Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4478 - Investigating the Influence of Gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal on Gastric Per Oral Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy Results
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Michelle Neice, MD
LSU Health
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Maryam Mubashir, MD1, Lena Kawji, MD1, Omar Khan, MD1, Britanny Pass, BS1, Praveen Penagulari, MD1, Shazia Rashid, MD1, Daniyal Raza, MD2, Raza Syed, MD2, Natalie Roppolo, MS1, Michael Tran, MD1, Michelle Neice, MD1, Qiang Cai, MD1
1LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 2Louisiana State University Health, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Gastroparesis remains an elusive and debilitating disorder. Despite progress in treatment options such as gastric per oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (G-POEM), the optimal timing and selection criteria for G-POEM remains unclear. Prior research suggests that patients with gastroparesis demonstrate dysfunction and depletion in the numbers of gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC). To further elucidate this relationship and better anticipate procedural effect, we performed a longitudinal analysis between the number of ICC and the outcome of G-POEM.
Methods: The study was performed at two institutes over two different time periods by one expert endoscopist from August 2019 to December 2019 and December 2022 to June 2023. All patients who underwent G-POEM with concurrent gastric muscle biopsy were enrolled. This technique is detailed in prior publication. Patient consent was obtained at the initial visit and Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) scores were recorded before the procedure and during the follow-up period.
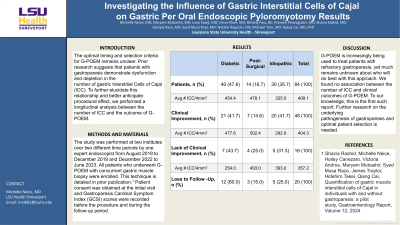
Results: This study included 84 patients with an average age of 48.6 years and 77.6% were female. Diabetes was the most common etiology at 47.6% followed by 35.7% idiopathic. Only 37% of diabetics had adequate control with an A1C of 7% or below. All patients had failed prior medical therapy for their gastroparesis. Most patients, 70%, were discharged on the same day as their G-POEM. The average time to follow up was 5 months when a post-procedure GCSI score was measured. Overall, 57.4% of patients achieved clinical success defined as a reduction of average GCSI score of 1 or more from the baseline, 19% of patients did not have clinical improvement according to GCSI. Unfortunately, 20 patients were lost to follow up and post procedure GCSI could not be obtained. The average number of ICC/4mmsq was 409.14 and did not correlate with G-POEM success. There was also no difference in outcomes among diabetic, post-surgical or idiopathic gastroparesis patients. Lastly, clinical success was independent of the percentage retention at baseline Gastric Emptying Study.
Discussion: G-POEM is increasingly being used to treat patients with refractory gastroparesis, yet much remains unknown about who will do best with this approach. We found no association between the number of ICC and clinical outcomes of G-POEM. To our knowledge, this is the first such report. Further research on the underlying pathogenesis of gastroparesis and optimal patient selection is needed.
Disclosures:
Maryam Mubashir, MD1, Lena Kawji, MD1, Omar Khan, MD1, Britanny Pass, BS1, Praveen Penagulari, MD1, Shazia Rashid, MD1, Daniyal Raza, MD2, Raza Syed, MD2, Natalie Roppolo, MS1, Michael Tran, MD1, Michelle Neice, MD1, Qiang Cai, MD1. P4478 - Investigating the Influence of Gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal on Gastric Per Oral Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy Results, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 2Louisiana State University Health, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Gastroparesis remains an elusive and debilitating disorder. Despite progress in treatment options such as gastric per oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (G-POEM), the optimal timing and selection criteria for G-POEM remains unclear. Prior research suggests that patients with gastroparesis demonstrate dysfunction and depletion in the numbers of gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC). To further elucidate this relationship and better anticipate procedural effect, we performed a longitudinal analysis between the number of ICC and the outcome of G-POEM.
Methods: The study was performed at two institutes over two different time periods by one expert endoscopist from August 2019 to December 2019 and December 2022 to June 2023. All patients who underwent G-POEM with concurrent gastric muscle biopsy were enrolled. This technique is detailed in prior publication. Patient consent was obtained at the initial visit and Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) scores were recorded before the procedure and during the follow-up period.
Results: This study included 84 patients with an average age of 48.6 years and 77.6% were female. Diabetes was the most common etiology at 47.6% followed by 35.7% idiopathic. Only 37% of diabetics had adequate control with an A1C of 7% or below. All patients had failed prior medical therapy for their gastroparesis. Most patients, 70%, were discharged on the same day as their G-POEM. The average time to follow up was 5 months when a post-procedure GCSI score was measured. Overall, 57.4% of patients achieved clinical success defined as a reduction of average GCSI score of 1 or more from the baseline, 19% of patients did not have clinical improvement according to GCSI. Unfortunately, 20 patients were lost to follow up and post procedure GCSI could not be obtained. The average number of ICC/4mmsq was 409.14 and did not correlate with G-POEM success. There was also no difference in outcomes among diabetic, post-surgical or idiopathic gastroparesis patients. Lastly, clinical success was independent of the percentage retention at baseline Gastric Emptying Study.
Discussion: G-POEM is increasingly being used to treat patients with refractory gastroparesis, yet much remains unknown about who will do best with this approach. We found no association between the number of ICC and clinical outcomes of G-POEM. To our knowledge, this is the first such report. Further research on the underlying pathogenesis of gastroparesis and optimal patient selection is needed.
Disclosures:
Maryam Mubashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lena Kawji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Britanny Pass indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Praveen Penagulari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shazia Rashid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniyal Raza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raza Syed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Natalie Roppolo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Tran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michelle Neice indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qiang Cai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maryam Mubashir, MD1, Lena Kawji, MD1, Omar Khan, MD1, Britanny Pass, BS1, Praveen Penagulari, MD1, Shazia Rashid, MD1, Daniyal Raza, MD2, Raza Syed, MD2, Natalie Roppolo, MS1, Michael Tran, MD1, Michelle Neice, MD1, Qiang Cai, MD1. P4478 - Investigating the Influence of Gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal on Gastric Per Oral Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy Results, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
