Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4463 - Impact of High-Volume Crystalloid Infusion and Indomethacin Prophylaxis on Post-ERCP Complication Rates
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- NM
Nitish Mittal, MD
University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Nitish Mittal, MD1, Parvir Aujla, MD1, Andrew Sullivan, MD2, Rachel Mortan, MD1, Dwight Fan, MD1, Sruthi Kapliyil. Subramanian, MD, FACG1, Abdullah S. Aleem, MD3, Veda Kulkarni, BS1, Mairin Joseph-Talreja, MD, FACG1, Srinivas Ramireddy, MD, FACG1, Pritesh R. Mutha, MD, FACG1, Vaibhav Wadhwa, MD, FACG1, Nirav Thosani, MD4, Roy T. DaVee, MD, FACG1
1University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas at Houston, Houston, TX; 4McGovern Medical School at UTHealth, Houston, TX
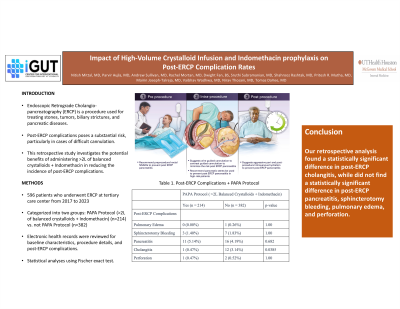
Introduction: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a procedure used for treating stones, tumors, biliary strictures, and pancreatic diseases. It combines X-ray and the use of an endoscope. Post-ERCP complications poses a substantial risk, particularly in cases involving difficult cannulation. This retrospective study investigates the potential benefits of administering greater than 2 liters of balanced crystalloids, combined with indomethacin, in reducing the incidence of post-ERCP complications.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted, involving 596 patients who underwent ERCP at a multi-center institution from 2017 to 2023. Patients were categorized into two groups: those who received a high volume ( >2 liters) of balanced crystalloids and indomethacin (n=214), and those who did not receive this combination (n=382). Electronic health records were reviewed for baseline characteristics, procedural details, and post-ERCP complications. Statistical analyses were employed using the Fisher exact test.
Results: Both groups have similar demographics and indications for ERCP. The findings revealed a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of post-ERCP cholangitis (p=0.00385) in the patients with the intervention group compared to the control group. The findings did not reveal a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of post-ERCP pancreatitis (p = 0.682), sphincterotomy bleeding (p = 1.0), pulmonary edema (p = 1.0) and perforation (p = 1.0).
Discussion: This retrospective analysis found a statistical difference in post-ERCP cholangitis while did not find a statistical difference in post-ERCP pancreatitis, sphincterotomy bleeding, pulmonary edema and perforation. Patients receiving rectal indomethacin and ≥ 2L of balanced crystalloids per American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) guidelines helped in reduction of certain post-ERCP complications. The small sample size may have limited the statistical power to detect differences for all the complications. Further prospective, large randomized controlled trials are needed to assess the benefit of receiving rectal indomethacin and high-volume balanced crystalloids in preventing post-ERCP complications in a high-risk subset of patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Nitish Mittal, MD1, Parvir Aujla, MD1, Andrew Sullivan, MD2, Rachel Mortan, MD1, Dwight Fan, MD1, Sruthi Kapliyil. Subramanian, MD, FACG1, Abdullah S. Aleem, MD3, Veda Kulkarni, BS1, Mairin Joseph-Talreja, MD, FACG1, Srinivas Ramireddy, MD, FACG1, Pritesh R. Mutha, MD, FACG1, Vaibhav Wadhwa, MD, FACG1, Nirav Thosani, MD4, Roy T. DaVee, MD, FACG1. P4463 - Impact of High-Volume Crystalloid Infusion and Indomethacin Prophylaxis on Post-ERCP Complication Rates, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas at Houston, Houston, TX; 4McGovern Medical School at UTHealth, Houston, TX
Introduction: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a procedure used for treating stones, tumors, biliary strictures, and pancreatic diseases. It combines X-ray and the use of an endoscope. Post-ERCP complications poses a substantial risk, particularly in cases involving difficult cannulation. This retrospective study investigates the potential benefits of administering greater than 2 liters of balanced crystalloids, combined with indomethacin, in reducing the incidence of post-ERCP complications.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted, involving 596 patients who underwent ERCP at a multi-center institution from 2017 to 2023. Patients were categorized into two groups: those who received a high volume ( >2 liters) of balanced crystalloids and indomethacin (n=214), and those who did not receive this combination (n=382). Electronic health records were reviewed for baseline characteristics, procedural details, and post-ERCP complications. Statistical analyses were employed using the Fisher exact test.
Results: Both groups have similar demographics and indications for ERCP. The findings revealed a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of post-ERCP cholangitis (p=0.00385) in the patients with the intervention group compared to the control group. The findings did not reveal a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of post-ERCP pancreatitis (p = 0.682), sphincterotomy bleeding (p = 1.0), pulmonary edema (p = 1.0) and perforation (p = 1.0).
Discussion: This retrospective analysis found a statistical difference in post-ERCP cholangitis while did not find a statistical difference in post-ERCP pancreatitis, sphincterotomy bleeding, pulmonary edema and perforation. Patients receiving rectal indomethacin and ≥ 2L of balanced crystalloids per American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) guidelines helped in reduction of certain post-ERCP complications. The small sample size may have limited the statistical power to detect differences for all the complications. Further prospective, large randomized controlled trials are needed to assess the benefit of receiving rectal indomethacin and high-volume balanced crystalloids in preventing post-ERCP complications in a high-risk subset of patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Nitish Mittal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Parvir Aujla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Sullivan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Mortan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dwight Fan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sruthi Subramanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Aleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Veda Kulkarni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mairin Joseph-Talreja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srinivas Ramireddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pritesh Mutha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaibhav Wadhwa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nirav Thosani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Roy DaVee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nitish Mittal, MD1, Parvir Aujla, MD1, Andrew Sullivan, MD2, Rachel Mortan, MD1, Dwight Fan, MD1, Sruthi Kapliyil. Subramanian, MD, FACG1, Abdullah S. Aleem, MD3, Veda Kulkarni, BS1, Mairin Joseph-Talreja, MD, FACG1, Srinivas Ramireddy, MD, FACG1, Pritesh R. Mutha, MD, FACG1, Vaibhav Wadhwa, MD, FACG1, Nirav Thosani, MD4, Roy T. DaVee, MD, FACG1. P4463 - Impact of High-Volume Crystalloid Infusion and Indomethacin Prophylaxis on Post-ERCP Complication Rates, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

