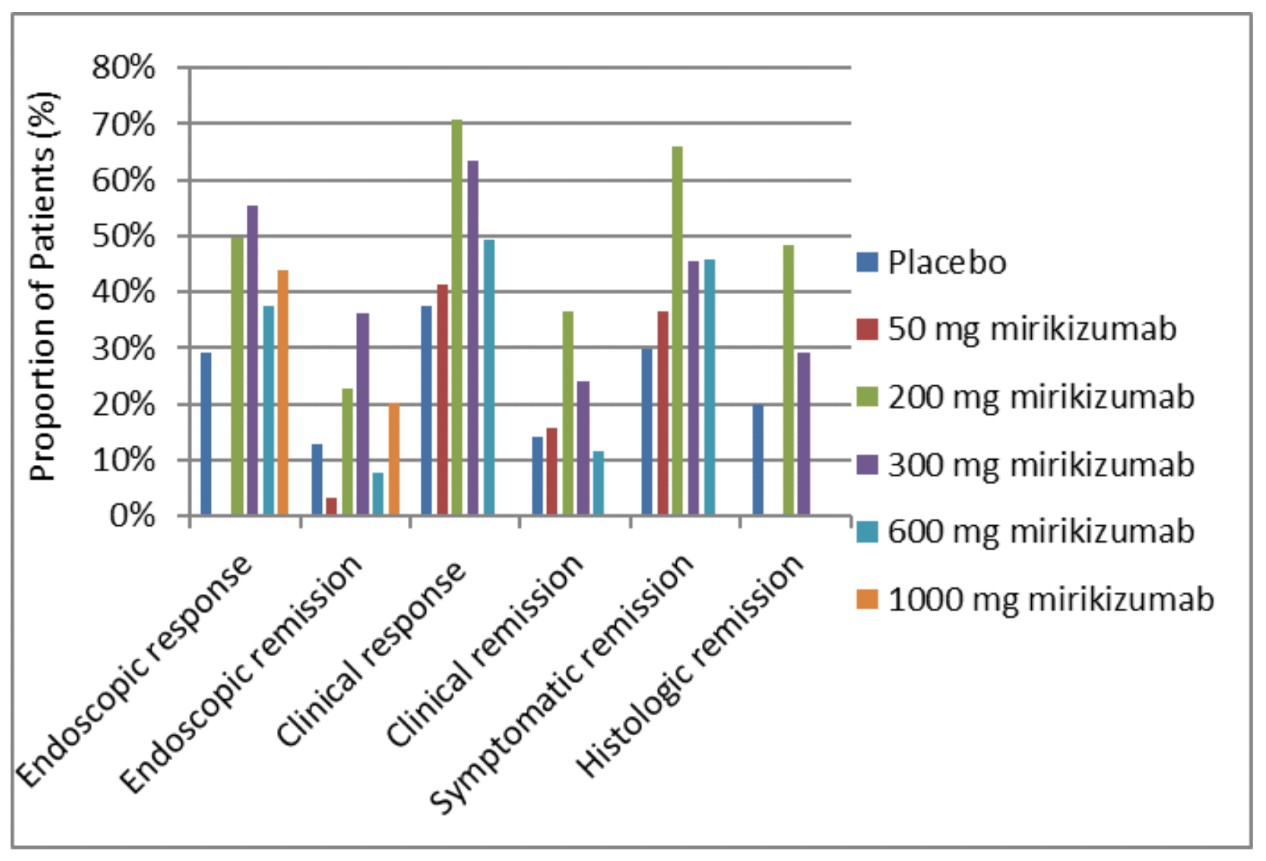
Results: Four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating IBD management with Mirikizumab against placebo were included. For all doses (Figure 1), there was significant improvement in endoscopic and clinical remissions and responses (p< 0.005), and symptomatic and histologic remissions (p< 0.005). Mirikizumab 200 mg dosing displayed the highest efficacy across all outcomes, as shown in Figure 1, except for endoscopic remission. For all doses, IBD questionnaire scores at 12 weeks showed major improvement. Reduction was seen in fecal calprotectin levels and bowel urgency (p< 0.005). Mirikizumab lowered the risk of serious AEs (RR 0.44, 95% CI: 0.28-0.72, p=0.0008) but did not significantly reduce all-cause mortality (RR 0.16, 95% CI: 0.01-4.03, p=0.27). Its effects were more pronounced in Crohn’s disease than in UC, despite only one RCT focusing on Crohn’s disease. Table 1 summarizes the results.
Discussion: Mirikizumab, particularly 200 mg dosing, demonstrated significant efficacy in IBD treatment, with major improvements across endoscopic, clinical, symptomatic, and histologic measures. Mirikizumab improved patient's quality of life, as evidenced by positive IBD questionnaire scores and a significant reduction in bowel urgency. The decrease in fecal calprotectin levels underscores its strong anti-inflammatory effects, serving as a reliable treatment response biomarker. However, further trials are needed to confirm these findings and to integrate Mirikizumab into treatment protocols for managing IBD.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB1, Mohammad Jawwad, MBBS2, Muhammad Ismail, MD3, Muhammad H N. Chaudhary, MBChB4, Umna Naveed, MBChB, MBA, MPH5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Ajeet Singh, MBBS7, Monazza Riaz, MBBS8, Abdul Arham, MD9, Oluwagbenga Serrano, MD, FACG10, Syed Abdul Basit, MD11. P4382 - The Efficacy of Mirikizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Indiana University Southwest, Evansville, IN; 2Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3Indiana University Southwest, Cedar Rapids, IA; 4Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust, Stockport, England, United Kingdom; 5NHS, Liverpool, England, United Kingdom; 6Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 7Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Dow Medical College, Norwich, England, United Kingdom; 9Baystate Medical Center, Chicopee, MA; 10Good Samaritan Hospital, Vincennes, IN; 11Southern Hills Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is integral to intestinal homeostasis and inflammation, contributing significantly to the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This cytokine's proinflammatory roles have prompted the development of Mirikizumab (Omvoh®), a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody targeting IL-23p19. Our meta-analysis, the first of its kind, assesses the efficacy and safety of Mirikizumab in managing ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov, were used to conduct a systematic literature review of studies focusing on Mirikizumab’s effectiveness and safety. We extracted data regarding endoscopic, clinical and symptomatic remission. Dose-dependent response, adverse events, and overall efficacy when compared with placebo were also evaluated. Rstudio was used to pool outcome data under the common effects (CE) model. RevMan 5.4 calculated rush risk ratios (RR) and mean differences (MDs) within a random-effects model.
Results: Four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating IBD management with Mirikizumab against placebo were included. For all doses (Figure 1), there was significant improvement in endoscopic and clinical remissions and responses (p< 0.005), and symptomatic and histologic remissions (p< 0.005). Mirikizumab 200 mg dosing displayed the highest efficacy across all outcomes, as shown in Figure 1, except for endoscopic remission. For all doses, IBD questionnaire scores at 12 weeks showed major improvement. Reduction was seen in fecal calprotectin levels and bowel urgency (p< 0.005). Mirikizumab lowered the risk of serious AEs (RR 0.44, 95% CI: 0.28-0.72, p=0.0008) but did not significantly reduce all-cause mortality (RR 0.16, 95% CI: 0.01-4.03, p=0.27). Its effects were more pronounced in Crohn’s disease than in UC, despite only one RCT focusing on Crohn’s disease. Table 1 summarizes the results.
Discussion: Mirikizumab, particularly 200 mg dosing, demonstrated significant efficacy in IBD treatment, with major improvements across endoscopic, clinical, symptomatic, and histologic measures. Mirikizumab improved patient's quality of life, as evidenced by positive IBD questionnaire scores and a significant reduction in bowel urgency. The decrease in fecal calprotectin levels underscores its strong anti-inflammatory effects, serving as a reliable treatment response biomarker. However, further trials are needed to confirm these findings and to integrate Mirikizumab into treatment protocols for managing IBD.

Figure: Figure 1: Bar chart showing direct comparison of placebo versus various Mirikizumab dosing on endoscopic, clinical, symptomatic, and histologic remission and response.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Jawwad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umna Naveed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ajeet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monazza Riaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Arham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Oluwagbenga Serrano: MERCK – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Syed Abdul Basit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB1, Mohammad Jawwad, MBBS2, Muhammad Ismail, MD3, Muhammad H N. Chaudhary, MBChB4, Umna Naveed, MBChB, MBA, MPH5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Ajeet Singh, MBBS7, Monazza Riaz, MBBS8, Abdul Arham, MD9, Oluwagbenga Serrano, MD, FACG10, Syed Abdul Basit, MD11. P4382 - The Efficacy of Mirikizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
